
Which reagent is used for the following conversion?
A. $\text{Na}$
B. $\text{aq}\text{. KOH}$
C. alcoholic $\text{KOH}$ followed by $\text{NaN}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$
D. $\text{Zn}$

Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: The dihalide is geminal in nature, as both the halo groups are attached to one carbon atom only. The question will be easy to solve if we go through the mechanism method. Sodium metal extracts acidic hydrogen, $\text{aq}\text{. KOH}$ adds $-\text{OH}$ group replacing halo group, alcoholic $\text{KOH}$ followed by $\text{NaN}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$ are reagents of elimination and zinc removes halo groups only.
Complete answer:
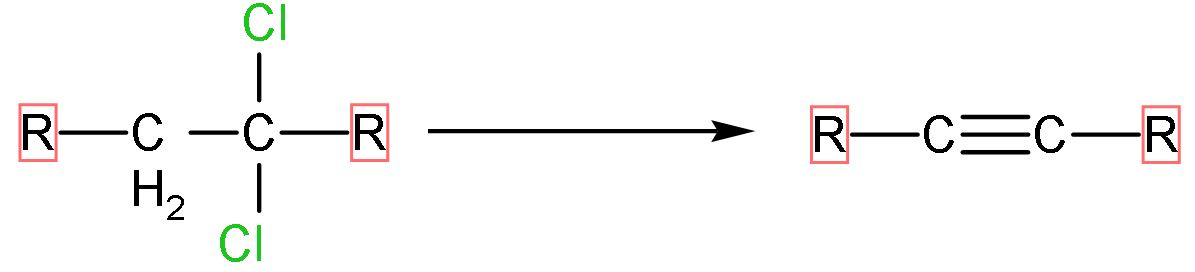
Let us discuss this conversion through its mechanism using a general reaction at first;
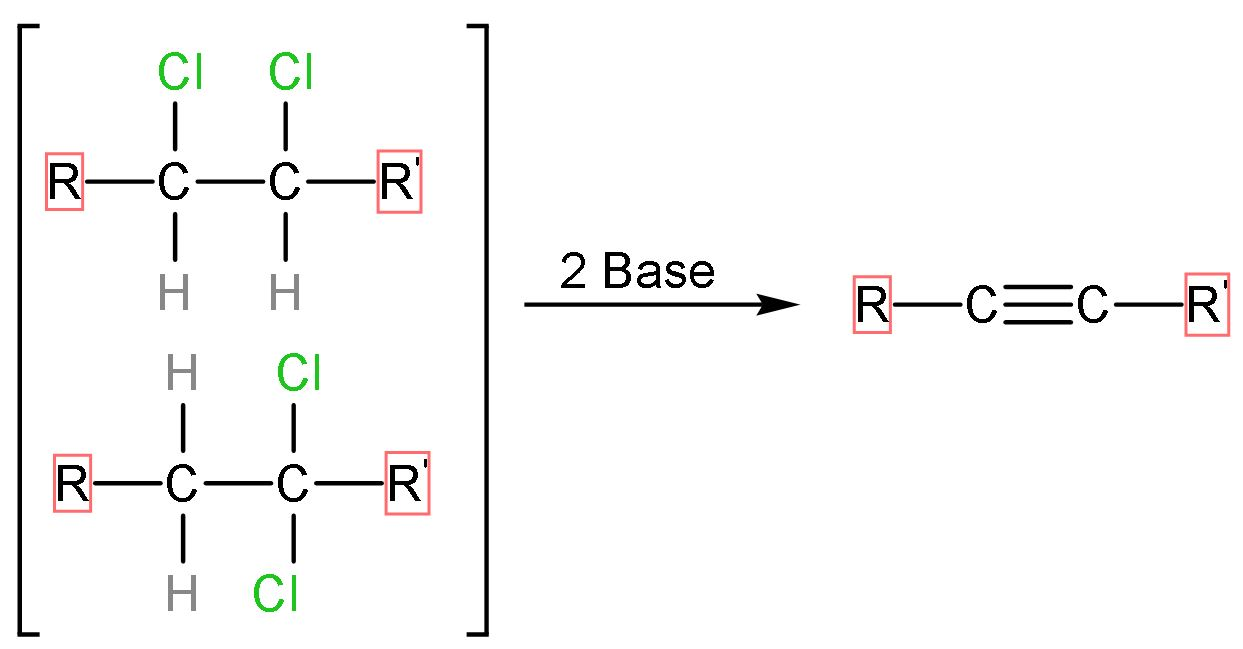
If the halogens are attached to the same carbon (geminal) or adjacent carbon atom (vicinal) and it reacts with base, the base extracts the hydrogen atoms and halogen atoms along with it. The general reaction of dihaloalkane elimination is
Let us see the mechanism of this question,
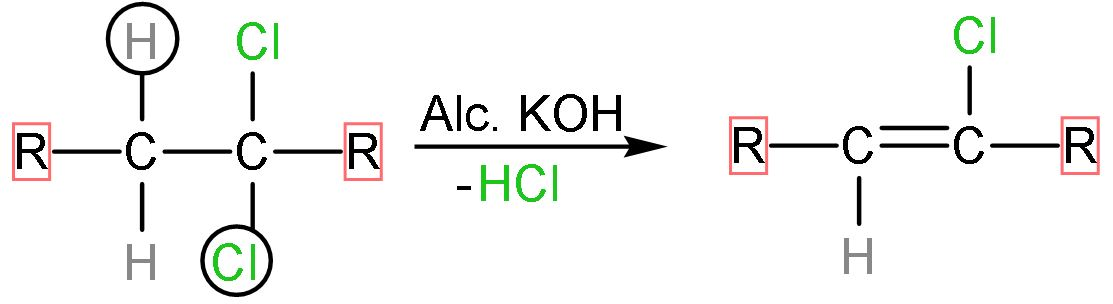
Step (1)- The dihaloalkane is reacted with alcoholic $\text{KOH}$, the halogen attached to it and the hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon atom will be removed by it as $\text{alc}\text{. KOH}$ is a strong base. The hydrochloric acid is removed and a double appears replacing the atoms. The reaction follows as
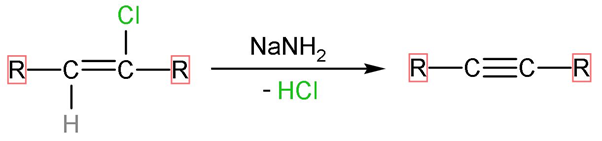
Step (2)- The forward is reaction carried out by $\text{NaN}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$ which is very strong base, as it denotes its lone pair and negative charge to incoming electrophiles. The hydrogen atom and chlorine atom present on adjacent carbon atoms are removed by adding one more bond between the two which is $\pi $- bond. The reaction looks like,
The correct answer to this question is ‘b’. Alcoholic $\text{KOH}$ followed by $\text{NaN}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$ reagent is used for the following conversion.
Note:
The moles of bases required to convert dihaloalkanes to terminal (in which triple bond is between ${{\text{C}}_{1}}-{{\text{C}}_{2}}$) alkynes are 3 not 2. The terminal alkynes are acidic in nature, as they readily react with bases to remove acidic hydrogens from them. $\text{RC}\equiv \text{CH}+\text{Base}\to \text{RC}\equiv {{\text{C}}^{-}}\text{bas}{{\text{e}}^{+}}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$. As, one of the base molecules will remove the terminal hydrogen instead of one of the halides.
Complete answer:
Let us discuss this conversion through its mechanism using a general reaction at first;
If the halogens are attached to the same carbon (geminal) or adjacent carbon atom (vicinal) and it reacts with base, the base extracts the hydrogen atoms and halogen atoms along with it. The general reaction of dihaloalkane elimination is

