
Write Gauss's theorem of electrostatic. Find out the intensity of the electric field at a point outside a uniformly charged thin spherical shell with its help.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint:Gauss's law is used to calculate the electric field in a closed surface. The evaluation of electric fields becomes easier if the object placed in a closed surface is symmetrical.
Step-by-Step Explanation:
Step I:
According to Gauss's law for the electric field, The electric flux through any closed surface is directly proportional to the total electric charge enclosed by this surface.
According to Gauss's law
$\oint\limits_S {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}} $ ---(i)
Where $\overrightarrow E $ is the electric field
$q$ is the charge enclosed
${\varepsilon _o}$ is the electric permittivity of free space
Step II:
Consider a spherical shell of radius R. Let P Be any point outside the shell where electric field intensity is to be calculated. The distance of point P From the centre of the sphere is OP=r. The surface at point P is taken as Gaussian surface. The unit vector $n$ , is radially directed outwards such that $\theta $ is equal to 0.
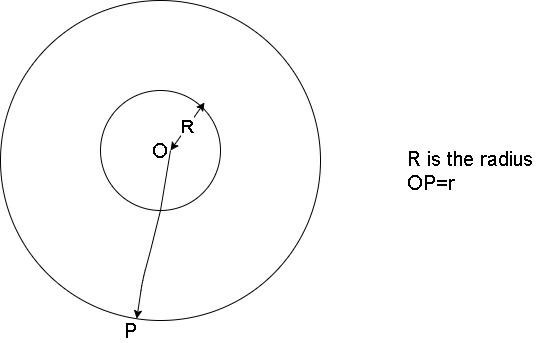
Step III:
From equation (i)
\[\oint\limits_S {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} } = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}\]
$E\oint {\overrightarrow n .dS} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}$ ---(ii)
$n$is a unit vector. So $\overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow n = 1$
Using dot product of vectors, \[\overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow b = (\overrightarrow a )(\overrightarrow a )\cos \theta \]
Since $\cos \theta = 0$
Therefore, $\overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow {dS} = \overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow n .\cos 0$
$\overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow {dS} = dS$
Substitute the value in equation (ii),
$E\oint {dS = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}} $
Surface area of sphere$ = 4\pi {r^2}$
$E.4\pi {r^2} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}$
$E = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _o}}}$
Step IV:
Electric field intensity is given by $E = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _o}}}$ .
Step V:
Therefore the electric field outside a uniformly charged spherical shell is the same as if all the charge is concentrated as a point charge at the centre of the shell.
Note:Gauss's law Is used to find out the number of electric field lines passing through any closed surface. It is to be noted that Gauss's Law Does not depend on the shape or size of the surface. Also Gauss's Law Is independent of the surface and the radius of the given area.
Step-by-Step Explanation:
Step I:
According to Gauss's law for the electric field, The electric flux through any closed surface is directly proportional to the total electric charge enclosed by this surface.
According to Gauss's law
$\oint\limits_S {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}} $ ---(i)
Where $\overrightarrow E $ is the electric field
$q$ is the charge enclosed
${\varepsilon _o}$ is the electric permittivity of free space
Step II:
Consider a spherical shell of radius R. Let P Be any point outside the shell where electric field intensity is to be calculated. The distance of point P From the centre of the sphere is OP=r. The surface at point P is taken as Gaussian surface. The unit vector $n$ , is radially directed outwards such that $\theta $ is equal to 0.

Step III:
From equation (i)
\[\oint\limits_S {\overrightarrow E .\overrightarrow {dS} } = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}\]
$E\oint {\overrightarrow n .dS} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}$ ---(ii)
$n$is a unit vector. So $\overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow n = 1$
Using dot product of vectors, \[\overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow b = (\overrightarrow a )(\overrightarrow a )\cos \theta \]
Since $\cos \theta = 0$
Therefore, $\overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow {dS} = \overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow n .\cos 0$
$\overrightarrow n .\overrightarrow {dS} = dS$
Substitute the value in equation (ii),
$E\oint {dS = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}} $
Surface area of sphere$ = 4\pi {r^2}$
$E.4\pi {r^2} = \dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _o}}}$
$E = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _o}}}$
Step IV:
Electric field intensity is given by $E = \dfrac{q}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _o}}}$ .
Step V:
Therefore the electric field outside a uniformly charged spherical shell is the same as if all the charge is concentrated as a point charge at the centre of the shell.
Note:Gauss's law Is used to find out the number of electric field lines passing through any closed surface. It is to be noted that Gauss's Law Does not depend on the shape or size of the surface. Also Gauss's Law Is independent of the surface and the radius of the given area.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




