
Write the equation involved in the following reaction:
(i) Reimer – Tiemann reaction
(ii) Williamson ether synthesis
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint:We know that Reimer – Tiemann reaction is an organic reaction which involves the formation of ortho hydroxy benzaldehyde when phenol is treated with chloroform and the Williamson synthesis is the most common method used for the formation of an ether and it occurs by following the ${S_N}2$ mechanism.
Complete step-by-step answer:Reimer – Tiemann reaction:
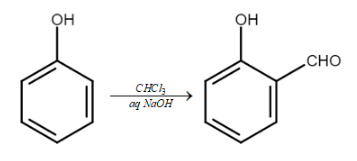
It is a reaction which is used for the ortho – formylation of phenols to form ortho hydroxybenzaldehyde. The example we will take is of conversion of phenols into salicylaldehyde.
So, when we treat phenols with chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide, an aldehyde group will be attached at the ortho position of the phenol ring. This will therefore lead to the formation of ortho – hydroxybenzaldehyde also known as salicylaldehyde.
The equation of the reaction will be:
Williamson ether synthesis:
Williamson synthesis involves the preparation of ethers by nucleophilic substitution reaction. Also, we know that in alkyl halides the carbon halogen bond is polar due to the higher electronegativity of the halogen atom. So, because of that a positive charge develops on the carbon. Alkoxide ion acts as a nucleophile and substitutes the halide ion from alkyl halide. This reaction occurs by following the ${S_N}2$mechanism.
The general reaction is: $R' - {O^ - }N{a^ + } + {R^{\delta + }} - {R^{\delta - }} \to \,R' - O - R + \,N{a^ + }{X^ - }$.
For example,
$C{H_3}C{H_2} - {O^ - }N{a^ + } + C{H_3}C{H_2} - Cl \to C{H_3}C{H_2}OC{H_2}C{H_3} + N{a^ + }C{l^ - }$
Note:In the Reimer – Tiemann reaction, we see that the ortho product is the major product formed as we know that the inductive effect dies with distance, so the ortho position will have more electrons as compared to the para position. While in Williamson ether synthesis we know that the reaction proceeds with the ${S_N}2$ mechanism so the reactivity of the alkyl halide will also follow the same order as it was in ${S_N}2$ mechanism i.e. ${1^ \circ } > {2^ \circ } > {3^ \circ }$.
Complete step-by-step answer:Reimer – Tiemann reaction:
It is a reaction which is used for the ortho – formylation of phenols to form ortho hydroxybenzaldehyde. The example we will take is of conversion of phenols into salicylaldehyde.
So, when we treat phenols with chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide, an aldehyde group will be attached at the ortho position of the phenol ring. This will therefore lead to the formation of ortho – hydroxybenzaldehyde also known as salicylaldehyde.
The equation of the reaction will be:

Williamson ether synthesis:
Williamson synthesis involves the preparation of ethers by nucleophilic substitution reaction. Also, we know that in alkyl halides the carbon halogen bond is polar due to the higher electronegativity of the halogen atom. So, because of that a positive charge develops on the carbon. Alkoxide ion acts as a nucleophile and substitutes the halide ion from alkyl halide. This reaction occurs by following the ${S_N}2$mechanism.
The general reaction is: $R' - {O^ - }N{a^ + } + {R^{\delta + }} - {R^{\delta - }} \to \,R' - O - R + \,N{a^ + }{X^ - }$.
For example,
$C{H_3}C{H_2} - {O^ - }N{a^ + } + C{H_3}C{H_2} - Cl \to C{H_3}C{H_2}OC{H_2}C{H_3} + N{a^ + }C{l^ - }$
Note:In the Reimer – Tiemann reaction, we see that the ortho product is the major product formed as we know that the inductive effect dies with distance, so the ortho position will have more electrons as compared to the para position. While in Williamson ether synthesis we know that the reaction proceeds with the ${S_N}2$ mechanism so the reactivity of the alkyl halide will also follow the same order as it was in ${S_N}2$ mechanism i.e. ${1^ \circ } > {2^ \circ } > {3^ \circ }$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