Let us see the mechanism of this question,
Step (1)- The dihaloalkane is reacted with alcoholic $\text{KOH}$, the halogen attached to it and the hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon atom will be removed by it as $\text{alc}\text{. KOH}$ is a strong base. The hydrochloric acid is removed and a double appears replacing the atoms. The reaction follows as

Step (2)- The forward is reaction carried out by $\text{NaN}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$ which is very strong base, as it denotes its lone pair and negative charge to incoming electrophiles. The hydrogen atom and chlorine atom present on adjacent carbon atoms are removed by adding one more bond between the two which is $\pi $- bond. The reaction looks like,

The correct answer to this question is ‘b’. Alcoholic $\text{KOH}$ followed by $\text{NaN}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$ reagent is used for the following conversion.
Note:
The moles of bases required to convert dihaloalkanes to terminal (in which triple bond is between ${{\text{C}}_{1}}-{{\text{C}}_{2}}$) alkynes are 3 not 2. The terminal alkynes are acidic in nature, as they readily react with bases to remove acidic hydrogens from them. $\text{RC}\equiv \text{CH}+\text{Base}\to \text{RC}\equiv {{\text{C}}^{-}}\text{bas}{{\text{e}}^{+}}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{\text{H}}_{2}}$. As, one of the base molecules will remove the terminal hydrogen instead of one of the halides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




