
Which reaction results in the formation of pair enantiomers?
(A)
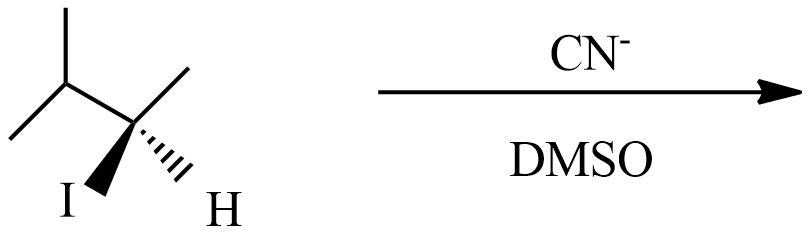
(B)
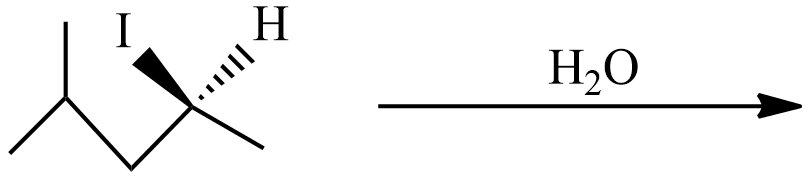
(C)
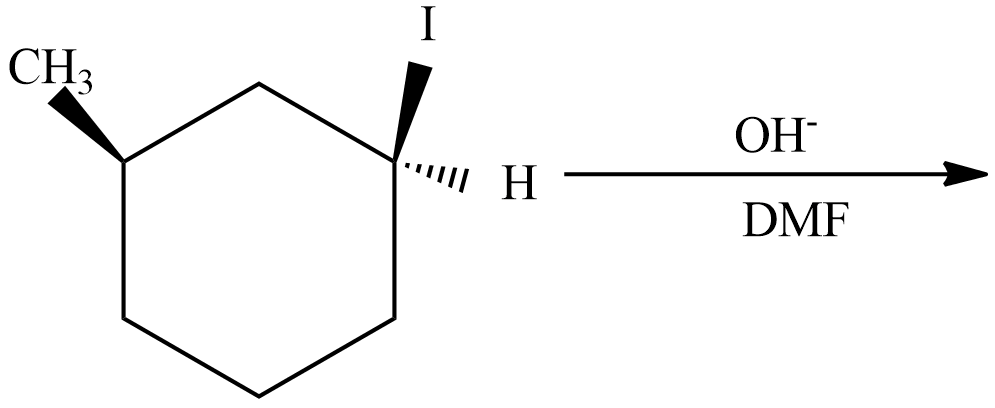
(D)
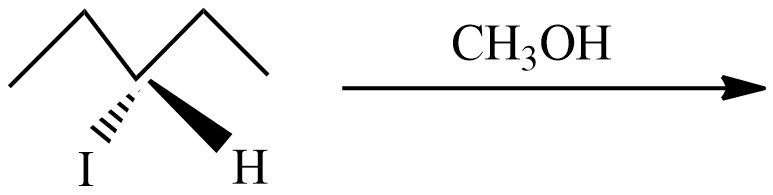
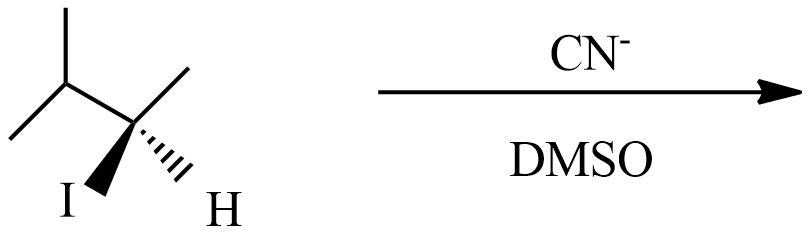
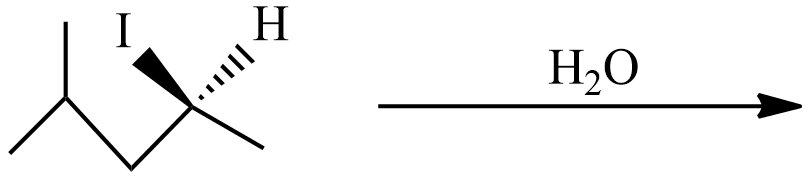

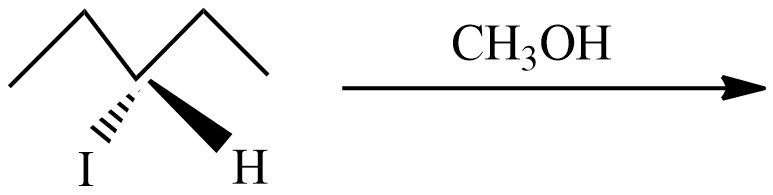
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: When a carbon with four different groups in a tetrahedral geometry, then it is a chiral carbon atom. This phenomenon is observed only in tetrahedral geometry which allows neighboring groups to get a little farther from each other. Simple tetrahedral compounds do not have cis-trans isomers, unlike square planar compounds.
