
Write the importance of Hess’s law of constant heat summation.
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Hess's Law of Constant Heat Summation or simply Hess's Law tells that even if there are multiple steps and stages in a reaction, the resultant enthalpy change for the reaction will be the sum of all changes. This law is a proof for the quantity called enthalpy is a state function. These details may help you to solve this question.
Complete answer:
The Hess’s law of constant heat summation was derived by a Swiss-born Russian chemist and physician, Germain Hess. This is a relationship in thermochemistry for measuring the standard reaction enthalpy for a several step process. It basically makes use of the characteristics of state functions. As the state function is not dependable on the path taken by the process to complete instead depends only on the state at the moment.
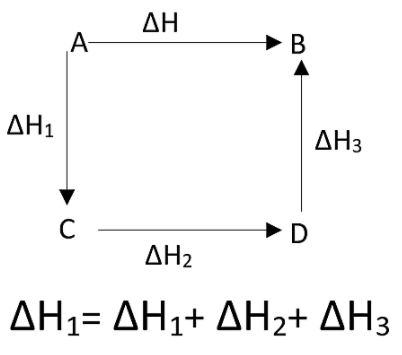
As we already mentioned that the enthalpy is a state function, therefore it is independent of the path it took to complete the process. In accordance with Hess’s law, for a multistep process, the standard enthalpy of reaction is independent of the path taken or number of steps of the process. It is the sum of standard enthalpies of intermediate steps of the reactions that happened at the similar temperature.
The purpose behind this law is to calculate the enthalpies of neutralization for basically the acid-base processes which use the information and help to calculate the reaction enthalpies for two salts in an aqueous solution. Hess's law of heat summation is of great importance as it chemically represents the laws of thermodynamics and the conservation of energy. Therefore the answer for this question is obtained.
Note:
This law is having applications in several chemical reactions. An example is the heats of formation for the unstable intermediates like $CO$ and $NO$ can be determined using this law. And also the heat variations in phase transitions and allotropic transitions are found using this law.
Complete answer:
The Hess’s law of constant heat summation was derived by a Swiss-born Russian chemist and physician, Germain Hess. This is a relationship in thermochemistry for measuring the standard reaction enthalpy for a several step process. It basically makes use of the characteristics of state functions. As the state function is not dependable on the path taken by the process to complete instead depends only on the state at the moment.

As we already mentioned that the enthalpy is a state function, therefore it is independent of the path it took to complete the process. In accordance with Hess’s law, for a multistep process, the standard enthalpy of reaction is independent of the path taken or number of steps of the process. It is the sum of standard enthalpies of intermediate steps of the reactions that happened at the similar temperature.
The purpose behind this law is to calculate the enthalpies of neutralization for basically the acid-base processes which use the information and help to calculate the reaction enthalpies for two salts in an aqueous solution. Hess's law of heat summation is of great importance as it chemically represents the laws of thermodynamics and the conservation of energy. Therefore the answer for this question is obtained.
Note:
This law is having applications in several chemical reactions. An example is the heats of formation for the unstable intermediates like $CO$ and $NO$ can be determined using this law. And also the heat variations in phase transitions and allotropic transitions are found using this law.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




