
Write Ampere’s circuital law. A long straight wire of a circular cross-section (radius $a$ ) carrying steady current. Current is uniformly distributed in the wire. Calculate magnetic field inside the region ( $r < a$ ) in the wire.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint:The law of Ampere is a mathematical assertion of the relation between currents and their induced magnetic fields. The law of Ampere helps one to cross the distance between electricity and magnetism, that is, it gives us a quantitative relationship between electric currents and magnetic fields.
Complete step by step answer:
Ampere’s circuital law states that the magnetic field integral of the closed line around a current bearing conductor is proportional to absolute permeability times the overall passing current of the conductor.
Mathematically it is given by-
$\oint {\overrightarrow I } .\overrightarrow {dl} = {\mu _ \circ }{I_{enclosed}}$, where ${\mu _ \circ } = $ permeability of free space, $dl = $ small parts of length
Now we have to calculate the magnetic field inside the region ( $r < a$ ) in the wire where current is uniformly distributed and the wire has a circular cross-section. The current is steady current.
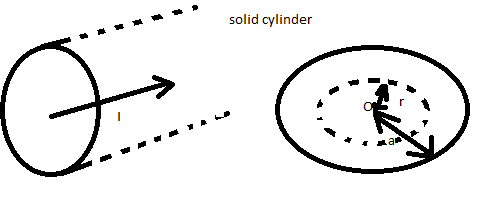
Now let us consider the given figure-
In this figure, magnetic field lines form concentric circles centred on O. The axis of the cylindrical string.
Hence, it is the preferred part of the loop. Here there are two concentric circles. The radius of the large circle is $a$ and the radius of the smaller circle is $r$ .
Now consider a loop of radius $a < r$
The cross-sectional area ( $\pi {a^2}$ ) current is $I$
Then, the enclosed current for area $\pi {r^2}$ is ${I_{enclosed}} = \dfrac{{{r^2}}}{{{a^2}}}I$
Taking the integral magnetic field around the coil, we get-
$\oint {\overrightarrow B } .\overrightarrow {dl} = B \times 2\pi r$
Using Ampere’s circuital law, we get-
$
B \times 2\pi r = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }I{r^2}}}
{{{a^2}}} \\
B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }rI}}
{{2\pi {a^2}}} \\
$
Note:
While calculating the magnetic field using Ampere’s circuital law we have to see that the current flowing in the conductor is steady current. Otherwise the law will not be valid. Also the direction of the magnetic field can be found using Fleming’s left hand rule.
Complete step by step answer:
Ampere’s circuital law states that the magnetic field integral of the closed line around a current bearing conductor is proportional to absolute permeability times the overall passing current of the conductor.
Mathematically it is given by-
$\oint {\overrightarrow I } .\overrightarrow {dl} = {\mu _ \circ }{I_{enclosed}}$, where ${\mu _ \circ } = $ permeability of free space, $dl = $ small parts of length
Now we have to calculate the magnetic field inside the region ( $r < a$ ) in the wire where current is uniformly distributed and the wire has a circular cross-section. The current is steady current.

Now let us consider the given figure-
In this figure, magnetic field lines form concentric circles centred on O. The axis of the cylindrical string.
Hence, it is the preferred part of the loop. Here there are two concentric circles. The radius of the large circle is $a$ and the radius of the smaller circle is $r$ .
Now consider a loop of radius $a < r$
The cross-sectional area ( $\pi {a^2}$ ) current is $I$
Then, the enclosed current for area $\pi {r^2}$ is ${I_{enclosed}} = \dfrac{{{r^2}}}{{{a^2}}}I$
Taking the integral magnetic field around the coil, we get-
$\oint {\overrightarrow B } .\overrightarrow {dl} = B \times 2\pi r$
Using Ampere’s circuital law, we get-
$
B \times 2\pi r = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }I{r^2}}}
{{{a^2}}} \\
B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }rI}}
{{2\pi {a^2}}} \\
$
Note:
While calculating the magnetic field using Ampere’s circuital law we have to see that the current flowing in the conductor is steady current. Otherwise the law will not be valid. Also the direction of the magnetic field can be found using Fleming’s left hand rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




