
Write the converse of the Pythagoras Theorem and prove it.
Answer
619.5k+ views
Hint: Let’s consider a two triangles PQR and ABC, such that $\angle Q={{90}^{\circ }}$ and AB = PQ and BC = QR then find out using Pythagoras theorem AC = PR, then use congruence to prove that $\angle B={{90}^{\circ }}$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
The statement of the common Pythagoras theorem is that in a triangle, if the square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the angle opposite to that side is the right angle.
Now we will prove it.
Consider a triangle ABC in which $A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}$.
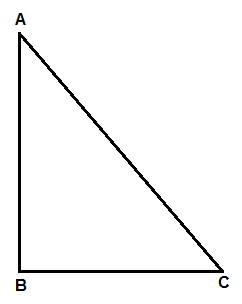
In this we have to prove that angle of B is ${{90}^{\circ }}.$
Now we will start by constructing a triangle PQR which is right angled at Q such that PQ = AB and QR = BC, as shown below:
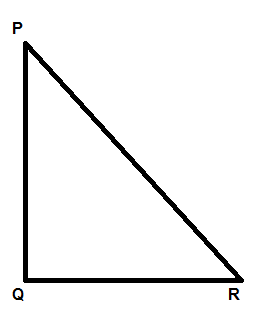
So, by using Pythagoras theorem in triangle PQR we can say that,
$P{{R}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}}$ as the angle Q is ${{90}^{\circ }}$ .
Now by constructing we said that PQ = AB and QR = BC then,
$P{{R}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}$
So, we can say that $P{{R}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$ as $A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}$ was given.
Hence, PR = AC.
Now in triangle ABC and PQR we can say that,
i) AB = PQ which can be said by construction.
ii) BC = QR which can also be said by construction.
iii) AC = PR which is proved in the above section.
So, we can say that the triangle ABC and triangle PQR is congruent to each other using side-side –side congruence.
So, we can say that all sides and angles are equal by CPCT, i.e., corresponding part of concurrent triangle.
So, $\angle B=\angle Q$ as we proved that triangle ABC and triangle PQR is congruent to each other.
We know $\angle Q={{90}^{\circ }}$ by construction, therefore we can say that $\angle B={{90}^{\circ }}$.
Hence the converse of Pythagoras theorem is proved.
Note: Students generally get confused while proving congruence of two triangles. They should know the rules of congruence by heart to prove these types of questions. This is a theorem, so proving it should not be a problem after the lesson is completed. Generally students don’t construct a triangle and get confused about how to prove this.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The statement of the common Pythagoras theorem is that in a triangle, if the square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the angle opposite to that side is the right angle.
Now we will prove it.
Consider a triangle ABC in which $A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}$.

In this we have to prove that angle of B is ${{90}^{\circ }}.$
Now we will start by constructing a triangle PQR which is right angled at Q such that PQ = AB and QR = BC, as shown below:
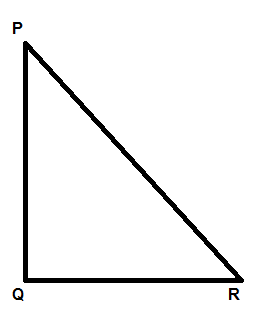
So, by using Pythagoras theorem in triangle PQR we can say that,
$P{{R}^{2}}=P{{Q}^{2}}+Q{{R}^{2}}$ as the angle Q is ${{90}^{\circ }}$ .
Now by constructing we said that PQ = AB and QR = BC then,
$P{{R}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}$
So, we can say that $P{{R}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$ as $A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}$ was given.
Hence, PR = AC.
Now in triangle ABC and PQR we can say that,
i) AB = PQ which can be said by construction.
ii) BC = QR which can also be said by construction.
iii) AC = PR which is proved in the above section.
So, we can say that the triangle ABC and triangle PQR is congruent to each other using side-side –side congruence.
So, we can say that all sides and angles are equal by CPCT, i.e., corresponding part of concurrent triangle.
So, $\angle B=\angle Q$ as we proved that triangle ABC and triangle PQR is congruent to each other.
We know $\angle Q={{90}^{\circ }}$ by construction, therefore we can say that $\angle B={{90}^{\circ }}$.
Hence the converse of Pythagoras theorem is proved.
Note: Students generally get confused while proving congruence of two triangles. They should know the rules of congruence by heart to prove these types of questions. This is a theorem, so proving it should not be a problem after the lesson is completed. Generally students don’t construct a triangle and get confused about how to prove this.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 7 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

List of coprime numbers from 1 to 100 class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

The plural of Chief is Chieves A True B False class 7 english CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE





