
Write a structural formula of the alcohol that results when acetaldehyde is reacted with \[C{H_3}MgBr\] in the presence of dry ether and the product is hydrolysed.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: Aldehydes when react with Grignard’s reagent results in organometallic compounds which on further hydrolysis gives in alcohol. We know that Grignard’s reagent is magnesium alkyl halide, RMgX which is formed when magnesium reacts with alkyl halide in presence of ether.
Complete step by step answer:
-Acetaldehyde is also known as ethanal. It belongs to the carbonyl functional group aldehyde having a short carbon chain. It reacts with Grignard reagent to give additional products which give secondary alcohol on hydrolysis. So, in short it is conversion of aldehyde to secondary alcohol.
-Grignard’s reagent is metal alkyl halide formed when alkyl halide reacts with metal such as magnesium, for example RMgX where R can be any alkyl group like methyl, ethyl, etc. They are the first source of carbanions or Lewis bases or electron-pair donors.
-We can say that the carbonyl carbon of acetaldehyde has positive charge and the oxygen has negative charge. So, when Grignard reagent attacks, it pushes the double bond between oxygen and carbon and leaves a lone pair on oxygen that contains a metal-carbon bond. This produces magnesium halide along with the product.
-The product formed is hydrolysed with water or aqueous acid and we get our main product i.e. secondary alcohol. The purpose of acid or water here is to protonate the negatively charged oxygen.
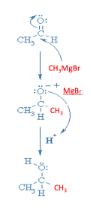
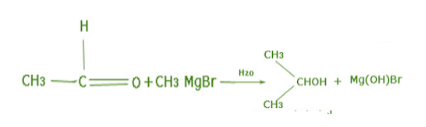
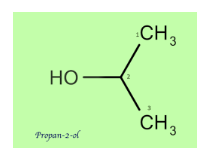
Acetaldehyde \[(C{H_3}CHO)\] on reacting with Grignard’s reagent \[(C{H_3}MgBr)\] in presence of diethyl ether will now result in a chain of three carbons which on hydrolysis gives the main product having secondary alcohol i.e. Propan-2-ol.
Note:
Except formaldehyde, all the other aldehydes reacting with Grignard’s reagent results in secondary alcohol. But formaldehyde gives primary alcohol because we can only add a single carbon atom and thus can’t form secondary alcohols.
Complete step by step answer:
-Acetaldehyde is also known as ethanal. It belongs to the carbonyl functional group aldehyde having a short carbon chain. It reacts with Grignard reagent to give additional products which give secondary alcohol on hydrolysis. So, in short it is conversion of aldehyde to secondary alcohol.
-Grignard’s reagent is metal alkyl halide formed when alkyl halide reacts with metal such as magnesium, for example RMgX where R can be any alkyl group like methyl, ethyl, etc. They are the first source of carbanions or Lewis bases or electron-pair donors.
-We can say that the carbonyl carbon of acetaldehyde has positive charge and the oxygen has negative charge. So, when Grignard reagent attacks, it pushes the double bond between oxygen and carbon and leaves a lone pair on oxygen that contains a metal-carbon bond. This produces magnesium halide along with the product.
-The product formed is hydrolysed with water or aqueous acid and we get our main product i.e. secondary alcohol. The purpose of acid or water here is to protonate the negatively charged oxygen.

Acetaldehyde \[(C{H_3}CHO)\] on reacting with Grignard’s reagent \[(C{H_3}MgBr)\] in presence of diethyl ether will now result in a chain of three carbons which on hydrolysis gives the main product having secondary alcohol i.e. Propan-2-ol.


Note:
Except formaldehyde, all the other aldehydes reacting with Grignard’s reagent results in secondary alcohol. But formaldehyde gives primary alcohol because we can only add a single carbon atom and thus can’t form secondary alcohols.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




