
Why is a Virus not alive?
Answer
490.2k+ views
Hint: Virus is an organism which depends its life upon hosts. We can call a virus dead when it leaves the host’s body such as growing over a rock or lich areas. The moment a virus gets into a body it becomes alive. And it takes up all the nutrients and spreads infection while residing inside the host’s body. Hence, the majority of organisms where viruses live have cell walls.
Complete answer:
Cell walls have robust layers and the best is known in plants, fungi, algae and bacteria.
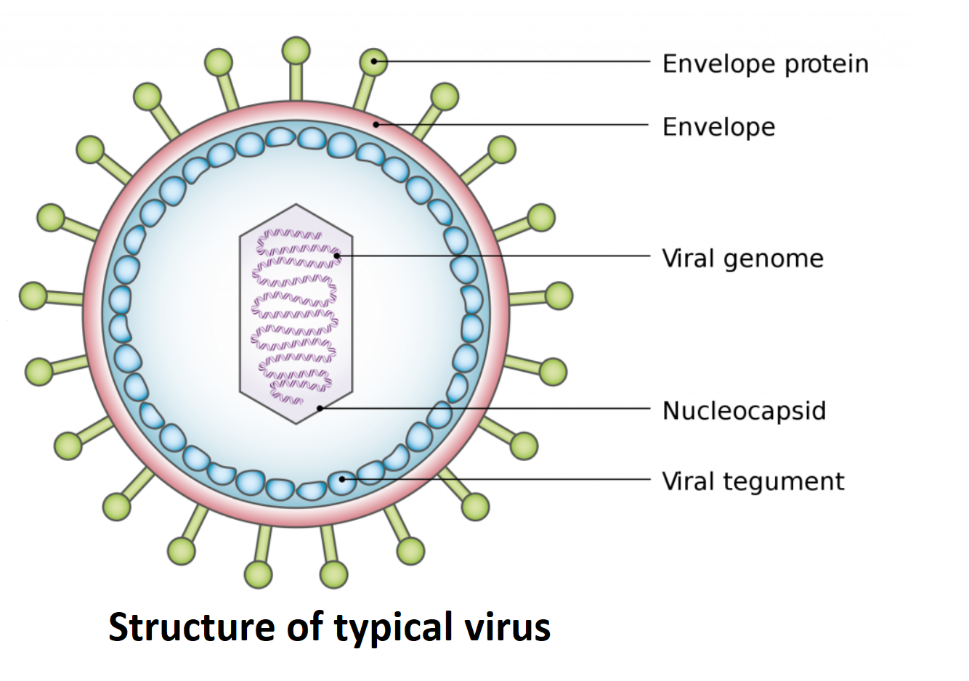
The virus which lives inside bacteria are called bacteriophages. Also, virions have nucleic acids and protein coat as capsid. Viruses actually do not have a proper cell wall on their own but they possess a protective layer around the body called capsid. Capsid functions as a protective layer and shells the viral genome from nucleases.
Depending upon what body surfaces it chooses until it gets transferred or killed viruses are neither considered to be alive fully nor dead. Viruses are basically in different shapes and sizes just like-bacteria and all the virus particles have a protein coat which surrounds the nucleic acid genome. The instructions to make protein subunits come from the genome of the virus so that it remains protected.
Virus can infect the host’s body by infecting the host’s nucleus. It enters the cells by digging through its capsid which have spines over it to pierce through the cells and directly it inserts its viral genome to the host’s cell nucleus replacing the host’s cell DNA or RNA with its own viral DNA or RNA. Actually, viruses are not made of cells, they are not stable structures, they only have a viral genome which keeps them alive and they do not grow in size and cannot have their own energy. they take up the host’s diet host’s DNA.
Note:
All viruses are not lethal and all do not have DNA and RNA both one can possess either of them. Viruses causing diseases such as- cylindrical helical virus type which cause tobacco mosaic virus, also envelope viruses like-influenza and HIV have lipid as protective envelope. Animal viruses have Icosahedral and spherical shape viruses.
Complete answer:
Cell walls have robust layers and the best is known in plants, fungi, algae and bacteria.
The virus which lives inside bacteria are called bacteriophages. Also, virions have nucleic acids and protein coat as capsid. Viruses actually do not have a proper cell wall on their own but they possess a protective layer around the body called capsid. Capsid functions as a protective layer and shells the viral genome from nucleases.
Depending upon what body surfaces it chooses until it gets transferred or killed viruses are neither considered to be alive fully nor dead. Viruses are basically in different shapes and sizes just like-bacteria and all the virus particles have a protein coat which surrounds the nucleic acid genome. The instructions to make protein subunits come from the genome of the virus so that it remains protected.
Virus can infect the host’s body by infecting the host’s nucleus. It enters the cells by digging through its capsid which have spines over it to pierce through the cells and directly it inserts its viral genome to the host’s cell nucleus replacing the host’s cell DNA or RNA with its own viral DNA or RNA. Actually, viruses are not made of cells, they are not stable structures, they only have a viral genome which keeps them alive and they do not grow in size and cannot have their own energy. they take up the host’s diet host’s DNA.

Note:
All viruses are not lethal and all do not have DNA and RNA both one can possess either of them. Viruses causing diseases such as- cylindrical helical virus type which cause tobacco mosaic virus, also envelope viruses like-influenza and HIV have lipid as protective envelope. Animal viruses have Icosahedral and spherical shape viruses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




