
Which substance is not present in nucleic acids?
A. Cytosine
B. Adenine
C. Thymine
D. Guanidine
Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: A monomer is a molecule that forms the basic unit of a polymer, which are the building blocks of proteins. Monomers bind to other monomers to form repeating chain molecules through a process known as polymerization. All nucleic acids are made up of the same building blocks (monomers) known as “nucleotides”
Complete step by step answer:
The monomers of the nucleic acid are linked by a link known as N- glycosidic linkage or glycosidic
linkage.
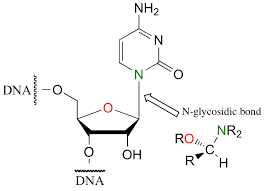
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
In the case of nucleic acids, the nitrogen bases of the nucleic acids are,
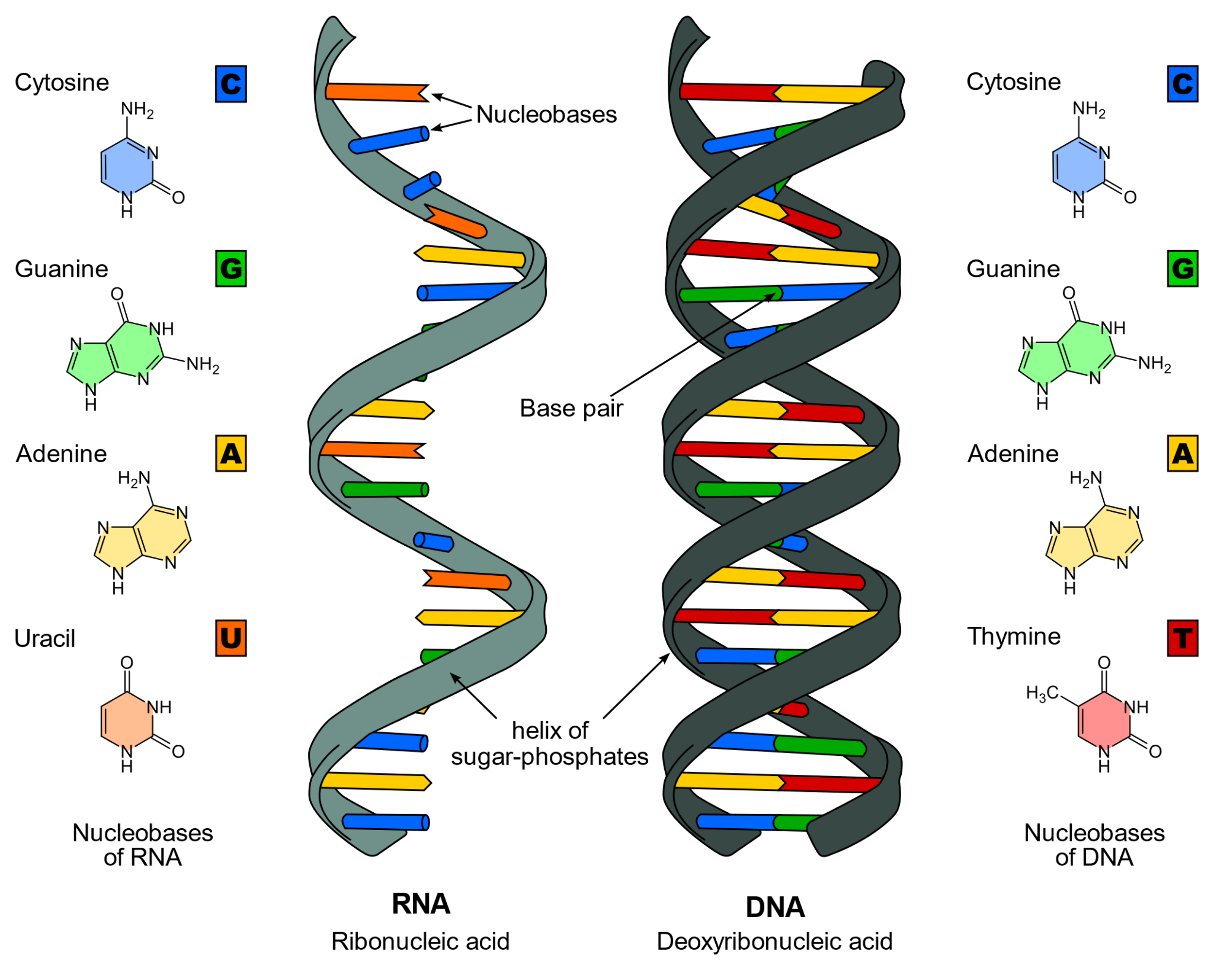
So, among the given options, the guideline is not present in nucleic acid.
So, the correct answer is, D.
Additional information:
amino acids are the monomeric units of proteins. Proteins like DNA, RNA is made of amino acids. There are different kinds of amino acids, which are, $\alpha $ -amino acids, $\beta $ - amino acids, $\gamma $ -amino etc.
The name of the amino acids is based on the positions of the group attached to the carbon atoms of the molecules.
Among all kinds of amino acids \[\alpha \] -amino acids are very much important. Among all amino acids there are some essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids.
Those amino acids which cannot be prepared inside the body are known as essential amino acids. For example, leucine, lysine, histidine, etc. And those amino acids which can be produced in our body are called non-essential amino acids. For example: aspartic acid, glycine, proline, etc.
Note: Glycosidic bonds are labeled according to the identity of the atom on the second carbohydrate or functional group. It can be broken by hydrolysis, which is the addition of a water molecule, to form two monosaccharides.
Complete step by step answer:
The monomers of the nucleic acid are linked by a link known as N- glycosidic linkage or glycosidic
linkage.

A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
In the case of nucleic acids, the nitrogen bases of the nucleic acids are,

So, among the given options, the guideline is not present in nucleic acid.
So, the correct answer is, D.
Additional information:
amino acids are the monomeric units of proteins. Proteins like DNA, RNA is made of amino acids. There are different kinds of amino acids, which are, $\alpha $ -amino acids, $\beta $ - amino acids, $\gamma $ -amino etc.
The name of the amino acids is based on the positions of the group attached to the carbon atoms of the molecules.
Among all kinds of amino acids \[\alpha \] -amino acids are very much important. Among all amino acids there are some essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids.
Those amino acids which cannot be prepared inside the body are known as essential amino acids. For example, leucine, lysine, histidine, etc. And those amino acids which can be produced in our body are called non-essential amino acids. For example: aspartic acid, glycine, proline, etc.
Note: Glycosidic bonds are labeled according to the identity of the atom on the second carbohydrate or functional group. It can be broken by hydrolysis, which is the addition of a water molecule, to form two monosaccharides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




