
‘X’ can be
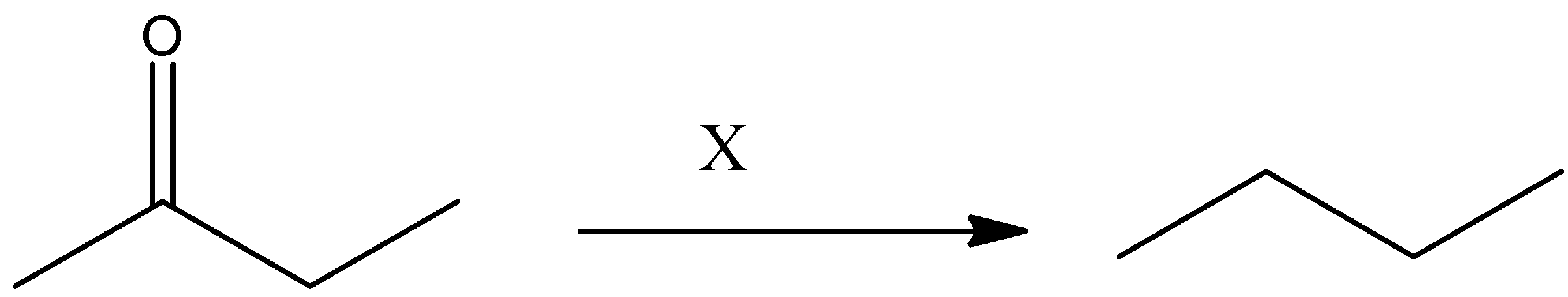
(A) ${{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{/OEt, }\Delta $
(B) $\text{Red}\,\text{P/}\,\text{HI}$
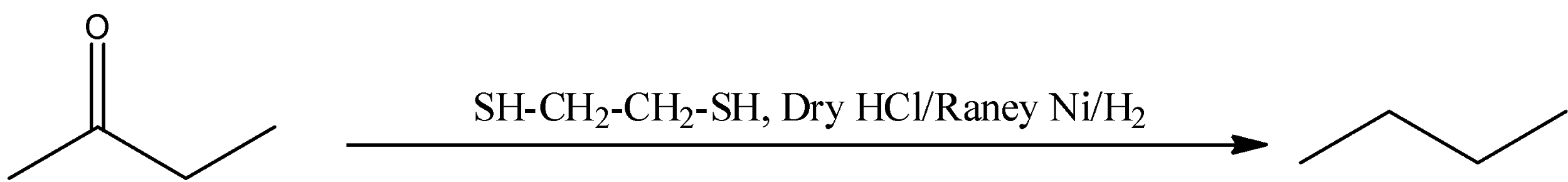
(C) $\text{HS-C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{-C}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{-SH(dithiol), Dry}\,\text{HCl/Raney}\,\text{Ni/}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$
(D) All of these
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: Carbonyl compounds can be converted into respective hydrocarbons by treating with á$\text{Zn/HCl and }{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{(hydrazine)/}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\text{ONa}$, these reagents known as Clemmensen and Wolff-Kishner reagent respectively.
- Raney nickel $\text{(Ni)}$ is like palladium on carbon $\text{(Pt/C)}$ reducing agent, which is mainly used for the hydrogenation of alkene and alkynes. Raney nickel is mainly used for the reduction of $\text{C-S}$ bond to $\text{C-H}$ bond. This reagent can be used as an alternative means for the conversion ketone to alkane.
- Red phosphorus with hydrogen iodide acts as a strong reducing agent by producing nascent hydrogen atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
(A) Aldehyde and ketone are reduced by hydrazine $\text{(N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{-N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}$ in the presence $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{-C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ONa}$ and form hydrocarbon, this reaction is known as Wolff-Kishner reduction. So $\text{buten-2-one}$ reacts with hydrazine in the basic medium gives $\text{n-butane}$. This reaction is represented by following reaction-
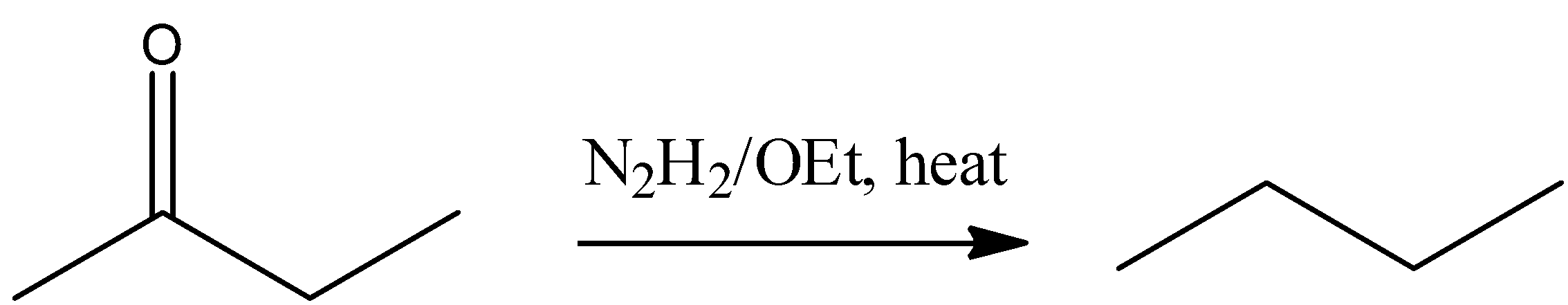
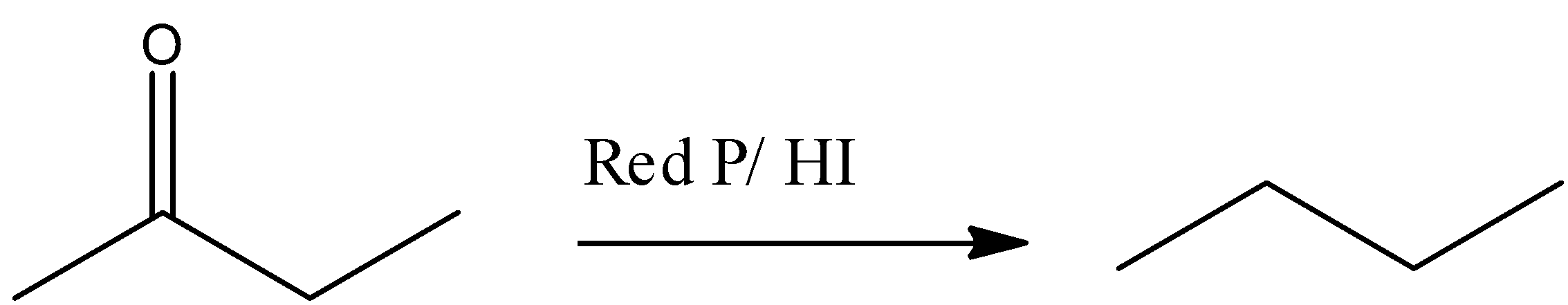
(B) $\text{Red}\,\text{P/}\,\text{HI}$, acts as a powerful reducing agent, it will give alkane ($\text{n-butane}$) after the complete reduction carbonyl group of $\text{buten-2-one}$ . This reaction is represented by following reaction –
(C) Thiols will react in the acidic medium with the carbonyl group of $\text{buten-2-one}$ (ketone) to form thioketal. After reacting with Raney nickel removal of the sulphur group takes place and finally forms $\text{n-butane}$. This reaction is represented in the following reaction.
The correct answer is option “D” .
