
Write the main product:


Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: As we know that given reaction between methyl tert-butyl ether and hydrogen iodide follows ${S_N}1$ reaction mechanism and the product formation is decided by the stability of the carbocation formed.
Complete Step by step answer: As we have already learnt that the reaction between methyl tert-butyl ether and hydrogen iodide follows ${S_N}1$ reaction mechanism which is nucleophilic substitution unimolecular mechanism of reaction and it is a two-step reaction involving the slow ionisation of substrate in the first step hence called the rate determining step and rapid reaction between the carbocation formed and the nucleophile in the second step. Here the ionisation of tert butyl ether will take place and result in the formation of carbocation called tert butyl carbonium and then the iodide ion acting as a nucleophile will attack the carbocation and hydrogen will attack the oxygen with lone pairs of electron and result in the formation of products. We can represent it as:
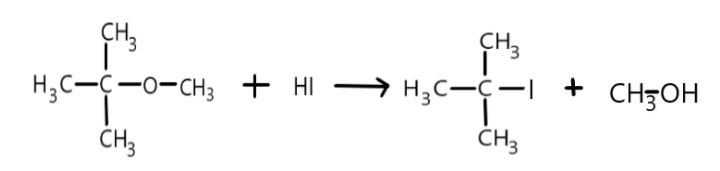
Therefore the main products formed are tert butyl-iodide and methanol. ${S_N}1$ reaction generally proceeds in the polar protic solvents such as water, methanol, methanoic acid etc. The tert butyl carbonium ion is more stable as compared to the methyl carbonium ion. Hence there will be production of tert butyl carbocation instead of methyl carbocation.
Note: The rate of reaction in the rate determining step depends upon the concentration of main reactant which is tert butyl ether only and is independent of the concentration of nucleophile and the greater the stability of the carbocation, greater will be its ease of formation of product and faster will be the rate of reaction.
Complete Step by step answer: As we have already learnt that the reaction between methyl tert-butyl ether and hydrogen iodide follows ${S_N}1$ reaction mechanism which is nucleophilic substitution unimolecular mechanism of reaction and it is a two-step reaction involving the slow ionisation of substrate in the first step hence called the rate determining step and rapid reaction between the carbocation formed and the nucleophile in the second step. Here the ionisation of tert butyl ether will take place and result in the formation of carbocation called tert butyl carbonium and then the iodide ion acting as a nucleophile will attack the carbocation and hydrogen will attack the oxygen with lone pairs of electron and result in the formation of products. We can represent it as:

Therefore the main products formed are tert butyl-iodide and methanol. ${S_N}1$ reaction generally proceeds in the polar protic solvents such as water, methanol, methanoic acid etc. The tert butyl carbonium ion is more stable as compared to the methyl carbonium ion. Hence there will be production of tert butyl carbocation instead of methyl carbocation.
Note: The rate of reaction in the rate determining step depends upon the concentration of main reactant which is tert butyl ether only and is independent of the concentration of nucleophile and the greater the stability of the carbocation, greater will be its ease of formation of product and faster will be the rate of reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




