
Write the equation involved in the following reactions.
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(ii) Williamson synthesis
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint:Formylation of phenol in presence of chloroform is known as the Reimer-Tiemann reaction. The Reimer-Tiemann reaction takes place in the basic medium. The formation of ether by the reaction of an alkyl halide with alcohol is known as Williamson synthesis. Williamson synthesis also takes pale in basic medium.
Complete answer:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
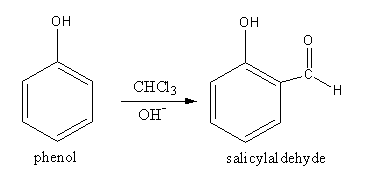
By the formation of phenol in presence of chloroform in basic medium salicylaldehyde forms.
The mechanism for the conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde is as follows:
A base abstracts the proton from chloroform. Chloroform then removes a chloride ion and forms dichlorocarbene.
$\rm{CHCl_3 + NaOH \to \,\,:CCl_2}$
Base abstract protons form phenol forming phenoxide ions. The delocalization of negative charge forms a carbanion. This carbanion attacks the dichlorocarbene. Then base hydrolysis takes place to form salicylaldehyde.
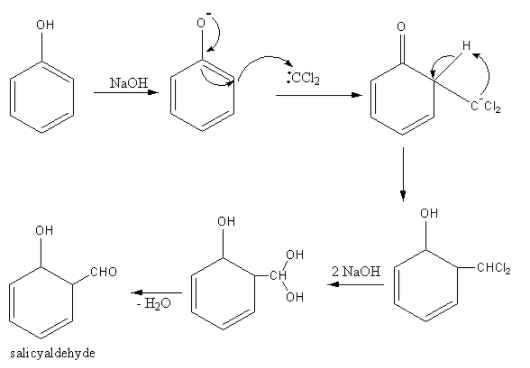
So, the equation involved in the Reimer-Tiemann reaction is as follows:
(ii) Williamson synthesis
By the nucleophilic substitution of an alkyl halide in presence of basic medium ether forms.
The mechanism for the conversion of the alkyl halide to ether is as follows:
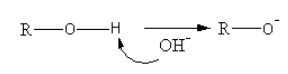
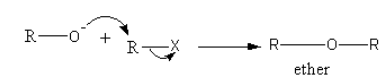
A base abstracts the proton from alcohol forming an alkoxide ion.
Alkoxide ion attacks on alkyl groups, so ether forms and halides are removed.
So, the equation involved in Williamson synthesis is as follows:
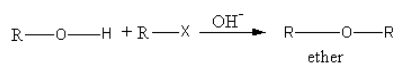
Note:
The reaction of phenol with chloroform and base gives salicylaldehyde. When chloroform is replaced with carbon tetrachloride, the product form is salicylic acid in the Riemer Tiemann reaction. The Riemer Tiemann reaction has selectivity for the ortho position. Williamson synthesis follows the mechanism. As halide removes from one side and alkoxide ion attacks from the backside.
Complete answer:
(i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
By the formation of phenol in presence of chloroform in basic medium salicylaldehyde forms.
The mechanism for the conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde is as follows:
A base abstracts the proton from chloroform. Chloroform then removes a chloride ion and forms dichlorocarbene.
$\rm{CHCl_3 + NaOH \to \,\,:CCl_2}$
Base abstract protons form phenol forming phenoxide ions. The delocalization of negative charge forms a carbanion. This carbanion attacks the dichlorocarbene. Then base hydrolysis takes place to form salicylaldehyde.

So, the equation involved in the Reimer-Tiemann reaction is as follows:

(ii) Williamson synthesis
By the nucleophilic substitution of an alkyl halide in presence of basic medium ether forms.
The mechanism for the conversion of the alkyl halide to ether is as follows:


A base abstracts the proton from alcohol forming an alkoxide ion.
Alkoxide ion attacks on alkyl groups, so ether forms and halides are removed.
So, the equation involved in Williamson synthesis is as follows:
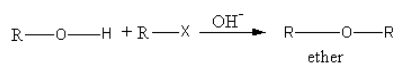
Note:
The reaction of phenol with chloroform and base gives salicylaldehyde. When chloroform is replaced with carbon tetrachloride, the product form is salicylic acid in the Riemer Tiemann reaction. The Riemer Tiemann reaction has selectivity for the ortho position. Williamson synthesis follows the mechanism. As halide removes from one side and alkoxide ion attacks from the backside.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




