
Write the structures of the products of the following reactions.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)



Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: The answer to this question includes Markovnikov’s addition and sodium borohydrate is a reducing agent which converts aldehydes and ketones to primary and secondary alcohols respectively.
Complete step by step answer:
We have studied in our chemistry topics about the organic reactions that involve addition reactions, substitution and elimination reactions and also oxidation and reduction processes.
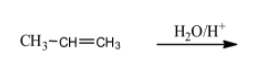
Here in the first question that is
(i) Alkene (here propene) is treated with water and acid which is basically called a hydration reaction which means that the compound combines with water.
This reaction follows Markovnikov’s addition rule which states that the $-OH$ group attaches to that carbon which is having less number of hydrogen atoms.
Therefore, here the $-OH$ group attached to second carbon [naming based on IUPAC rules] and the product is as follows,
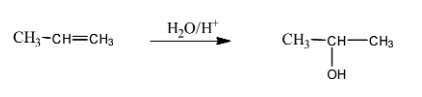
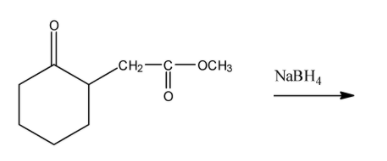
(ii) In the second question the given ketone derivative is treated with sodium borohydride. This acts as a reducing agent.
Here since the compound given is having an ester group attached to it the reduction takes place to the ketone group attached to the ring and $NaB{{H}_{4}}$is unreactive towards the ester group.
Thus the following reaction taking place is,
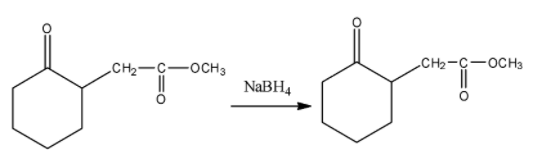
Thus, ketone is converted to secondary alcohol.
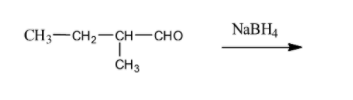
(iii) In the last question, the compound consists of only one functional group that is an aldehydic group and the reduction takes place at that place as shown below,
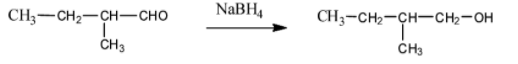
Therefore we get primary alcohol by the reduction of aldehyde with$NaB{{H}_{4}}$.
Note: Sodium borohydride is actually less reactive compared to that of lithium aluminium hydride and it is powerful enough for the reduction of aldehydes, ketones and acid chlorides to alcohols and is unreactive towards esters, amides, acids and nitriles. This point helps for easy guessing of answers.
Complete step by step answer:
We have studied in our chemistry topics about the organic reactions that involve addition reactions, substitution and elimination reactions and also oxidation and reduction processes.
Here in the first question that is
(i) Alkene (here propene) is treated with water and acid which is basically called a hydration reaction which means that the compound combines with water.
This reaction follows Markovnikov’s addition rule which states that the $-OH$ group attaches to that carbon which is having less number of hydrogen atoms.
Therefore, here the $-OH$ group attached to second carbon [naming based on IUPAC rules] and the product is as follows,
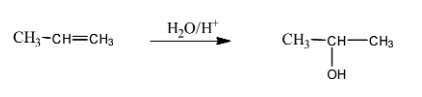
(ii) In the second question the given ketone derivative is treated with sodium borohydride. This acts as a reducing agent.
Here since the compound given is having an ester group attached to it the reduction takes place to the ketone group attached to the ring and $NaB{{H}_{4}}$is unreactive towards the ester group.
Thus the following reaction taking place is,

Thus, ketone is converted to secondary alcohol.
(iii) In the last question, the compound consists of only one functional group that is an aldehydic group and the reduction takes place at that place as shown below,

Therefore we get primary alcohol by the reduction of aldehyde with$NaB{{H}_{4}}$.
Note: Sodium borohydride is actually less reactive compared to that of lithium aluminium hydride and it is powerful enough for the reduction of aldehydes, ketones and acid chlorides to alcohols and is unreactive towards esters, amides, acids and nitriles. This point helps for easy guessing of answers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




