
Write the names and structural formulae of the raw materials used in the preparation of Nylon-6,6.
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Nylon-6,6 is prepared from adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine by condensation polymerisation process.
Complete step by step answer:
Nylon-6,6 is synthesised by condensation polymerisation of adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine that is by loss of water molecule. There are six carbon atoms in each of the starting materials that is adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine thus we get the name “Nylon-6,6”. This process occurs at high temperature and high pressure.
Raw materials required for the preparation of Nylon-6,6 are
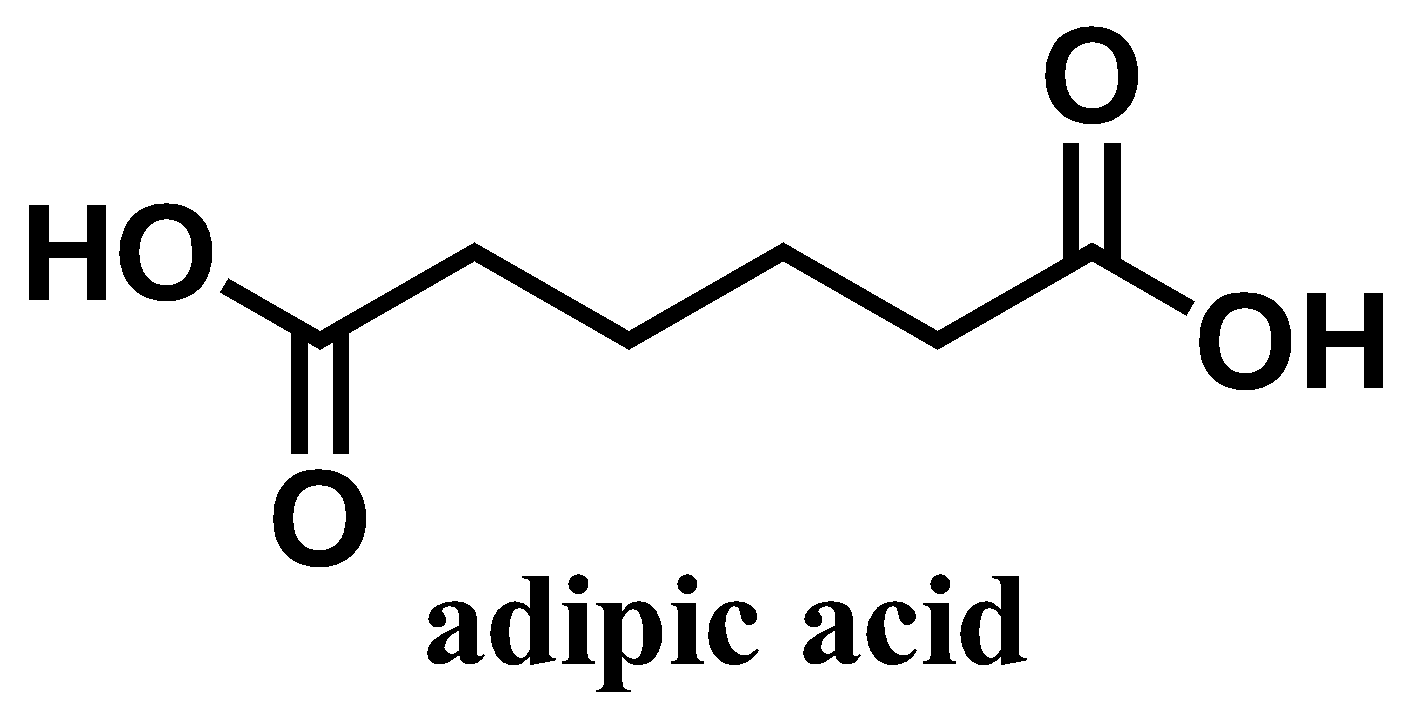
Adipic acid-\[{\text{HOOC(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{)}}_{{\text{4}}}}{\text{COOH}}{\text{}}\]
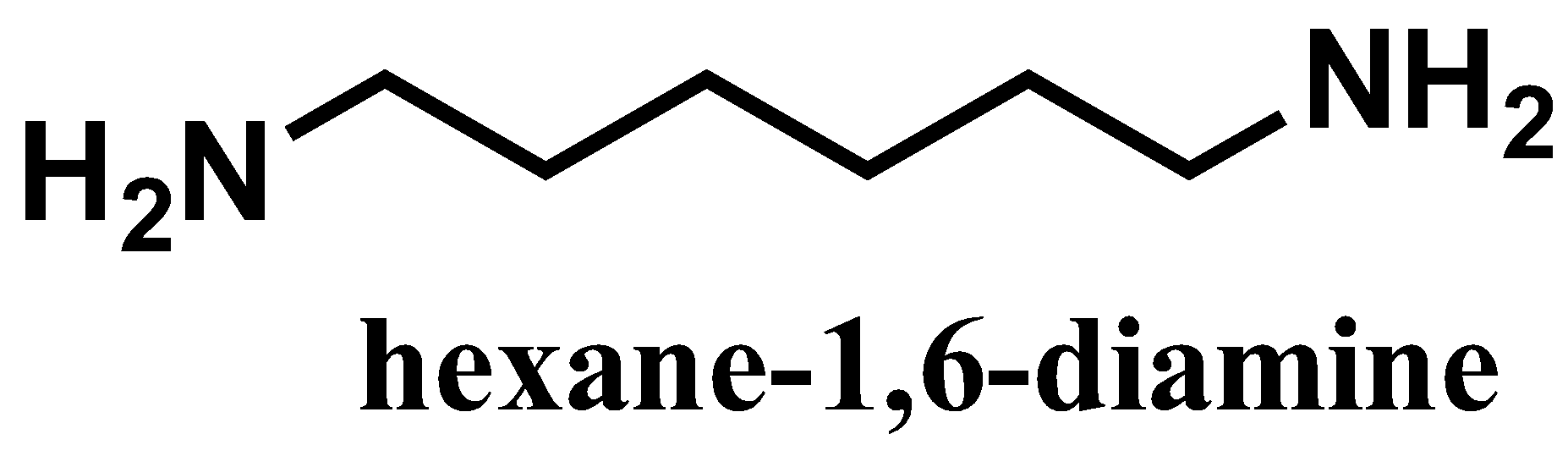
Hexamethylenediamine- \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{N(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{2}}}}\]
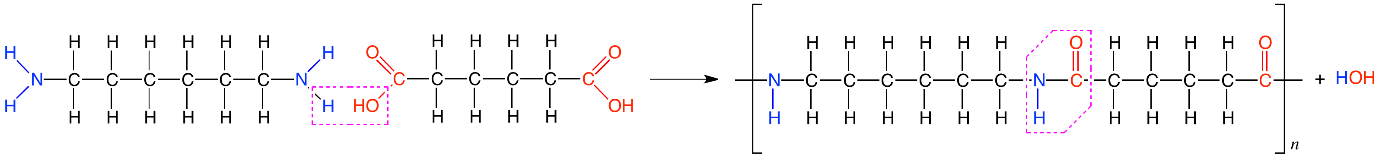
Nylon 6,6 has high mechanical strength, rigidity, and good stability. Besides, they are heat and chemical resistant in most conditions. It has wide applications in plastic and textile industries. It is used in fibres for textiles and carpets and moulded parts. It is also popularly used in guitar nut material due to its high tensile strength.
Note:
There is a quite similar polymer name nylon 6 which can cause confusion but they are two different polymers. Both Nylon 6 and 6,6 materials are easy to process, provide incredible strength, they’re very tough. While they’re very similar, each offers separate and distinct benefits. Nylon 6 is made from a caprolactam monomer having six carbon atoms whereas Nylon 6,6 is prepared from adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine. Unlike nylon 6,6, in which the direction of the amide bond reverses at each bond, all nylon 6 amide bonds lie in the same direction.
