
With the help of a neat ray diagram. Discuss the construction and working of optical fibre.
Answer
562.5k+ views
Hint: Optical fibre technology is the technology in which electrical signals are converted into optical signals. These signals are transmitted through thin fibres made of glass. The optical signals thus transmitted are again converted into electrical signals at the reception point.
Complete step by step solution:
We can define an optical fibre as a cylindrical waveguide made of a transparent dielectric material (like plastic or glass). The light waves are guided along their length by a phenomenon called total internal reflection.
The basic principle of optical fibre is total internal reflection. If the angle of incidence is greater than a particular angle called critical angle, the ray will not pass through the material, but it will trace its way back to the surface itself. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection. The light enters from one end of the fibre and undergoes continuous total internal reflections from the sidewalls of the fibre. The light will travel through the fibre in a zigzag path.
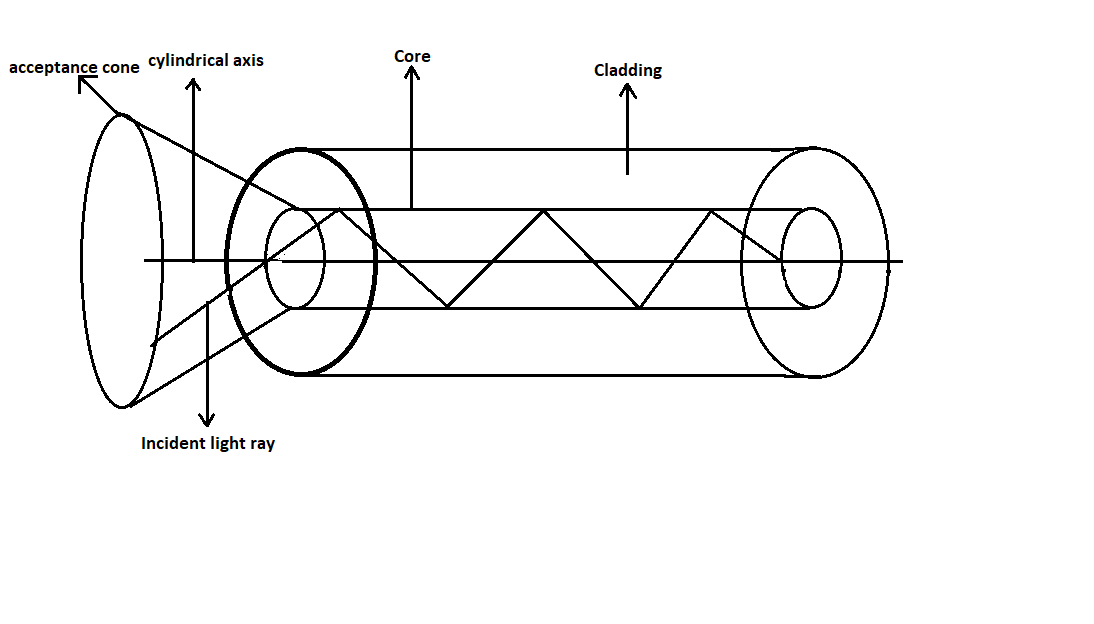
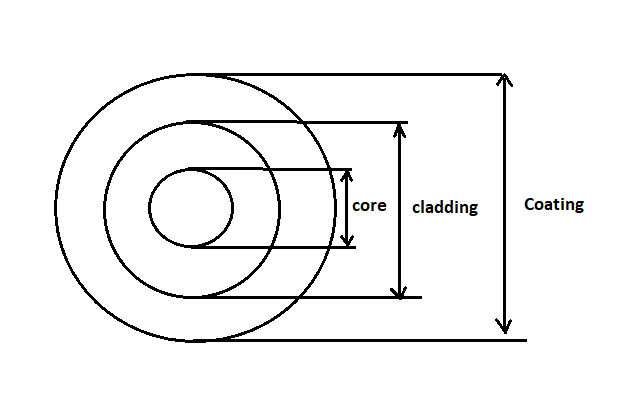
Practically optical is made in a cylindrical shape. Usually, optical fibre has three coaxial regions as shown in the figure.
The innermost region is called the core. This is the part through which light is guided.
The order of the diameter of the region ranges from $8.5\mu m$ to $62.5\mu m$.
The core is surrounded by a middle region called the cladding. The diameter of cladding is in the order of $125\mu m$. The refractive index of the cladding will be lesser than that of the refractive index of the core.
The light will enter into the core and due to the change in refractive index between the core and the cladding, it will undergo total internal reflection and propagate through the fibre and reach its destination.
The outermost region is called buffer coating or the sheath. This coating of plastic is given to the optic fibre for protection. This coating will provide physical and environment protection for the fibre.
Note:
The optic fibre system is used to transmit signals over a long distance efficiently and with minimum loss in the signal. There is a source of light where the electrical signal is converted into light at the beginning of the fibre and a photodetector that decodes the light signal into electrical signal at the end of the fibre.
Complete step by step solution:
We can define an optical fibre as a cylindrical waveguide made of a transparent dielectric material (like plastic or glass). The light waves are guided along their length by a phenomenon called total internal reflection.
The basic principle of optical fibre is total internal reflection. If the angle of incidence is greater than a particular angle called critical angle, the ray will not pass through the material, but it will trace its way back to the surface itself. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection. The light enters from one end of the fibre and undergoes continuous total internal reflections from the sidewalls of the fibre. The light will travel through the fibre in a zigzag path.


Practically optical is made in a cylindrical shape. Usually, optical fibre has three coaxial regions as shown in the figure.
The innermost region is called the core. This is the part through which light is guided.
The order of the diameter of the region ranges from $8.5\mu m$ to $62.5\mu m$.
The core is surrounded by a middle region called the cladding. The diameter of cladding is in the order of $125\mu m$. The refractive index of the cladding will be lesser than that of the refractive index of the core.
The light will enter into the core and due to the change in refractive index between the core and the cladding, it will undergo total internal reflection and propagate through the fibre and reach its destination.
The outermost region is called buffer coating or the sheath. This coating of plastic is given to the optic fibre for protection. This coating will provide physical and environment protection for the fibre.
Note:
The optic fibre system is used to transmit signals over a long distance efficiently and with minimum loss in the signal. There is a source of light where the electrical signal is converted into light at the beginning of the fibre and a photodetector that decodes the light signal into electrical signal at the end of the fibre.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




