
Write any two reactions of glucose which cannot be explained by the open chain structure of glucose molecules.
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Glucose in its open-chain form has an open and an unbranched backbone of six carbon atoms. There are some reactions which cannot be explained by the open chain structure of glucose even with the presence of few functional groups.
Complete step by step answer:
In the open chain of glucose, there is a backbone of unbranched six carbon atoms, i.e., from C - 1 through C - 6. In this structure an aldehyde group (-CHO) is attached to the first carbon and the rest five carbon are attached to the hydroxyl group (-OH). The open chain structure is given below:
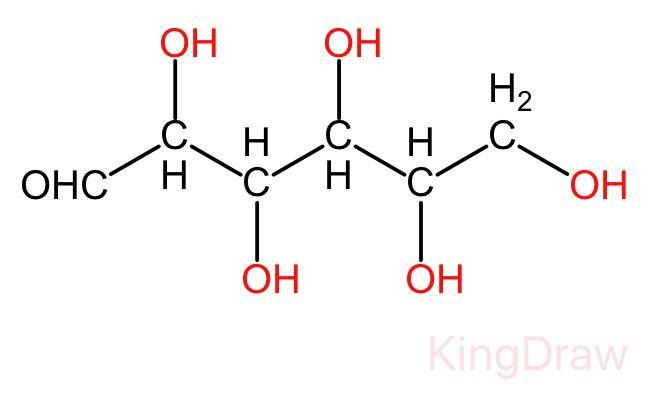
Glucose in nothing but the polyhydroxy aldehyde, It is a type of aldohexose. It also exists in cyclic form.
The following are the reactions that cannot be explained by the open structure of glucose.
We know that, aldehydes and ketones give 2,4-DNP test and Schiff's test but despite having the aldehyde group, glucose does not give Schiff’s test, 2, 4- DNP test and it does not form the hydrogen-sulfite addition product with $NaHS{O}_{3}$.
The pentaacetate of glucose doesn't react with hydroxylamine to give oxim. This indicates that a free -CHO group is present in glucose molecules.
Also, glucose doesn't react with $NaHS{O}_{3}$.
Note: Despite having an aldehyde group, glucose shows different traits. Glucose on reaction with excess $C{H}_{3}I$ & $AgOH$ forms two different pentamethyl ether and neither exhibits aldehyde reactions. But acid hydrolysed pentamethyl ether derivatives, gave a tetramethyl derivative, that oxidized Tollen’s reagent and got reduced by sodium borohydride, like an aldehyde.
Complete step by step answer:
In the open chain of glucose, there is a backbone of unbranched six carbon atoms, i.e., from C - 1 through C - 6. In this structure an aldehyde group (-CHO) is attached to the first carbon and the rest five carbon are attached to the hydroxyl group (-OH). The open chain structure is given below:

Glucose in nothing but the polyhydroxy aldehyde, It is a type of aldohexose. It also exists in cyclic form.
The following are the reactions that cannot be explained by the open structure of glucose.
We know that, aldehydes and ketones give 2,4-DNP test and Schiff's test but despite having the aldehyde group, glucose does not give Schiff’s test, 2, 4- DNP test and it does not form the hydrogen-sulfite addition product with $NaHS{O}_{3}$.
The pentaacetate of glucose doesn't react with hydroxylamine to give oxim. This indicates that a free -CHO group is present in glucose molecules.
Also, glucose doesn't react with $NaHS{O}_{3}$.
Note: Despite having an aldehyde group, glucose shows different traits. Glucose on reaction with excess $C{H}_{3}I$ & $AgOH$ forms two different pentamethyl ether and neither exhibits aldehyde reactions. But acid hydrolysed pentamethyl ether derivatives, gave a tetramethyl derivative, that oxidized Tollen’s reagent and got reduced by sodium borohydride, like an aldehyde.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




