




What Makes Aquatic Animals Unique? Key Traits and Examples
The animals that live in water for most or all of its lifetime (basically survive in water) are known as aquatic animals. They can be found in ponds, lakes, rivers, and oceans. They do not have the adaptation to survive on land and consume food on land and hence are restricted to water. There are certain characteristics that one animal needs to have to survive underwater.
These animals have various structural modifications in their body that allow them to survive in aquatic habitats. Their bodies are streamlined, which means the two ends of the body are pointed or narrow, whereas the central part is wide, allowing them to swim easily.
Characteristics of Aquatic Animals
These animals have gills as respiratory organs, which is a key characteristic for any aquatic animal.
These animals have various structural modifications in their body that allow them to survive in aquatic habitats.
These animals have locomotory organs called the fins, which are basically a muscle wrapped on a foldable bony structure.
There are different types of fins in different fishes, i.e., dorsal fins, pectoral fins, caudal fins, etc.
The entire body has small appendages covering the skin, known as scales, and are used for protection.
A few fishes can have a modified swim bladder that can allow them to float in a certain depth of water and change their position vertically by releasing or taking in air into them.
Types of Aquatic Animals
The aquatic organisms can be classified into three broad types: plankton, nekton, and benthos.
Plankton
These are microscopic or very minute aquatic organisms that cannot move on their own. These move from one point to another by the action of water currents. They live in the photic zone. This group includes phytoplankton and zooplankton.
Phytoplankton is a group of bacteria and algae that can make their own food using sunlight and other inorganic resources. Zooplankton is a group of tiny animals that eat phytoplankton as their nutrition and energy source.
Nekton
These are the aquatic animals that can swim and thus can move on their own within the water. They may live in the photic (where the sunlight reaches properly underwater) or aphotic zone (regions where very minimum to no sunlight penetrates underwater).
These obtain nutrition by either consuming the plankton or weaker nekton. Examples of nekton include fish and shrimp.
Benthos
These are the aquatic organisms that mostly crawl at the bottom of the water body. A few of these organisms are decomposers. It might include organisms like sponges, clams, and anglerfish.
List of Some Aquatic Animals
Fish
They are cold-blooded vertebrates and have special organs for respiration, circulation, and excretion underwater. It is one of the most diverse animal species, which is aquatic and vertebrate.
Fishes are either oviparous (animals that lay eggs) or ovoviviparous (animals that lay fertilised eggs, and they hatch immediately after being laid). Fishes are found in all sorts of water, i.e., freshwater, saltwater, marine, and brackish water. They are mainly carnivorous in nutrition, but very few species are herbivorous. They exhibit having a swim bladder and fins that are common amongst all kinds of fishes.
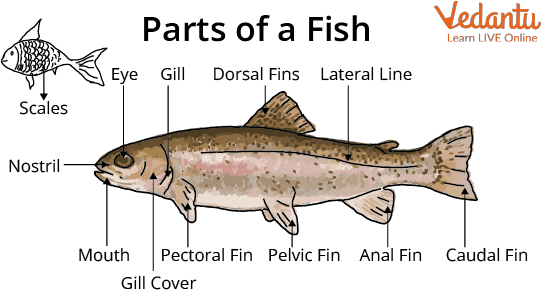
Different Parts of a Fish
Octopus
These organisms are soft-bodied animals with bulb-like heads and eight arms, and that is the reason they are called octopuses. This very name originated from the Greek word meaning number eight.
These marine animals do not have a skeletal system. These animals are carnivores and consume other organisms such as clams, shellfish, shrimp, lobsters, and fish.

A Full-grown Octopus.
Whale
These are considered to be the largest mammals on earth. They do not have gills, and they breathe air through holes in their heads. These are warm-blooded animals and give birth to young ones.
Crab
These are animals that are decapod (10 legs) crustaceans. They can be very small, from pea size to about 4 m in width. Crabs are mostly oviparous. They have two compound eyes, often on stalks. They have proper gills for breathing purposes.
A Marine Full-sized Crab.
Summary
Aquatic animals can vary in huge numbers and can have very different characteristics from each other. A very common similarity is that most aquatic animals majorly need gills to breathe. They consume aquatic organisms for nutrition. Their characteristics might vary based on the depths that they are in.
FAQs on Characteristics of Aquatic Animals Explained
1. What are the most common characteristics of animals that live in water?
Aquatic animals have several special adaptations to thrive in water. The most common characteristics include:
Gills: Most aquatic animals possess gills, which are special organs that allow them to extract dissolved oxygen from the water to breathe.
Streamlined Body: Many have a smooth, streamlined body shape that is pointed at the ends and wider in the middle. This shape reduces friction and helps them swim through water with ease.
Fins and Flippers: They use fins, flippers, or tails to propel, steer, and balance themselves in the water.
2. How do fish breathe underwater?
Fish breathe using specialised organs called gills. A fish takes water into its mouth and forces it out through the gill openings. As water passes over the thin walls of the gills, dissolved oxygen moves into the blood, while carbon dioxide moves out of the blood and into the water. This process allows them to breathe continuously without needing to come to the surface for air.
3. Why is a streamlined body an important feature for aquatic animals?
A streamlined body is crucial because it minimises water resistance, also known as drag. This shape—typically narrow at the front and back and wider in the middle—allows an animal like a fish or a dolphin to cut through the water efficiently. This adaptation helps them swim faster while using less energy, which is vital for hunting prey and escaping predators.
4. Can you give some examples of different types of aquatic animals?
Aquatic animals are very diverse. Some common examples include:
Fish: Such as tuna, clownfish, and sharks.
Mammals: Such as dolphins, whales, and seals.
Molluscs: Such as octopus, squid, and snails.
Crustaceans: Such as crabs, lobsters, and shrimp.
Insects: Such as dragonfly nymphs and water striders.
5. How are aquatic mammals like dolphins and whales different from fish?
While both live in water, aquatic mammals and fish are very different. The key distinction lies in their breathing mechanism; dolphins and whales have lungs and must surface to breathe air, whereas fish use gills to get oxygen from water. Additionally, aquatic mammals are warm-blooded and give birth to live young, while most fish are cold-blooded and lay eggs.
6. Do all aquatic animals live their entire lives in water?
No, not all aquatic animals spend their entire life in water. A key example is amphibians, like frogs. They begin their life as tadpoles, which live completely underwater and breathe with gills. As they grow into adult frogs, they develop lungs and can live on land, though they usually stay near water. Some insects, like dragonflies, also have an aquatic larval stage before becoming winged adults.
7. How do an animal's characteristics relate to its specific aquatic habitat, like a fast-flowing river versus a calm pond?
An animal's characteristics are finely tuned to its habitat. For instance, fish in fast-flowing rivers often have stronger, more muscular bodies to swim against the current. In contrast, animals in a calm pond might have adaptations for living among dense vegetation or on the muddy bottom. For example, a catfish has barbels (whiskers) to feel for food in murky pond water, a feature less common in clear, fast rivers.









