
What is \[Y\] in the following reaction ?
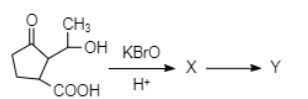

Answer
547.5k+ views
Hint:The process of oxidation can be identified by the loss of electrons, meaning, if the oxidation state of a compound or atom increases, then we can say the substance has gone through oxidation.
Similarly, reduction can be identified by gain of electrons, as in, if a compound has a lower oxidation state or it is becoming more negative, then we could say, it has gone through the process of reduction.
Complete step-by-step answer:Oxidation is the process in which electrons are donated to the compound which is going under the process of oxidation. Or in terms of protons we can say that oxidation is the process in which removal of protons takes place. And $KBrO$ which is used as a reagent in the given question, is an oxidising agent, and we can see there is a methyl group attached to the original compound, and so it will get oxidised and the bromine group from the reagent would get attached to it. The whole reaction is represented below.
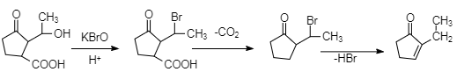
In the reaction as we can see, in the first step the alcoholic group gets substituted by bromine. And then the carboxylic group leaves the compound as carbon dioxide in order to form a product. In the next step, the bromine group leaves, taking a proton from the adjacent carbon and then forms a hydrogen bromide and leaves, giving rise to a double bond across the carbons. So, our final product is \[2-\]methylcyclopent-\[2-\]en-\[1\]-one. But, we were asked the name of the compound Y, which is formed in the second step, so the answer would be \[2-\] (\[1\]-bromoethyl)cyclopentane-\[1\]-one.
Note:The oxidising agents are the ones which themselves get reduced in order to oxidise some other substance. Potassium hypobromite is an oxidising agent which substitutes the alcoholic group with a bromine group in a compound.
Similarly, reduction can be identified by gain of electrons, as in, if a compound has a lower oxidation state or it is becoming more negative, then we could say, it has gone through the process of reduction.
Complete step-by-step answer:Oxidation is the process in which electrons are donated to the compound which is going under the process of oxidation. Or in terms of protons we can say that oxidation is the process in which removal of protons takes place. And $KBrO$ which is used as a reagent in the given question, is an oxidising agent, and we can see there is a methyl group attached to the original compound, and so it will get oxidised and the bromine group from the reagent would get attached to it. The whole reaction is represented below.

In the reaction as we can see, in the first step the alcoholic group gets substituted by bromine. And then the carboxylic group leaves the compound as carbon dioxide in order to form a product. In the next step, the bromine group leaves, taking a proton from the adjacent carbon and then forms a hydrogen bromide and leaves, giving rise to a double bond across the carbons. So, our final product is \[2-\]methylcyclopent-\[2-\]en-\[1\]-one. But, we were asked the name of the compound Y, which is formed in the second step, so the answer would be \[2-\] (\[1\]-bromoethyl)cyclopentane-\[1\]-one.
Note:The oxidising agents are the ones which themselves get reduced in order to oxidise some other substance. Potassium hypobromite is an oxidising agent which substitutes the alcoholic group with a bromine group in a compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




