
Write Newton's formula for refraction of light through a lens. Explain the meaning of symbols used.
Answer
477k+ views
Hint: In optics, the relationship between the distances of an object $ u $ , the distance of the image $ v $ and, the focal length $ f $ of the lens is given by the lens formula. This exists in two forms: one is the Gaussian form and the Newton formula. This lens formula is applicable for both concave and convex lenses. These lenses are usually thin lenses whose thickness of the lens is smaller than its diameter. This thickness allows rays to refract.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
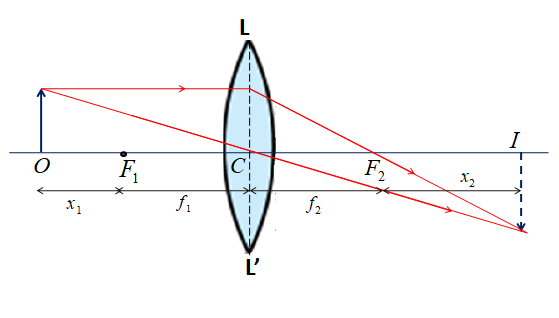
Explanation: From the diagram, $ {x_1} = O{F_1} $ ; $ {x_2} = {F_2}I $.Here $ {F_1} $ and $ {F_2} $ are the principal foci.$ {f_1} $ and $ {f_2} $ are said to be the focal lengths of the two halves of the lens.Newton’s law states that the product of the distance of the object and image from respective foci length is equal to the product of the foci lengths of half lenses.Mathematically this can be written as,
${x_1} \times {x_2} = {f_1} \times {f_2} $
By sign conventions, $ {f_1} $ and $ {x_1} $ are negative. $ {f_2} $ and $ {x_2} $ are positive. If the medium on either side of the lens is the same we can write,
$ {f_2} = - {f_1} $
$\therefore {x_1} \times {x_2} = - {f^2} $
Therefore the above equation represents Newton’s formula for refraction through lenses.
Additional Information:
The above-mentioned Newton’s formula can also be written in the Gaussian form.
$ \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} $
Here $ u $ is the distance of the object from the optical center of the lens.
$ v $ is the distance of the image which is measured from the optical center of the lens.
$ f $ is the distance measured from the principal focus from the optical center of the lens.
Note: To use this formula, we need to follow some sign conventions. These sign conventions are called Cartesian sign conventions. For lenses, we assume the optical center as the origin. The conventions are given below.
-The object is always kept to the left of the optical center.
-We measure all the distance from the optical center.
-The distance of the image and object we measure will be positive and negative respectively. -That distance measured to the left side of the lens will always be negative and the right side of the lens will always be positive.
-The height that we measure above the principal axis will be positive and below the principal axis will always be negative.
-The focal length of the convex lens is positive and the focal length of the concave lens will be negative.
Complete Step By Step Answer:

Explanation: From the diagram, $ {x_1} = O{F_1} $ ; $ {x_2} = {F_2}I $.Here $ {F_1} $ and $ {F_2} $ are the principal foci.$ {f_1} $ and $ {f_2} $ are said to be the focal lengths of the two halves of the lens.Newton’s law states that the product of the distance of the object and image from respective foci length is equal to the product of the foci lengths of half lenses.Mathematically this can be written as,
${x_1} \times {x_2} = {f_1} \times {f_2} $
By sign conventions, $ {f_1} $ and $ {x_1} $ are negative. $ {f_2} $ and $ {x_2} $ are positive. If the medium on either side of the lens is the same we can write,
$ {f_2} = - {f_1} $
$\therefore {x_1} \times {x_2} = - {f^2} $
Therefore the above equation represents Newton’s formula for refraction through lenses.
Additional Information:
The above-mentioned Newton’s formula can also be written in the Gaussian form.
$ \dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} $
Here $ u $ is the distance of the object from the optical center of the lens.
$ v $ is the distance of the image which is measured from the optical center of the lens.
$ f $ is the distance measured from the principal focus from the optical center of the lens.
Note: To use this formula, we need to follow some sign conventions. These sign conventions are called Cartesian sign conventions. For lenses, we assume the optical center as the origin. The conventions are given below.
-The object is always kept to the left of the optical center.
-We measure all the distance from the optical center.
-The distance of the image and object we measure will be positive and negative respectively. -That distance measured to the left side of the lens will always be negative and the right side of the lens will always be positive.
-The height that we measure above the principal axis will be positive and below the principal axis will always be negative.
-The focal length of the convex lens is positive and the focal length of the concave lens will be negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