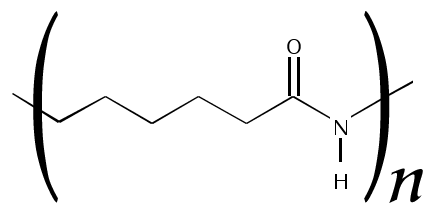
Structure of Nylon 6
Complete step by step answer:
Nylon-6,6 is synthesised by condensation polymerisation of adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine that is by loss of water molecule. There are six carbon atoms in each of the starting materials that is adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine thus we get the name “Nylon-6,6”. This process occurs at high temperature and high pressure.
Raw materials required for the preparation of Nylon-6,6 are
Adipic acid-\[{\text{HOOC(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{)}}_{{\text{4}}}}{\text{COOH}}{\text{}}\]
Hexamethylenediamine- \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{N(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{6}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{2}}}}\]


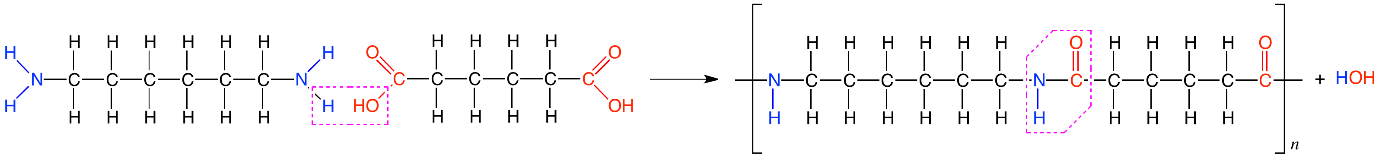
Nylon 6,6 has high mechanical strength, rigidity, and good stability. Besides, they are heat and chemical resistant in most conditions. It has wide applications in plastic and textile industries. It is used in fibres for textiles and carpets and moulded parts. It is also popularly used in guitar nut material due to its high tensile strength.
Note:
There is a quite similar polymer name nylon 6 which can cause confusion but they are two different polymers. Both Nylon 6 and 6,6 materials are easy to process, provide incredible strength, they’re very tough. While they’re very similar, each offers separate and distinct benefits. Nylon 6 is made from a caprolactam monomer having six carbon atoms whereas Nylon 6,6 is prepared from adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine. Unlike nylon 6,6, in which the direction of the amide bond reverses at each bond, all nylon 6 amide bonds lie in the same direction.

Structure of Nylon 6
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




