
write the product of the following reaction.
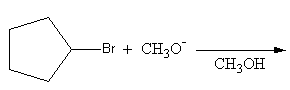
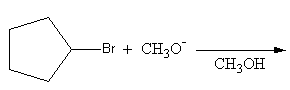
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: To answer this question we should know what is primary. Secondary or tertiary halides and what is protic an aprotic solvent and how do they affect the mechanism of the reaction. First, we will see the reactant and then solvent and then decide the type of mechanism that should be followed by the reaction. After that, we will determine the product.
Complete step by step answer:
First we will check the reactant as follows:
The primary and secondary alkyl halide goes through ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$ or${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$mechanism. The tertiary alkyl halide${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{1}}}$ mechanism.
The given alkyl halide is a secondary alkyl halide so, the reaction will proceed through
${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$ or${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$.
Now we will check the solvent as follows:
Polar protic solvent favour the ${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$ mechanism and polar aprotic solvent favours the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The given solvent is methanol ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH}}$ which is a polar protic solvent. So, the given reaction will proceed through ${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$ mechanism.
${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$ is known as a bimolecular elimination mechanism. In this mechanism a base abstract the proton from the alkyl halide forming a negative charge. The negative charge shifts to the next carbon forming a carbon-carbon double bond and simultaneously the leaving group leaves.
The reaction of given alkyl halide with methoxy base in presence of methanol is shown as follows:
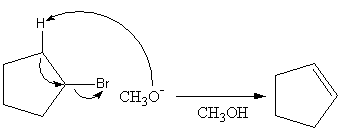
So, the product of the reaction is cyclopentene.
Note: In primary and secondary alkyl halide if the reaction proceed through ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{1}}}$ it cannot form highly stable tertiary carbocation so, the reaction will proceed through ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$ or${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$. The stability order of carbocation is tertiary > secondary > primary. The solvent which can form hydrogen bond or we can say have hydroxy group are known as polar protic solvent. The solvent that cannot form hydrogen bond are known as a polar aprotic solvent.
Complete step by step answer:
First we will check the reactant as follows:
The primary and secondary alkyl halide goes through ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$ or${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$mechanism. The tertiary alkyl halide${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{1}}}$ mechanism.
The given alkyl halide is a secondary alkyl halide so, the reaction will proceed through
${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$ or${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$.
Now we will check the solvent as follows:
Polar protic solvent favour the ${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$ mechanism and polar aprotic solvent favours the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The given solvent is methanol ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{OH}}$ which is a polar protic solvent. So, the given reaction will proceed through ${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$ mechanism.
${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$ is known as a bimolecular elimination mechanism. In this mechanism a base abstract the proton from the alkyl halide forming a negative charge. The negative charge shifts to the next carbon forming a carbon-carbon double bond and simultaneously the leaving group leaves.
The reaction of given alkyl halide with methoxy base in presence of methanol is shown as follows:

So, the product of the reaction is cyclopentene.
Note: In primary and secondary alkyl halide if the reaction proceed through ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{1}}}$ it cannot form highly stable tertiary carbocation so, the reaction will proceed through ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}$ or${{\text{E}}_{\text{2}}}$. The stability order of carbocation is tertiary > secondary > primary. The solvent which can form hydrogen bond or we can say have hydroxy group are known as polar protic solvent. The solvent that cannot form hydrogen bond are known as a polar aprotic solvent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




