
Write any ten examples of IUPAC nomenclature of alcohol.
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: As we have learnt that alcohols are the compounds possessing hydroxyl functional groups attached with an aliphatic carbon atom. Alcoholic compounds possess $s{p^3}$ hybridised oxygen as central atom.
Complete step by step solution: Alcohols may be classified as mono, di, tri-or polyhydric compounds depending upon the number of hydroxyl groups respectively in their structures. The IUPAC name of an alcohol is derived from the name of an alkane and adding the suffix “ol” in place of ‘e’ in alkane. For example:
Methane+ ol = methanol $(C{H_3}OH)$
Ethane + ol = ethanol $({C_2}{H_5}OH)$
Propane + ol = propanol $({C_3}{H_7}OH)$
Butane + ol = butanol $({C_4}{H_9}OH)$
Pentane + ol = pentanol $({C_5}{H_{11}}OH)$
Vinylic alcohol = $C{H_2} = CH - OH$
For naming of polyhydric alcohols, the ‘e’ of alkane is retained and the ending “ol” is added. The number of $ - OH$ groups is indicated by adding the multiplicative prefix di, tri, etc. before ‘ol’. Let us take an example:
$HO - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - OH$ the name of this alcoholic compound is $ethane - 1,2 - diol$.
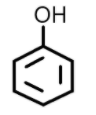
Similarly benzylic alcohols can also be named using the suffix ‘ol’. For example: Phenol $({C_6}{H_5}OH)$
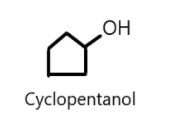
Cyclic alcohols can also be named using prefix cyclo and suffix ‘ol’ considering the hydroxyl group is attached to the first carbon atom of the ring. For example: Cyclopentanol $({C_5}{H_8}OH)$
We can also name the branched compounds by adding a number of branches and suffix ‘ol’ at the end. For example: $2 - Methylpropan - 2 - ol$${(C{H_3})_3} - C - OH$
so we can easily give the name of ten alcoholic compounds as:
Methanol, Ethanol, Propanol, Butanol, Pentanol, Phenol, Cyclopentaol, $2 - Methylpropan - 2 - ol$,$ethane - 1,2 - diol$and vinylic alcohol.
Note: Some basic rules for naming alcohol includes the longest continuous chain containing $ - OH$ group is the parent chain and the parent compound, alkane is replaced by the suffix ‘ol’ at ‘e’ in alkane and in cyclic alcohols the carbon atom bearing the $ - OH$ is designated as $C1$ but the name does not include $1$.
Complete step by step solution: Alcohols may be classified as mono, di, tri-or polyhydric compounds depending upon the number of hydroxyl groups respectively in their structures. The IUPAC name of an alcohol is derived from the name of an alkane and adding the suffix “ol” in place of ‘e’ in alkane. For example:
Methane+ ol = methanol $(C{H_3}OH)$
Ethane + ol = ethanol $({C_2}{H_5}OH)$
Propane + ol = propanol $({C_3}{H_7}OH)$
Butane + ol = butanol $({C_4}{H_9}OH)$
Pentane + ol = pentanol $({C_5}{H_{11}}OH)$
Vinylic alcohol = $C{H_2} = CH - OH$
For naming of polyhydric alcohols, the ‘e’ of alkane is retained and the ending “ol” is added. The number of $ - OH$ groups is indicated by adding the multiplicative prefix di, tri, etc. before ‘ol’. Let us take an example:
$HO - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - OH$ the name of this alcoholic compound is $ethane - 1,2 - diol$.
Similarly benzylic alcohols can also be named using the suffix ‘ol’. For example: Phenol $({C_6}{H_5}OH)$

Cyclic alcohols can also be named using prefix cyclo and suffix ‘ol’ considering the hydroxyl group is attached to the first carbon atom of the ring. For example: Cyclopentanol $({C_5}{H_8}OH)$

We can also name the branched compounds by adding a number of branches and suffix ‘ol’ at the end. For example: $2 - Methylpropan - 2 - ol$${(C{H_3})_3} - C - OH$
so we can easily give the name of ten alcoholic compounds as:
Methanol, Ethanol, Propanol, Butanol, Pentanol, Phenol, Cyclopentaol, $2 - Methylpropan - 2 - ol$,$ethane - 1,2 - diol$and vinylic alcohol.
Note: Some basic rules for naming alcohol includes the longest continuous chain containing $ - OH$ group is the parent chain and the parent compound, alkane is replaced by the suffix ‘ol’ at ‘e’ in alkane and in cyclic alcohols the carbon atom bearing the $ - OH$ is designated as $C1$ but the name does not include $1$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




