
Write the structure of chlorous acid $\left[ {HOClO} \right]$ .
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: Chlorous acid is an inorganic compound with formula $HCl{O_2}$ . It is a weak acid. Chlorine has oxidation state $ + 3$ in this acid. It consists of one chlorine atom, one hydrogen atom, and two oxygen atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of chlorous acid is as follows:
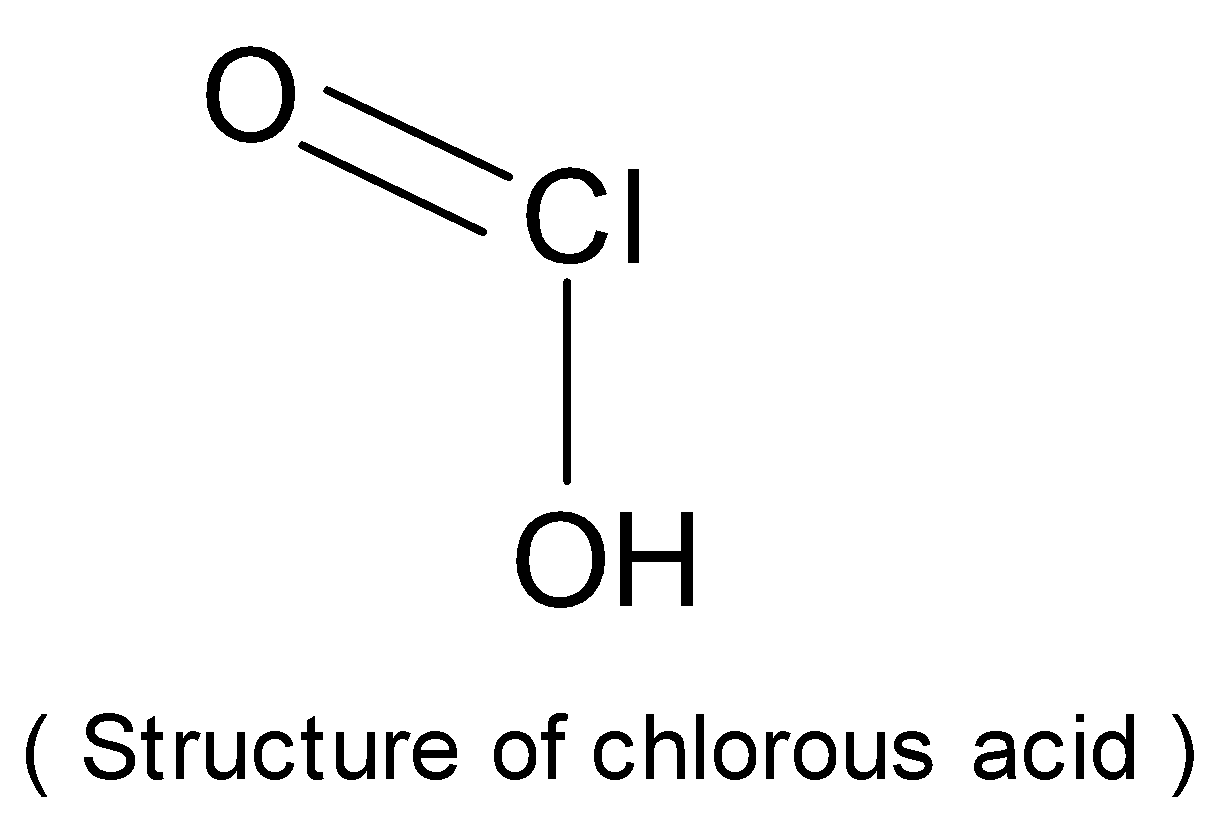
Chlorous acid is a chlorine oxoacid. It is a conjugate acid of chlorite.
The pure chlorous acid is unstable, disprotionating to hypochlorous acid ( $Cl$ oxidation state of $ + 1$ ) and chloric acid ( $Cl$ oxidation state of $ + 5$ ).
$2HCl{O_2} \to HClO + HCl{O_3}$
The acid is difficult to obtain in pure substances; the conjugate base, chlorite, derived from this acid is stable.
One example of a salt of this anion is well known sodium chloride.
This and salts related to this are sometimes used in production of chlorine dioxide.
$HCl{O_2}$ can be prepared through the reaction of lead chloride and dilute sulphuric acid.
$Ba{\left( {Cl{O_2}} \right)_2} + {H_2}S{O_4} \to BaS{O_4} + 2HCl{O_2}$
$Pb{\left( {Cl{O_2}} \right)_2} + {H_2}S{O_4} \to PbS{O_4} + 2HCl{O_2}$
Chlorous acid is a very powerful oxidizing agent, although its tendency to disproportionation counteracts its oxidizing potential.
Additional Information:
Chlorine is the only halogen to form an isolable acid of formula $HX{O_2}$ . Neither bromous acid nor iodous acid has ever been isolated.
A few salts of bromous acid, bromites, are known, but no iodites.
Uses:
The use of chlorous acid is very limited due to its instability. However, its conjugate base chlorite is used as a salt of sodium that is used in some industrial processes as the production of chlorine dioxide.
The physical properties of chlorous acid have not been correctly determined due to its high instability. It has $1.96\,p{{\text{K}}_a}$ and it is determined as the stability of the conjugate base of a determined acid. A value of $1.96$ means the conjugate base chlorite $Cl{O_2}$ is stable.
Note:
As many compounds that contain chlorine, chlorous acid is extremely harmful if swallowed or inhaled. It can cause severe damages in eyes, mucous and skin. It is a strong oxidizing agent, however its reactivity is limited by its poor stability.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of chlorous acid is as follows:

Chlorous acid is a chlorine oxoacid. It is a conjugate acid of chlorite.
The pure chlorous acid is unstable, disprotionating to hypochlorous acid ( $Cl$ oxidation state of $ + 1$ ) and chloric acid ( $Cl$ oxidation state of $ + 5$ ).
$2HCl{O_2} \to HClO + HCl{O_3}$
The acid is difficult to obtain in pure substances; the conjugate base, chlorite, derived from this acid is stable.
One example of a salt of this anion is well known sodium chloride.
This and salts related to this are sometimes used in production of chlorine dioxide.
$HCl{O_2}$ can be prepared through the reaction of lead chloride and dilute sulphuric acid.
$Ba{\left( {Cl{O_2}} \right)_2} + {H_2}S{O_4} \to BaS{O_4} + 2HCl{O_2}$
$Pb{\left( {Cl{O_2}} \right)_2} + {H_2}S{O_4} \to PbS{O_4} + 2HCl{O_2}$
Chlorous acid is a very powerful oxidizing agent, although its tendency to disproportionation counteracts its oxidizing potential.
Additional Information:
Chlorine is the only halogen to form an isolable acid of formula $HX{O_2}$ . Neither bromous acid nor iodous acid has ever been isolated.
A few salts of bromous acid, bromites, are known, but no iodites.
Uses:
The use of chlorous acid is very limited due to its instability. However, its conjugate base chlorite is used as a salt of sodium that is used in some industrial processes as the production of chlorine dioxide.
The physical properties of chlorous acid have not been correctly determined due to its high instability. It has $1.96\,p{{\text{K}}_a}$ and it is determined as the stability of the conjugate base of a determined acid. A value of $1.96$ means the conjugate base chlorite $Cl{O_2}$ is stable.
Note:
As many compounds that contain chlorine, chlorous acid is extremely harmful if swallowed or inhaled. It can cause severe damages in eyes, mucous and skin. It is a strong oxidizing agent, however its reactivity is limited by its poor stability.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




