
Write one example of monosaccharide carbohydrate?
Answer
539.7k+ views
Hint :Carbohydrates, consisting of monosaccharide and disaccharide groups, are the sugars, starches and fibers found in fruits, grains, vegetables and milk products. A monosaccharide, having a general formula of${(C{H_2}O)_n}$, is said to be the most basic form of carbohydrates and they possess one sugar unit that cannot be further broken down.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
One example of a monosaccharide carbohydrate is Glucose which is of the molecular formula ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$. Glucose is actually a monosaccharide consisting of the six carbon atoms along with one aldehyde group. Therefore, we can say glucose is an aldohexose. The structure of glucose is shown below:
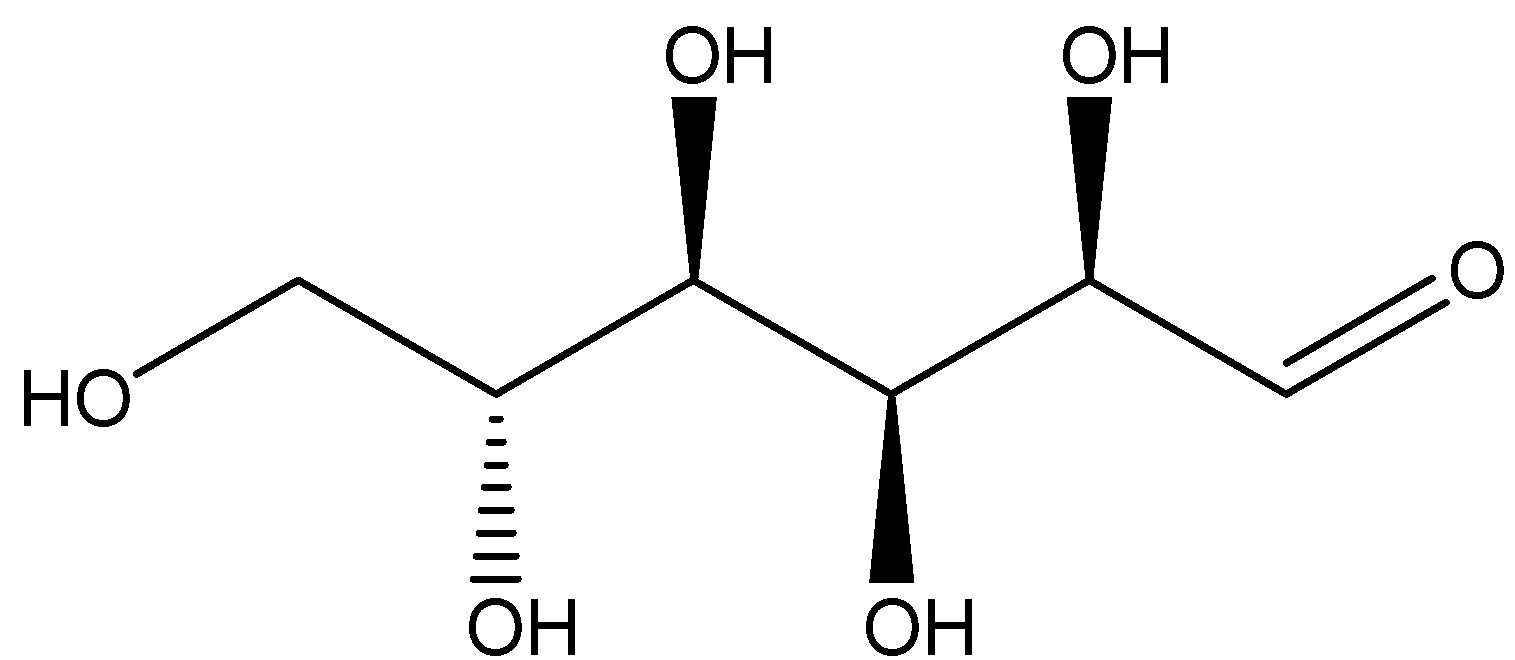
Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide carbohydrate. Glucose is usually present in solid state as a monohydrate with a closed pyran ring. Whereas in aqueous solution, it is an open-chain to a small extent and is present predominantly as α- or β-pyranose. From aqueous solutions, the three known forms can be crystallized: α-glucopyranose, β-glucopyranose and β-glucopyranose hydrate. Glucose is a building block of the disaccharides lactose and sucrose.