Note: In $\text{Red}\,\text{P/}\,\text{HI}$ , Red phosphorus acts as a catalyst and this reducing agent reduces carbonyl compounds to respective alkane. In this reduction process red phosphorus reacts with $\text{HI}$ and forms $\text{P}{{\text{I}}_{\text{3}}}$ . It is the reaction controlling agent. It removes iodine which is necessary because iodine is highly reactive. It will react with hydrocarbon and form haloalkane.
- Raney nickel $\text{(Ni)}$ is like palladium on carbon $\text{(Pt/C)}$ reducing agent, which is mainly used for the hydrogenation of alkene and alkynes. Raney nickel is mainly used for the reduction of $\text{C-S}$ bond to $\text{C-H}$ bond. This reagent can be used as an alternative means for the conversion ketone to alkane.
- Red phosphorus with hydrogen iodide acts as a strong reducing agent by producing nascent hydrogen atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
(A) Aldehyde and ketone are reduced by hydrazine $\text{(N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{-N}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{)}$ in the presence $\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{-C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{ONa}$ and form hydrocarbon, this reaction is known as Wolff-Kishner reduction. So $\text{buten-2-one}$ reacts with hydrazine in the basic medium gives $\text{n-butane}$. This reaction is represented by following reaction-
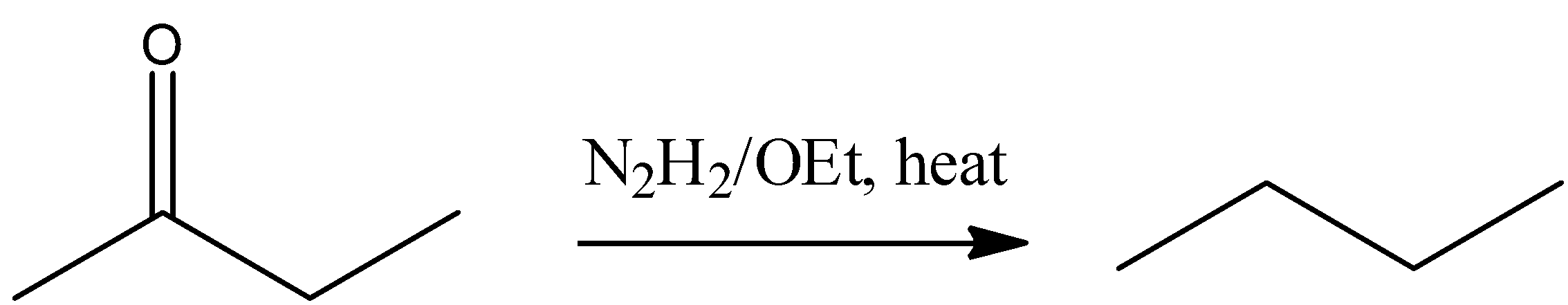
(B) $\text{Red}\,\text{P/}\,\text{HI}$, acts as a powerful reducing agent, it will give alkane ($\text{n-butane}$) after the complete reduction carbonyl group of $\text{buten-2-one}$ . This reaction is represented by following reaction –

(C) Thiols will react in the acidic medium with the carbonyl group of $\text{buten-2-one}$ (ketone) to form thioketal. After reacting with Raney nickel removal of the sulphur group takes place and finally forms $\text{n-butane}$. This reaction is represented in the following reaction.

The correct answer is option “D” .
Note: In $\text{Red}\,\text{P/}\,\text{HI}$ , Red phosphorus acts as a catalyst and this reducing agent reduces carbonyl compounds to respective alkane. In this reduction process red phosphorus reacts with $\text{HI}$ and forms $\text{P}{{\text{I}}_{\text{3}}}$ . It is the reaction controlling agent. It removes iodine which is necessary because iodine is highly reactive. It will react with hydrocarbon and form haloalkane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




