
Write the number of structural isomers of the compound having formula ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{9}}Br$.
(A)- 4
(B)- 5
(C)- 6
(D)- 7
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: When a compound has the same number of atoms of each element but is distinct from each other, because of bonds between them, is known to be the structural isomer.
Complete answer:
-Molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulas that have the same number of atoms of each element but distinct arrangements of atoms in space are known as Isomers and the phenomenon is known as Isomerism.
-In other words, the isomers in which the atoms are completely arranged in a different order with the same molecular formula is known as structural isomers.
-According to IUPAC, structural isomerism is also known as constitutional isomerism.
-There are three different types of structural isomerism which are chain isomerism, position isomerism and functional group isomerism.
-When there is a difference in the atomic arrangement of the carbon to carbon chain of the molecule, chain isomerism is found. If two or more compounds with the same molecular formula and different main chains, the phenomenon is known as skeletal isomerism.
-When there is a difference in the positions occupied by the substituent atoms or a group of atoms due to unsaturation occurring in the chain, position isomerism is found. When the position of the functional groups concerning main changes and atom changes, the phenomenon is known as position isomerism.
-When there is a presence of the odd number of functional groups with the same chemical formula, functional group isomerism is seen. When some compound has two different structures but the same chemical formula, the phenomenon is known as functional isomerism.
- To find the number of structural isomers, we will first draw a simple carbon chain of four-member and then will place bromine in all the possible ways. We will find that we have four constitutional isomers of ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{9}}Br$ which are given below-
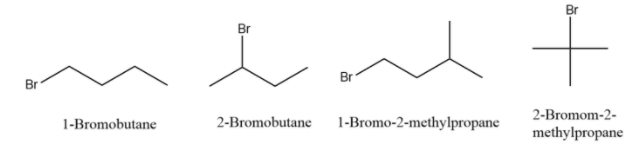
Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note: Enumeration or counting structural isomers for a compound is a difficult problem, one must take into account several bond types (both localized and delocalized ones), cyclic structures, the structure which cannot be possible due to valence or geometric constraints and non-separable tautomers and many other factors.
Complete answer:
-Molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulas that have the same number of atoms of each element but distinct arrangements of atoms in space are known as Isomers and the phenomenon is known as Isomerism.
-In other words, the isomers in which the atoms are completely arranged in a different order with the same molecular formula is known as structural isomers.
-According to IUPAC, structural isomerism is also known as constitutional isomerism.
-There are three different types of structural isomerism which are chain isomerism, position isomerism and functional group isomerism.
-When there is a difference in the atomic arrangement of the carbon to carbon chain of the molecule, chain isomerism is found. If two or more compounds with the same molecular formula and different main chains, the phenomenon is known as skeletal isomerism.
-When there is a difference in the positions occupied by the substituent atoms or a group of atoms due to unsaturation occurring in the chain, position isomerism is found. When the position of the functional groups concerning main changes and atom changes, the phenomenon is known as position isomerism.
-When there is a presence of the odd number of functional groups with the same chemical formula, functional group isomerism is seen. When some compound has two different structures but the same chemical formula, the phenomenon is known as functional isomerism.
- To find the number of structural isomers, we will first draw a simple carbon chain of four-member and then will place bromine in all the possible ways. We will find that we have four constitutional isomers of ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{9}}Br$ which are given below-

Hence the correct answer is option A.
Note: Enumeration or counting structural isomers for a compound is a difficult problem, one must take into account several bond types (both localized and delocalized ones), cyclic structures, the structure which cannot be possible due to valence or geometric constraints and non-separable tautomers and many other factors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




