
Which will react faster with NBS?
A. ${{\text{C}}_6}{{\text{H}}_6}$
B. ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_4}$
C. Toluene
D. Cyclopropane
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: NBS is a brominating agent. It is also used as an oxidizing agent. It gives bromine in lower concentration. NBS is used mostly in radical reactions. They are also used in electrophilic reactions. NBS is also known as N-Bromosuccinimide.
Complete step by step answer:
N-Bromo succinimide is abbreviated as NBS. It is a white solid. Molecular structure of NBS is given below:
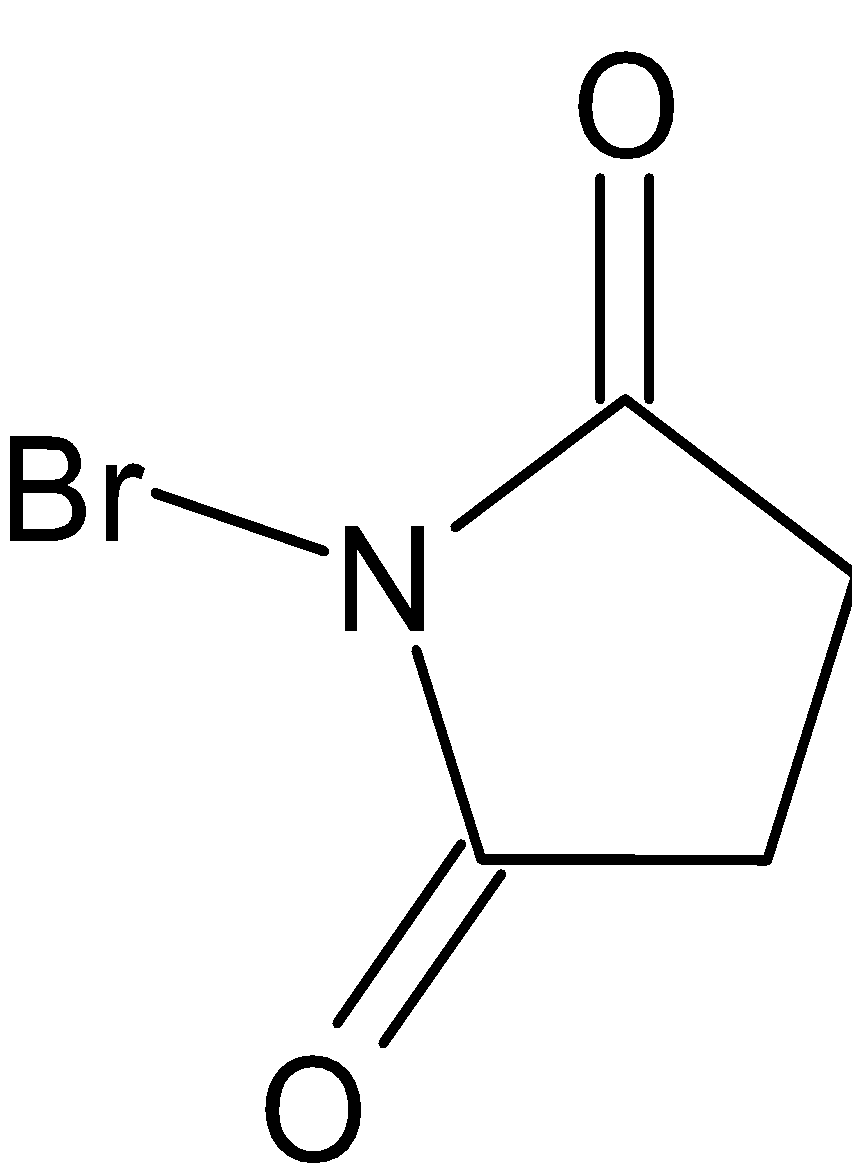
It is soluble in ${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_4}$ and insoluble in water.
It is prepared by reacting succinimide with ${\text{NaOH}}$ followed by bromination. It is used as an oxidizing agent. It oxidizes primary alcohols and primary amine to aldehydes and secondary alcohols and ketones. It is also used in conversion of monoenes to dienes and further to trienes.
NBS reagent is used for allylic bromination. It is the replacement of hydrogen on carbon near to a double bond or aromatic ring. NBS gives a lower concentration of bromine than ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2}$. NBS is used based on the allylic or benzylic bromination mechanism. It is a radical chain mechanism. NBS is a source of bromine radical.
So this mechanism needs alternative double bonds. Thus cyclopropane and methane does not react with NBS. And benzene is more stable than toluene. Toluene is more reactive to NBS.
Benzylic bromination occurs when NBS reacts with toluene. In toluene, benzyl ${\text{C}} - {\text{H}}$ bonds are weaker than ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$ hybridized ${\text{C}} - {\text{H}}$ bond. Therefore benzyl hydrogen produces benzyl halides in radical conditions.
Hence, option C is correct.
Additional information:
In the Wohl-Ziegler reaction, NBS is used as a brominating agent. In this reaction, cyclohexene is heated with NBS in the presence of ${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_4}$ to produce bromo cyclohexene and succinimide. It is also used for bromination of alcohols.
Note:
The mechanism of allylic bromination occurs by bromine atom abstracting the allylic hydrogen since the allylic hydrogen is resonance stabilized. The radical then reacts with bromine to continue the chain. NBS is used since it continually generates bromine in small amounts.
Complete step by step answer:
N-Bromo succinimide is abbreviated as NBS. It is a white solid. Molecular structure of NBS is given below:

It is soluble in ${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_4}$ and insoluble in water.
It is prepared by reacting succinimide with ${\text{NaOH}}$ followed by bromination. It is used as an oxidizing agent. It oxidizes primary alcohols and primary amine to aldehydes and secondary alcohols and ketones. It is also used in conversion of monoenes to dienes and further to trienes.
NBS reagent is used for allylic bromination. It is the replacement of hydrogen on carbon near to a double bond or aromatic ring. NBS gives a lower concentration of bromine than ${\text{B}}{{\text{r}}_2}$. NBS is used based on the allylic or benzylic bromination mechanism. It is a radical chain mechanism. NBS is a source of bromine radical.
So this mechanism needs alternative double bonds. Thus cyclopropane and methane does not react with NBS. And benzene is more stable than toluene. Toluene is more reactive to NBS.
Benzylic bromination occurs when NBS reacts with toluene. In toluene, benzyl ${\text{C}} - {\text{H}}$ bonds are weaker than ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$ hybridized ${\text{C}} - {\text{H}}$ bond. Therefore benzyl hydrogen produces benzyl halides in radical conditions.
Hence, option C is correct.
Additional information:
In the Wohl-Ziegler reaction, NBS is used as a brominating agent. In this reaction, cyclohexene is heated with NBS in the presence of ${\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_4}$ to produce bromo cyclohexene and succinimide. It is also used for bromination of alcohols.
Note:
The mechanism of allylic bromination occurs by bromine atom abstracting the allylic hydrogen since the allylic hydrogen is resonance stabilized. The radical then reacts with bromine to continue the chain. NBS is used since it continually generates bromine in small amounts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




