
With the help of a ray diagram, describe the construction, working of a compound microscope when the final image is formed at least distance of distinct vision (D= 25 cm). Derive an expression for magnifying power (m).
Answer
601.8k+ views
Hint: We will form the simple formation of the compound microscope by using distinct vision of 25 cm from the eyepiece and the image formation of an object. This image will be first formed by the right placement of an object. This image further will be formed at a distance of 25 cm from the eye piece.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{h}{{{F}_{\text{o}}}}=\dfrac{h'}{{{F}_{\text{o}}}}$ where h is height of AB and h’ is height of A’B’, ${{F}_{\text{o}}}$ is focal length of objective. Here, the magnification is going to be by using ${{m}_{e}}=\dfrac{\text{Distinct vision}}{{{F}_{e}}}$ where D is distinct vision.
Complete answer:
We will understand the question by making a diagram of a compound microscope.
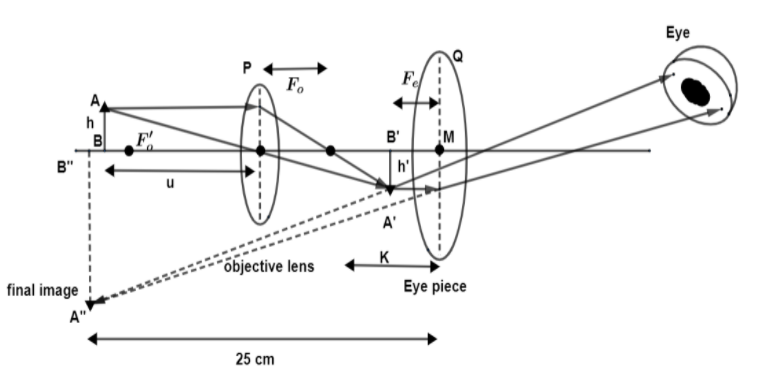
Compound microscope: There are two lenses that we will find in a microscope namely, objective lens and an eye piece. The objective lens is represented as P and is kept nearer to the object AB and the eye piece is denoted by Q from which the looking. These two lenses are convex lenses with a small focal length but comparatively, focal length of P is smaller than Q. Due to this comparison a brighter image is formed with magnification.
Working:
We see an object AB which is placed towards the objective lens. It is kept beyond principal focus $F{{'}_{\text{o}}}$. With such a lens we are able to see the image of it as a real, enlarged and inverted image of AB as A’B’. The eye lens’s optical center is at M and focus of the eye piece is at $F{{'}_{e}}$. With the help of eyepiece Q we are able to see the final image of AB which is virtual, magnified and inverted named as A”B”. This image is at a distance of distinct vision of 25 cm from the eye. The linear magnification of the object is done by the formula $\dfrac{h}{{{F}_{\text{o}}}}=\dfrac{h'}{{{F}_{\text{o}}}}$. Since, K is a distance between the focal length of object and eye piece then, $\dfrac{h'}{h}=\dfrac{K}{{{F}_{\text{o}}}}$.
Expression for magnifying power (m):
Here, the magnification is going to be by using ${{m}_{e}}=\dfrac{\text{Distinct vision}}{{{F}_{e}}}$. The total magnification after image formation at any point is measured by formula $m={{m}_{o}}\times {{m}_{e}}$.
Hence, after this type of construction we will find the image at a distinct division of D = 25 cm.
Note:
We should remember while performing such construction that we should adjust the object lens and eye lens such that the image A’B’ forms between focus and optical center denoted by M of the eye lens. This will result in a final image of at least the distance of distinct vision of 25 cm. Also, the formula of ${{m}_{e}}=\dfrac{\text{Distinct vision}}{{{F}_{e}}}$ and $m={{m}_{o}}\times {{m}_{e}}$ are very important here. In case the diagram is not drawn properly then, the whole solution will be wrong. The lenses used here are of convex nature. Expressing the derivation for magnifying power we should know the right notations in the diagram.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{h}{{{F}_{\text{o}}}}=\dfrac{h'}{{{F}_{\text{o}}}}$ where h is height of AB and h’ is height of A’B’, ${{F}_{\text{o}}}$ is focal length of objective. Here, the magnification is going to be by using ${{m}_{e}}=\dfrac{\text{Distinct vision}}{{{F}_{e}}}$ where D is distinct vision.
Complete answer:
We will understand the question by making a diagram of a compound microscope.

Compound microscope: There are two lenses that we will find in a microscope namely, objective lens and an eye piece. The objective lens is represented as P and is kept nearer to the object AB and the eye piece is denoted by Q from which the looking. These two lenses are convex lenses with a small focal length but comparatively, focal length of P is smaller than Q. Due to this comparison a brighter image is formed with magnification.
Working:
We see an object AB which is placed towards the objective lens. It is kept beyond principal focus $F{{'}_{\text{o}}}$. With such a lens we are able to see the image of it as a real, enlarged and inverted image of AB as A’B’. The eye lens’s optical center is at M and focus of the eye piece is at $F{{'}_{e}}$. With the help of eyepiece Q we are able to see the final image of AB which is virtual, magnified and inverted named as A”B”. This image is at a distance of distinct vision of 25 cm from the eye. The linear magnification of the object is done by the formula $\dfrac{h}{{{F}_{\text{o}}}}=\dfrac{h'}{{{F}_{\text{o}}}}$. Since, K is a distance between the focal length of object and eye piece then, $\dfrac{h'}{h}=\dfrac{K}{{{F}_{\text{o}}}}$.
Expression for magnifying power (m):
Here, the magnification is going to be by using ${{m}_{e}}=\dfrac{\text{Distinct vision}}{{{F}_{e}}}$. The total magnification after image formation at any point is measured by formula $m={{m}_{o}}\times {{m}_{e}}$.
Hence, after this type of construction we will find the image at a distinct division of D = 25 cm.
Note:
We should remember while performing such construction that we should adjust the object lens and eye lens such that the image A’B’ forms between focus and optical center denoted by M of the eye lens. This will result in a final image of at least the distance of distinct vision of 25 cm. Also, the formula of ${{m}_{e}}=\dfrac{\text{Distinct vision}}{{{F}_{e}}}$ and $m={{m}_{o}}\times {{m}_{e}}$ are very important here. In case the diagram is not drawn properly then, the whole solution will be wrong. The lenses used here are of convex nature. Expressing the derivation for magnifying power we should know the right notations in the diagram.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