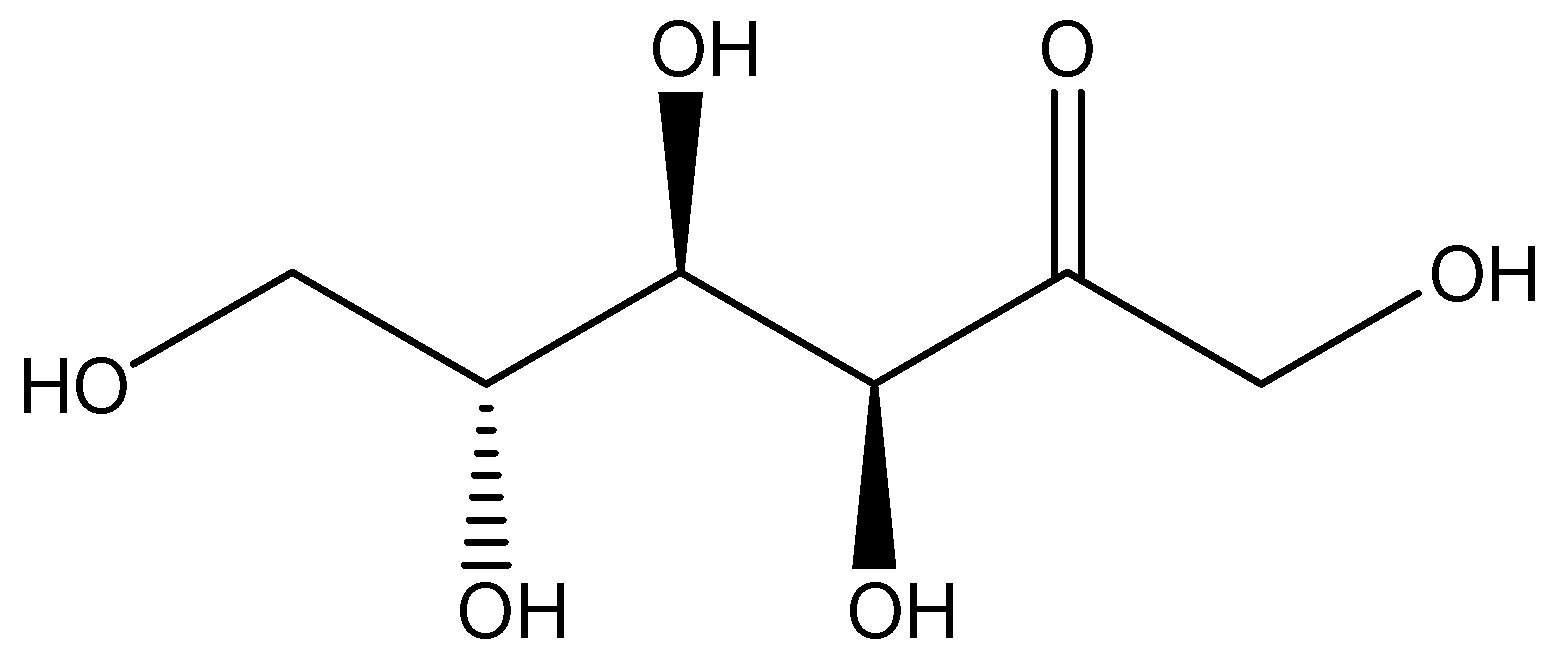
Another most common example of monosaccharide carbohydrate is fructose having the molecular formula of \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\]. Fructose is considered to be a simple ketonic monosaccharide which is found in many plants, and it is most often bonded to the glucose in order to form the disaccharide sucrose. The structure of fructose is shown below:
Additional Information:
Most of the carbohydrates are polymers. Polymers are said to be large, complex molecules composed of long chains of monomers. Monomers are small, basic molecular units. Carbohydrates can be divided into three different classes based on the number of sugar units they possess: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Note :
Carbohydrates are the molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. There are always twice as many hydrogen atoms as carbon or oxygen atoms and they act as the source of energy an example is glucose, as a store of energy which is starch and glycogen and as structural units like cellulose in plants and chitins in insects.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
One example of a monosaccharide carbohydrate is Glucose which is of the molecular formula ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$. Glucose is actually a monosaccharide consisting of the six carbon atoms along with one aldehyde group. Therefore, we can say glucose is an aldohexose. The structure of glucose is shown below:

Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide carbohydrate. Glucose is usually present in solid state as a monohydrate with a closed pyran ring. Whereas in aqueous solution, it is an open-chain to a small extent and is present predominantly as α- or β-pyranose. From aqueous solutions, the three known forms can be crystallized: α-glucopyranose, β-glucopyranose and β-glucopyranose hydrate. Glucose is a building block of the disaccharides lactose and sucrose.
Another most common example of monosaccharide carbohydrate is fructose having the molecular formula of \[{C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}\]. Fructose is considered to be a simple ketonic monosaccharide which is found in many plants, and it is most often bonded to the glucose in order to form the disaccharide sucrose. The structure of fructose is shown below:

Additional Information:
Most of the carbohydrates are polymers. Polymers are said to be large, complex molecules composed of long chains of monomers. Monomers are small, basic molecular units. Carbohydrates can be divided into three different classes based on the number of sugar units they possess: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Note :
Carbohydrates are the molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. There are always twice as many hydrogen atoms as carbon or oxygen atoms and they act as the source of energy an example is glucose, as a store of energy which is starch and glycogen and as structural units like cellulose in plants and chitins in insects.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




