
Why \[BaC{l_2}\] is not a Lewis acid?
Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: Lewis acids can accept electrons to form bonds. They have vacant orbitals in them, so they form bonds by accepting electrons in vacant orbitals and so they are electron deficient molecules. \[BaC{l_2}\] is a salt. They do not have incomplete shells.
Complete answer:
Lewis acids are the species that accept an electron pair. They are electrophilic. This means that they are electron deficient and will attract electrons towards themselves. Lewis acids use their unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) to form bonds with the Lewis bases. These compounds have vacant orbitals in them so that they can accept the electrons from Lewis bases. Examples of Lewis acids are-all the cations, molecule having incomplete octet $(e.g.,B{F_3})$, molecules having multiple bonds between two different atoms of different electronegativities $\left( {e.g.,C{O_2}} \right)$ etc.
\[BaC{l_2}\] is an ionic salt. It is formed by the direct reaction of chlorine and barium. The Lewis structure of \[BaC{l_2}\] is as follows:
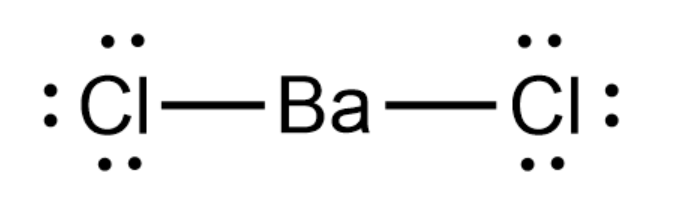
Here the valency of Barium is $2$ so it will lose two electrons to attain Nobel configuration and two chlorine atoms each having valency $1$ will accept those two electrons to attain Nobel configuration. So both species have a complete octet state. And we know that Lewis acids have an incomplete octet. Thus we can say that \[BaC{l_2}\] is not a Lewis acid.
Note:
Lewis acids act as a catalyst in most of the reactions. Their action can also be seen in photochemical reactions. Lewis bases are used as ligands in coordination chemistry. The compound \[BaC{l_2}\] is a dehydrated salt. When it is heated it decomposes at a very high temperature and forms \[S{O_2}\;\] gas. \[BaC{l_2}\] being a salt cannot be considered as an acid or a base so it is a neutral compound.
Complete answer:
Lewis acids are the species that accept an electron pair. They are electrophilic. This means that they are electron deficient and will attract electrons towards themselves. Lewis acids use their unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) to form bonds with the Lewis bases. These compounds have vacant orbitals in them so that they can accept the electrons from Lewis bases. Examples of Lewis acids are-all the cations, molecule having incomplete octet $(e.g.,B{F_3})$, molecules having multiple bonds between two different atoms of different electronegativities $\left( {e.g.,C{O_2}} \right)$ etc.
\[BaC{l_2}\] is an ionic salt. It is formed by the direct reaction of chlorine and barium. The Lewis structure of \[BaC{l_2}\] is as follows:
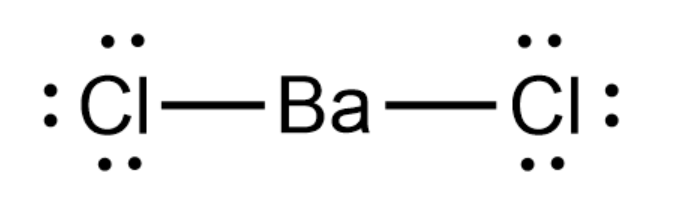
Here the valency of Barium is $2$ so it will lose two electrons to attain Nobel configuration and two chlorine atoms each having valency $1$ will accept those two electrons to attain Nobel configuration. So both species have a complete octet state. And we know that Lewis acids have an incomplete octet. Thus we can say that \[BaC{l_2}\] is not a Lewis acid.
Note:
Lewis acids act as a catalyst in most of the reactions. Their action can also be seen in photochemical reactions. Lewis bases are used as ligands in coordination chemistry. The compound \[BaC{l_2}\] is a dehydrated salt. When it is heated it decomposes at a very high temperature and forms \[S{O_2}\;\] gas. \[BaC{l_2}\] being a salt cannot be considered as an acid or a base so it is a neutral compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




