
Write the structure of compounds A, B and C in each of the following reactions:
I)${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Br}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Mg/dry ether}}}}{\text{A}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{b)}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ + }}}}]{{{\text{a)C}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{2(g)}}}}}}{\text{B}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}}}{\text{C}}$
II)${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CN}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{b)}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ + }}}}]{{{\text{a)SnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}}}{\text{A}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{dil}}{\text{.NaOH}}}}{\text{B}}\xrightarrow{{\text{\Delta }}}{\text{C}}$
Answer
544.5k+ views
Hint: In the above question, we are provided with two chemical reactions and we have to determine what are A, B and C. Here, Grignard reagent, carboxylic acid and aldehyde is going to be formed. Here, we are going to apply the Saytzeff Rule and the aldol reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:Let us look at the two reactions one by one.
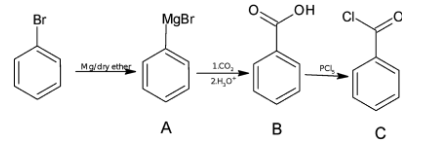
I) ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Br}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Mg/dry ether}}}}{\text{A}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{b)}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ + }}}}]{{{\text{a)C}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{2(g)}}}}}}{\text{B}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}}}{\text{C}}$
Alkyl halide reacts with Mg/ dry ether to form Grignard reagent. So, the formula of A is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{ - MgBr}}$
When Grignard reagent is added with carbon dioxide followed by hydrolysis, carboxylic acid is formed which have one more carbon atom.
Hence, the chemical formula of A is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{COOH}}$.
${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$used for replacing the –OH group by –Cl. Hence, the chemical formula of C is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{COCl}}$.
So, the above chemical reaction is illustrated as:
Now let us look at the second equation:
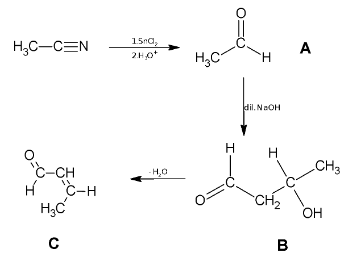
II)${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CN}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{b)}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ + }}}}]{{{\text{a)SnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}}}{\text{A}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{dil}}{\text{.NaOH}}}}{\text{B}}\xrightarrow{{\text{\Delta }}}{\text{C}}$
When a cyanide compound is reacted with tin chloride followed by hydrolysis, it leads to formation of aldehyde. So, the chemical formula of A is ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHO}}$.
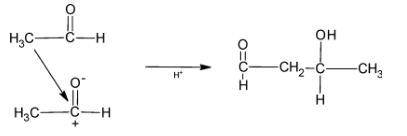
When NaOH is reacted with an aldehyde, aldol reaction takes place, that is, the H present at the alpha carbon is removed and the carbon gets attached to the aldehyde carbon group leading to the formation of 3 hydroxybutanal.
The reaction is illustrated as:
Now the compound undergoes dehydration which means removal of water molecule. The –OH molecule will be removed along with H atom from the beta carbon. The H will remove from the carbon atom which is accordance with Saytzeff-rule. According to Saytzeff rule, hydrogen is eliminated from the carbon which has less number of hydrogen. Hence, but-2-en-1-al is formed.
The whole reaction is illustrated as:
Note:Organic compounds are all around us. They are central to the economic growth of the United States in the rubber, plastics, fuel, pharmaceutical, cosmetics, detergent, coatings, dyestuff, and agrochemical industries, to name a few. The very foundations of biochemistry, biotechnology, and medicine are built on organic compounds and their role in life processes.
Complete step-by-step answer:Let us look at the two reactions one by one.
I) ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Br}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{Mg/dry ether}}}}{\text{A}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{b)}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ + }}}}]{{{\text{a)C}}{{\text{O}}_{{\text{2(g)}}}}}}{\text{B}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}}}{\text{C}}$
Alkyl halide reacts with Mg/ dry ether to form Grignard reagent. So, the formula of A is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{ - MgBr}}$
When Grignard reagent is added with carbon dioxide followed by hydrolysis, carboxylic acid is formed which have one more carbon atom.
Hence, the chemical formula of A is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{COOH}}$.
${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$used for replacing the –OH group by –Cl. Hence, the chemical formula of C is ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{COCl}}$.
So, the above chemical reaction is illustrated as:

Now let us look at the second equation:
II)${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CN}}\xrightarrow[{{\text{b)}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^{\text{ + }}}}]{{{\text{a)SnC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{/HCl}}}}{\text{A}}\xrightarrow{{{\text{dil}}{\text{.NaOH}}}}{\text{B}}\xrightarrow{{\text{\Delta }}}{\text{C}}$
When a cyanide compound is reacted with tin chloride followed by hydrolysis, it leads to formation of aldehyde. So, the chemical formula of A is ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CHO}}$.
When NaOH is reacted with an aldehyde, aldol reaction takes place, that is, the H present at the alpha carbon is removed and the carbon gets attached to the aldehyde carbon group leading to the formation of 3 hydroxybutanal.
The reaction is illustrated as:

Now the compound undergoes dehydration which means removal of water molecule. The –OH molecule will be removed along with H atom from the beta carbon. The H will remove from the carbon atom which is accordance with Saytzeff-rule. According to Saytzeff rule, hydrogen is eliminated from the carbon which has less number of hydrogen. Hence, but-2-en-1-al is formed.
The whole reaction is illustrated as:

Note:Organic compounds are all around us. They are central to the economic growth of the United States in the rubber, plastics, fuel, pharmaceutical, cosmetics, detergent, coatings, dyestuff, and agrochemical industries, to name a few. The very foundations of biochemistry, biotechnology, and medicine are built on organic compounds and their role in life processes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




