
Write the two types of secondary structures of proteins?
Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint: In proteins, we have primary structure that refers to the sequence of amino acids, whereas the secondary structure of proteins refers to the shape that can be taken up by its polypeptide chain.
Complete answer:In proteins, we have primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures where each one refers to different levels of complexity for example, in primary structure we look at the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chains of the protein. However, in the secondary structure we look at the shape of these chains. Let’s talk about the secondary structure in terms of its two different types namely $\alpha $-helix structure and $\beta $-pleated sheet structure.
Both of these shapes are results of hydrogen bonding. In polypeptide chains, we have carbonyl group $\left( { > {\rm{C}} = {\rm{O}}} \right)$ and \[ > {\rm{N}} - {\rm{H}}\] part. As we can see the hydrogen bonding can exist between the electronegative oxygen atom of the carbonyl group and the hydrogen atom attached to the nitrogen. Now, the different ways in which this hydrogen bonding takes place give rise to these two types of secondary structures.
In $\alpha $-helix structure, we have a polypeptide chain that has taken the shape of a twisted right handed screw because all possible hydrogen bonds are formed between the hydrogen and oxygen present on the adjacent turns. However, in $\beta $-pleated sheet structure, our polypeptide chains are arranged in a sheet form as they are stretched out and laid side by side. Hydrogen bonding is used to hold them together. The structures are shown below:
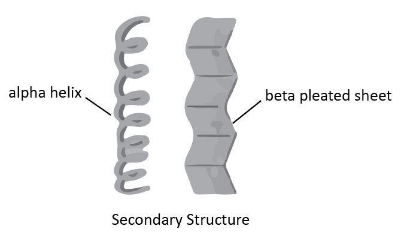
Note:The tertiary structure gives us the nature of folding of secondary to give fibrous and globular shapes. The quaternary structure of the protein refers to the relative spatial arrangement of subunits if a protein has any.
Complete answer:In proteins, we have primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures where each one refers to different levels of complexity for example, in primary structure we look at the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chains of the protein. However, in the secondary structure we look at the shape of these chains. Let’s talk about the secondary structure in terms of its two different types namely $\alpha $-helix structure and $\beta $-pleated sheet structure.
Both of these shapes are results of hydrogen bonding. In polypeptide chains, we have carbonyl group $\left( { > {\rm{C}} = {\rm{O}}} \right)$ and \[ > {\rm{N}} - {\rm{H}}\] part. As we can see the hydrogen bonding can exist between the electronegative oxygen atom of the carbonyl group and the hydrogen atom attached to the nitrogen. Now, the different ways in which this hydrogen bonding takes place give rise to these two types of secondary structures.
In $\alpha $-helix structure, we have a polypeptide chain that has taken the shape of a twisted right handed screw because all possible hydrogen bonds are formed between the hydrogen and oxygen present on the adjacent turns. However, in $\beta $-pleated sheet structure, our polypeptide chains are arranged in a sheet form as they are stretched out and laid side by side. Hydrogen bonding is used to hold them together. The structures are shown below:

Note:The tertiary structure gives us the nature of folding of secondary to give fibrous and globular shapes. The quaternary structure of the protein refers to the relative spatial arrangement of subunits if a protein has any.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE




