
When the width of slit aperture is increased by keeping ‘d’ constant in Young's experiment, then:
A. Fringe width increases
B. Fringe width decreases and then increases
C. Fringe width increases and then decreases
D. Gradually the fringes merge.
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: In the young’s double slit experiment we use two coherent light sources. The waves from these sources travel different lengths and due to this length variation the phase difference between the waves changes and the fringes are formed on the screen due to the phase change.
Formula used:
$w = \dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}$
Complete step by step answer:
Coherent sources in the sense the waves emitted from these sources will be having the same wavelength and frequency and the phase difference between them will not vary with time.
Example for the coherent source is the laser light while the example for in coherent source is the light from the normal incandescent bulb.
Since we use coherent sources in the YDSE experiment, the phase difference will not vary with time but it can vary due to the path difference created between the two waves. Due to this path difference, phase difference is generated and intensity of these waves will interfere and give maximum intensity at the bright fringe and give the minimum intensity at the dark fringe.
If the path difference between the two waves is multiple of the wavelength of the light then a bright fringe is formed. Fringes are formed on the screen which is at perpendicular distance D from the sources. ‘d’ is the distance between the slits and ‘y’ is the distance from the central bright fringe.
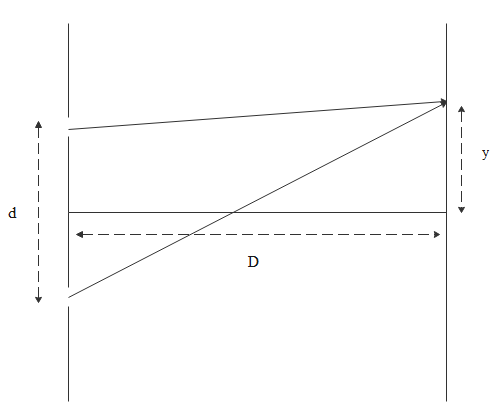
Now the fringe width will be $w = \dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}$
As long as ‘d’ is constant, the fringe width will be constant. But if the width of the slits increases then the intensity of the waves from the slits increases and gradually we cannot differentiate between the dark and the bright fringes as they will merge.
Hence option D will be the answer.
Note:
The given case can be viewed as if we pass light through the two broad holes then we can’t see any fringes. The shape of fringes formed on the screen depends upon the shape of the slits through which the light waves are passed. If the same experiment is repeated through the single small aperture then that is called diffraction.
Formula used:
$w = \dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}$
Complete step by step answer:
Coherent sources in the sense the waves emitted from these sources will be having the same wavelength and frequency and the phase difference between them will not vary with time.
Example for the coherent source is the laser light while the example for in coherent source is the light from the normal incandescent bulb.
Since we use coherent sources in the YDSE experiment, the phase difference will not vary with time but it can vary due to the path difference created between the two waves. Due to this path difference, phase difference is generated and intensity of these waves will interfere and give maximum intensity at the bright fringe and give the minimum intensity at the dark fringe.
If the path difference between the two waves is multiple of the wavelength of the light then a bright fringe is formed. Fringes are formed on the screen which is at perpendicular distance D from the sources. ‘d’ is the distance between the slits and ‘y’ is the distance from the central bright fringe.

Now the fringe width will be $w = \dfrac{{\lambda D}}{d}$
As long as ‘d’ is constant, the fringe width will be constant. But if the width of the slits increases then the intensity of the waves from the slits increases and gradually we cannot differentiate between the dark and the bright fringes as they will merge.
Hence option D will be the answer.
Note:
The given case can be viewed as if we pass light through the two broad holes then we can’t see any fringes. The shape of fringes formed on the screen depends upon the shape of the slits through which the light waves are passed. If the same experiment is repeated through the single small aperture then that is called diffraction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




