
Write the stages observed while studying the permanent slide of budding in yeast.
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: Asexual reproduction is typical in lower plants and in some lower animals. This is a method of accelerated replication in which the new species generated are genetically similar to the parent.
Complete answer:
Reproduction in organisms may be either sexual or asexual. The method of reproduction that happens without the development of gametes is called asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction is the type of reproduction in which fusion of the male and female gametes takes place.
Yeast is a unicellular organism that belongs to the Fungi kingdom. Most yeasts replicate asexually through the mechanism of asymmetric division called budding. Small buds are formed on the parent body as the nucleus separates. These buds grow into small individuals and when fully grown, detach themselves from the parent body and become new individuals.
Stages seen during budding in yeast are-
i) The parent cell produces small protuberance that develops into a bud.
ii) The nucleus of the parent cell divides and moves into the daughter cell.
iii) The bud is isolated from the body of the mother.
iv) Budding is replicated and a chain of buds is formed.
(v) The daughter cell formed during the budding is usually smaller than the mother cell.
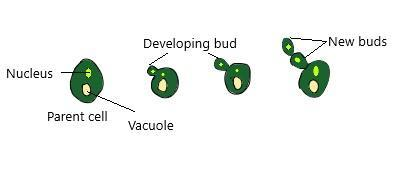
Fig: Budding in yeast
Note: Asexual reproduction may be of different forms, such as binary fission, multiple fission, fragmentation, spore formation, budding, and vegetative propagation.
Complete answer:
Reproduction in organisms may be either sexual or asexual. The method of reproduction that happens without the development of gametes is called asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction is the type of reproduction in which fusion of the male and female gametes takes place.
Yeast is a unicellular organism that belongs to the Fungi kingdom. Most yeasts replicate asexually through the mechanism of asymmetric division called budding. Small buds are formed on the parent body as the nucleus separates. These buds grow into small individuals and when fully grown, detach themselves from the parent body and become new individuals.
Stages seen during budding in yeast are-
i) The parent cell produces small protuberance that develops into a bud.
ii) The nucleus of the parent cell divides and moves into the daughter cell.
iii) The bud is isolated from the body of the mother.
iv) Budding is replicated and a chain of buds is formed.
(v) The daughter cell formed during the budding is usually smaller than the mother cell.

Fig: Budding in yeast
Note: Asexual reproduction may be of different forms, such as binary fission, multiple fission, fragmentation, spore formation, budding, and vegetative propagation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




