
Write notes on the following:
(i) Mustard oil reaction
(ii) Formation of Schiff’s base.
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: Hofmann mustard oil test is used for determination of primary ,secondary and tertiary amines using alcoholic carbon disulphide and excess of mercuric chloride.
Schiff’s base is formed by the condensation of primary amine and aldehyde which uses organic solvent such as methanol, tetrahydrofuran etc.
Complete answer:
(i) Mustard Oil reaction- This is known as Hofmann mustard oil reaction. When primary amines are heated with alcoholic carbon disulphide followed by warming with excess of mercuric chloride from isothiocyanates having a pungent smell similar to mustard oil. Reaction of ethyl amine with carbon disulphide (\[S = C = S\]) produces ethyl isothiocyanate is given below:
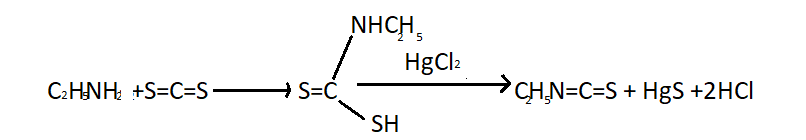
Secondary amines react with carbon disulphide to form dithiocarbamic acids but latter do not react to mercuric chloride. Tertiary amine do not react with \[S = C = S\].
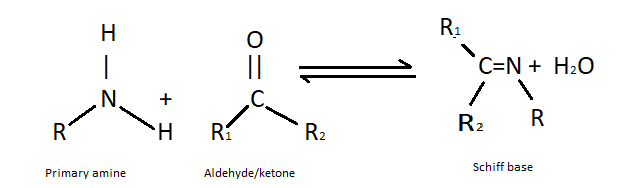
(ii) Formation of Schiff’s base- The formation of Schiff’s base is done by the condensation of primary amines and aldehydes in organic solvents. This reaction occurs under some basic conditions. It is used in anticancer activity, antiviral and antimicrobial. Schiff’s bases are very common ligands in organic chemistry . The general structure of Schiff’s base is ${R}_{2}C = N{R}^{'}$ where ${R}^{'} \ne H$. The reaction of formation of Schiff’s base is as follows:
Note: On reaction with primary amines it yields isothiocyanate which possess a pungent smell similar to that of mustard oil while secondary amines do not react with mercuric chloride. It reacts with $C{S_2}$. And tertiary amines do not show this test. Schiff base is formed when primary amine and aldehydes or ketone reacts under specific conditions. Schiff’s base is a widely used organic compound.
Schiff’s base is formed by the condensation of primary amine and aldehyde which uses organic solvent such as methanol, tetrahydrofuran etc.
Complete answer:
(i) Mustard Oil reaction- This is known as Hofmann mustard oil reaction. When primary amines are heated with alcoholic carbon disulphide followed by warming with excess of mercuric chloride from isothiocyanates having a pungent smell similar to mustard oil. Reaction of ethyl amine with carbon disulphide (\[S = C = S\]) produces ethyl isothiocyanate is given below:

Secondary amines react with carbon disulphide to form dithiocarbamic acids but latter do not react to mercuric chloride. Tertiary amine do not react with \[S = C = S\].
(ii) Formation of Schiff’s base- The formation of Schiff’s base is done by the condensation of primary amines and aldehydes in organic solvents. This reaction occurs under some basic conditions. It is used in anticancer activity, antiviral and antimicrobial. Schiff’s bases are very common ligands in organic chemistry . The general structure of Schiff’s base is ${R}_{2}C = N{R}^{'}$ where ${R}^{'} \ne H$. The reaction of formation of Schiff’s base is as follows:

Note: On reaction with primary amines it yields isothiocyanate which possess a pungent smell similar to that of mustard oil while secondary amines do not react with mercuric chloride. It reacts with $C{S_2}$. And tertiary amines do not show this test. Schiff base is formed when primary amine and aldehydes or ketone reacts under specific conditions. Schiff’s base is a widely used organic compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




