
Write the difference between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols through Victor Mayer’s method, only equations?
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: The procedure of Victor Mayer’s test is. First, react HI/Red Phosphorus +$I_2$, then react the product with Silver nitrite, then react the product with Nitrous acid ($HNO_2$) and in the final step add NaOH.
Considering the above procedure, write the proper products for each step, and write the characteristic colour for each different type of alcohol.
Complete step by step solution:
The overall scheme of the reactions in victor Mayer’s test for each kind of alcohol is as follows:
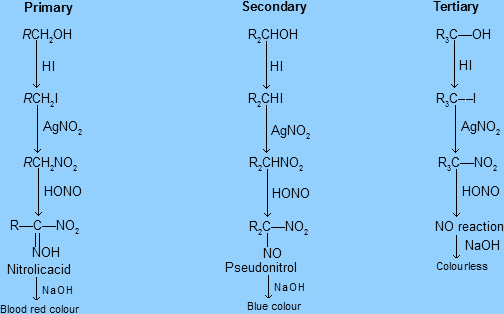
In the first step, we add HI or $I_2$ with red Phosphorus, and all the primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols get converted into corresponding primary, secondary and tertiary Halides respectively.
In next step, we react the above product (generally in lab conditions we add Silver nitrate to the same container, without separating products for impurities as this is a qualitative test, not quantitative test), and all the primary, secondary and tertiary Halides get converted into the corresponding primary, secondary and tertiary nitro compounds respectively.
In the next step, we add Nitrous acid ($HNO_2$)
-Here is the difference, Primary alcohols give Nitrolic acids, which upon addition of NaOH give distinct blood-red colour, which confirms the presence of primary alcohols.
-Here is the difference, Secondary alcohols give Pseudonitrols, which upon addition of NaOH give a distinct blue colour, which confirms the presence of secondary alcohols
-Meanwhile, the nitro compounds from tertiary alcohols don’t react with $HNO_2$, so after adding NaOH the solution/product found is colourless.
Note: Remember that Tertiary nitro compounds do not react further with Nitrous acid ($HNO_2$), it is not the case that the product formed is colourless no product is formed.
Considering the above procedure, write the proper products for each step, and write the characteristic colour for each different type of alcohol.
Complete step by step solution:
The overall scheme of the reactions in victor Mayer’s test for each kind of alcohol is as follows:

In the first step, we add HI or $I_2$ with red Phosphorus, and all the primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols get converted into corresponding primary, secondary and tertiary Halides respectively.
In next step, we react the above product (generally in lab conditions we add Silver nitrate to the same container, without separating products for impurities as this is a qualitative test, not quantitative test), and all the primary, secondary and tertiary Halides get converted into the corresponding primary, secondary and tertiary nitro compounds respectively.
In the next step, we add Nitrous acid ($HNO_2$)
-Here is the difference, Primary alcohols give Nitrolic acids, which upon addition of NaOH give distinct blood-red colour, which confirms the presence of primary alcohols.
-Here is the difference, Secondary alcohols give Pseudonitrols, which upon addition of NaOH give a distinct blue colour, which confirms the presence of secondary alcohols
-Meanwhile, the nitro compounds from tertiary alcohols don’t react with $HNO_2$, so after adding NaOH the solution/product found is colourless.
Note: Remember that Tertiary nitro compounds do not react further with Nitrous acid ($HNO_2$), it is not the case that the product formed is colourless no product is formed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




