
Write the formula of the compound of iodine which is obtained when concentrated nitric acid oxidises\[{{I}_{2}}\].
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Nitric acid is a very strong oxidising agent. Out of the halogens, nitric acid can oxidise only iodine. It oxidises iodine to give an acid which is used to standardise weak and strong bases during quantitative analysis.
Complete step by step solution:
Nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent. It can oxidise iodine molecules to iodic acid.
The reaction is as follows
\[10HN{{O}_{3}}+{{I}_{2}}\to 2HI{{O}_{3}}+10N{{O}_{2}}+4{{H}_{2}}O\]
The formula of iodic acid is \[HI{{O}_{3}}\].
Additional Information:
-Iodic acid is a white water-soluble solid. It has iodine with +5 oxidation state. Iodic acid is one of the most stable oxoacids of the halogens. When it is heated, it dehydrates to give iodine pentoxide. Further iodine pentoxide decomposes and gives a mixture of iodine, oxygen and lower oxides of iodine.
-Iodic acid has one hydrogen and 3 oxygen atoms. Out of the three oxygen atoms, two are doubly bonded to hydrogen.
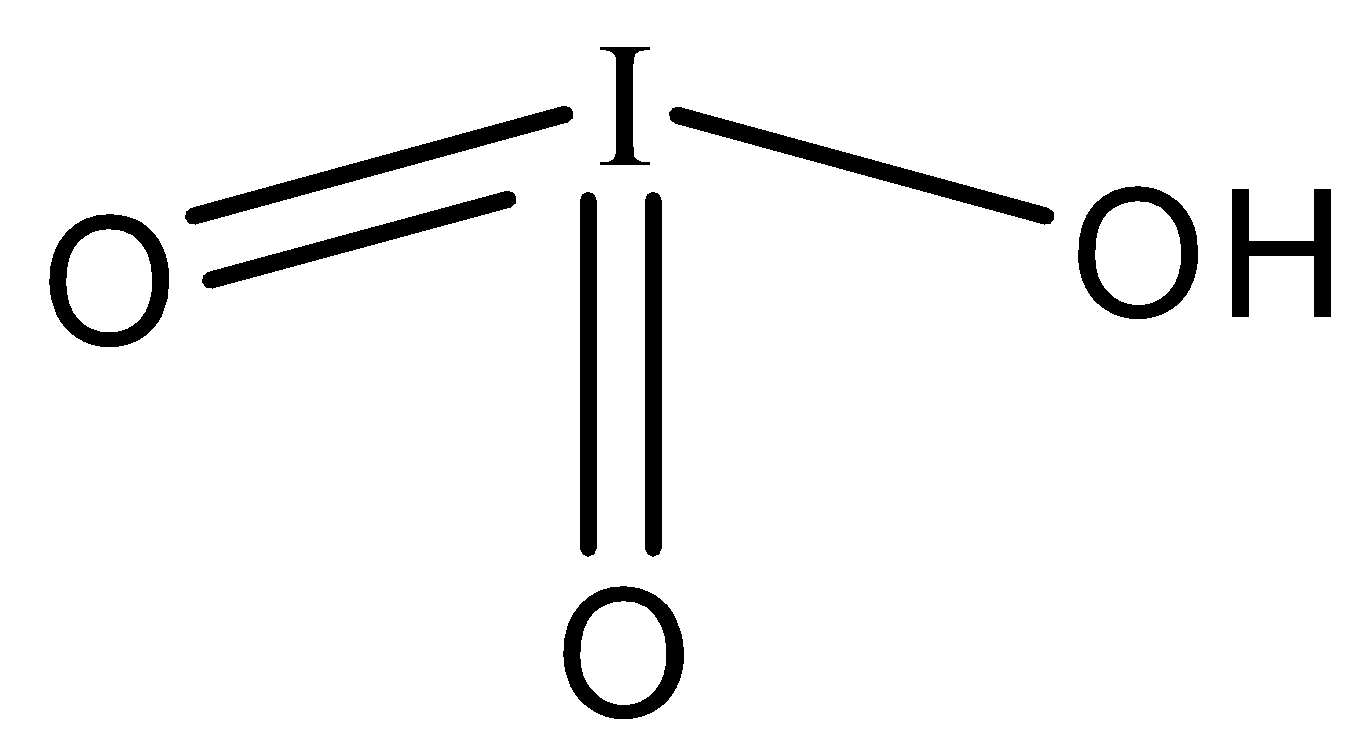
-Iodic acid is strongly oxidised in acidic solution and very less in basic solution. When it acts as an oxidizer, the products of the reaction are either iodine ion or iodine.
-Iodic acid is used to standardise solutions of both strong and weak bases. The indicators used for such titrations are methyl red or methyl orange.
-Nitric acid can only oxidise iodine in the halogen group. This is because the reduction potentials of all the other halides are higher than the reduction potential of nitrate molecules.
Note: \[HI{{O}_{4}}\] cannot be formed, when iodine reacts with nitric acid. This is because it is of higher oxidation state and nitric acid cannot oxide iodine to\[HI{{O}_{4}}\].
Complete step by step solution:
Nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent. It can oxidise iodine molecules to iodic acid.
The reaction is as follows
\[10HN{{O}_{3}}+{{I}_{2}}\to 2HI{{O}_{3}}+10N{{O}_{2}}+4{{H}_{2}}O\]
The formula of iodic acid is \[HI{{O}_{3}}\].
Additional Information:
-Iodic acid is a white water-soluble solid. It has iodine with +5 oxidation state. Iodic acid is one of the most stable oxoacids of the halogens. When it is heated, it dehydrates to give iodine pentoxide. Further iodine pentoxide decomposes and gives a mixture of iodine, oxygen and lower oxides of iodine.
-Iodic acid has one hydrogen and 3 oxygen atoms. Out of the three oxygen atoms, two are doubly bonded to hydrogen.

-Iodic acid is strongly oxidised in acidic solution and very less in basic solution. When it acts as an oxidizer, the products of the reaction are either iodine ion or iodine.
-Iodic acid is used to standardise solutions of both strong and weak bases. The indicators used for such titrations are methyl red or methyl orange.
-Nitric acid can only oxidise iodine in the halogen group. This is because the reduction potentials of all the other halides are higher than the reduction potential of nitrate molecules.
Note: \[HI{{O}_{4}}\] cannot be formed, when iodine reacts with nitric acid. This is because it is of higher oxidation state and nitric acid cannot oxide iodine to\[HI{{O}_{4}}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




