
Williamson synthesis of ether is example of
A) Nucleophilic addition
B) Electrophilic addition
C) Electrophilic substitution
D) Nucleophilic substitution
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: To answer this we must know the use of Williamson’s synthesis. Williamson’s synthesis is used for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. The synthesis of ethers is done using alkyl halides which react with sodium alkoxide.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that Williamson’s synthesis is used for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers.
In Williamson’s synthesis, alkyl halide $\left( {{\text{R}}' - {\text{X}}} \right)$ reacts with sodium alkoxide $\left( {{\text{R}}{{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }} \right)$ to produce ethers $\left( {{\text{R}} - {\text{O}} - {\text{R}}'} \right)$. Sodium halide $\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }{{\text{X}}^ - }} \right)$ is the by-product of the reaction.
The general reaction for the production of ethers using Williamson’s synthesis is as follows:
${\text{R}}{{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + } + {\text{R}}' - {\text{X}} \to {\text{R}} - {\text{O}} - {\text{R}}' + {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }{{\text{X}}^ - }$
Williamson’s synthesis is a nucleophilic substitution reaction.In alkyl halides, a positive charge develops on the carbon atom attached to the halogen atom. This is because the carbon halogen bond is polar in nature due to the high electronegativity of the halogen atom. As a result the carbon atom becomes electrophilic in nature.
The alkoxide ion acts as a nucleophile. The alkoxide ion substitutes the halide ion from the alkyl halide. The reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction i.e. ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction.
For example: Preparation of ethoxyethane from sodium ethanolate and chloroethane. The reaction is as follows:
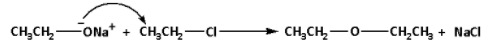
In the reaction, sodium ethanolate reacts with chloroethane and ethoxyethane is produced. The by-product of the reaction is sodium chloride. Thus, Williamson synthesis of ether is an example of nucleophilic substitution.
Thus the correct option is (D) nucleophilic substitution.
Note: The Williamson’s synthesis follows ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ mechanism i.e. bimolecular nucleophilic substitution mechanism. It is a one-step reaction. In the reaction, the bond breaking and bond making occurs simultaneously. No intermediate is formed in the reaction. The nucleophile attacks the alkyl halide from the back side and thus, the product formed has a reversed configuration.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that Williamson’s synthesis is used for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers.
In Williamson’s synthesis, alkyl halide $\left( {{\text{R}}' - {\text{X}}} \right)$ reacts with sodium alkoxide $\left( {{\text{R}}{{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }} \right)$ to produce ethers $\left( {{\text{R}} - {\text{O}} - {\text{R}}'} \right)$. Sodium halide $\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }{{\text{X}}^ - }} \right)$ is the by-product of the reaction.
The general reaction for the production of ethers using Williamson’s synthesis is as follows:
${\text{R}}{{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + } + {\text{R}}' - {\text{X}} \to {\text{R}} - {\text{O}} - {\text{R}}' + {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }{{\text{X}}^ - }$
Williamson’s synthesis is a nucleophilic substitution reaction.In alkyl halides, a positive charge develops on the carbon atom attached to the halogen atom. This is because the carbon halogen bond is polar in nature due to the high electronegativity of the halogen atom. As a result the carbon atom becomes electrophilic in nature.
The alkoxide ion acts as a nucleophile. The alkoxide ion substitutes the halide ion from the alkyl halide. The reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction i.e. ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ reaction.
For example: Preparation of ethoxyethane from sodium ethanolate and chloroethane. The reaction is as follows:

In the reaction, sodium ethanolate reacts with chloroethane and ethoxyethane is produced. The by-product of the reaction is sodium chloride. Thus, Williamson synthesis of ether is an example of nucleophilic substitution.
Thus the correct option is (D) nucleophilic substitution.
Note: The Williamson’s synthesis follows ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}2$ mechanism i.e. bimolecular nucleophilic substitution mechanism. It is a one-step reaction. In the reaction, the bond breaking and bond making occurs simultaneously. No intermediate is formed in the reaction. The nucleophile attacks the alkyl halide from the back side and thus, the product formed has a reversed configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