Complete Solution:
In a tetrahedral atom attached to four different functional groups, then the two ways are possible with four groups. The two compounds look like mirror images with each other. These images are called non-super imposable mirror images and this pair of stereoisomers is also called enantiomers.
These enantiomers consist of no mirror planes and no two equal, opposite halves. These are another example of stereoisomerism.
- Two enantiomers are equal but rotate oppositely plane-polarized light. (+) enantiomer and (-) enantiomer rotate light in clockwise and counter-clockwise direction respectively.
- When any compound with a chiral center participates in nucleophilic substitution reactions, then the product is formed as a pair of enantiomers.
Let us find out given four reactions, which product will form a pair of enantiomers as a product of the concern reaction!
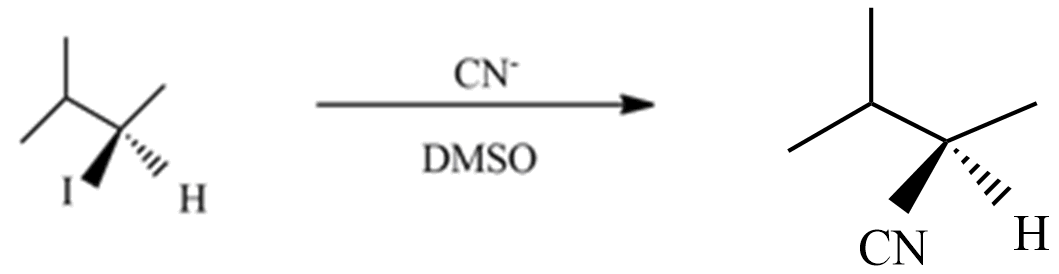
(A) This reaction is a type of \[{S_N}1\] nucleophilic substitution reaction because this reaction undergoes in DMSO which is a polar aprotic solvent, and the substation of $C{{N}^{-}}$ with ${{I}^{-}}$ enantiomer pairs will not form in product with an inverted proton.
(B) In this reaction, weak nucleophiles $O{{H}^{-}}$ from ${{H}_{2}}O$ replaces ${{I}^{-}}$. The intermediate carbocation is a square planar structure that would possibly react under \[{S_N}1\] or \[{S_N}1\]. So, the chiral carbon cation will form an enantiomer pair in the product.
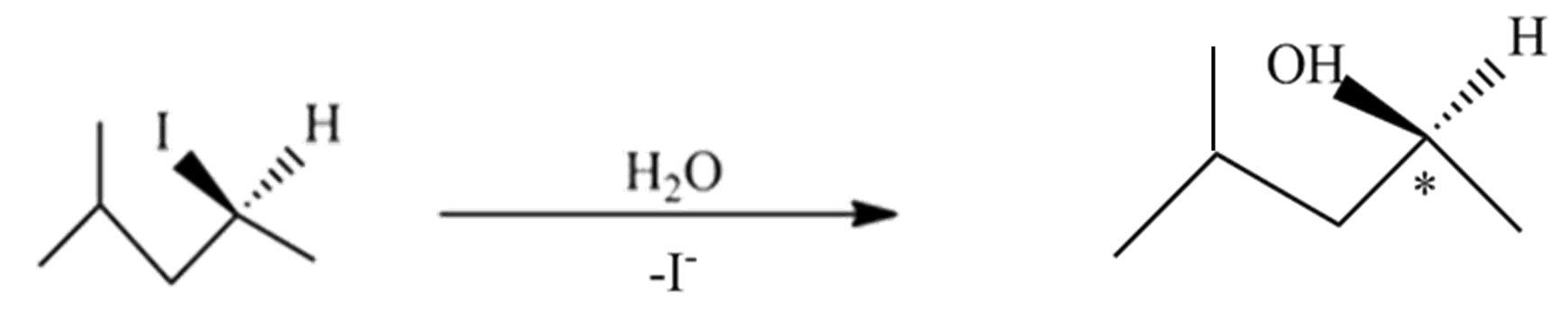
(C) This reaction undergoes with DMF-protic solvent with nucleophile $O{{H}^{-}}$ undergo $S{{N}^{2}}$, there are no enantiomer pairs that will form in the product.
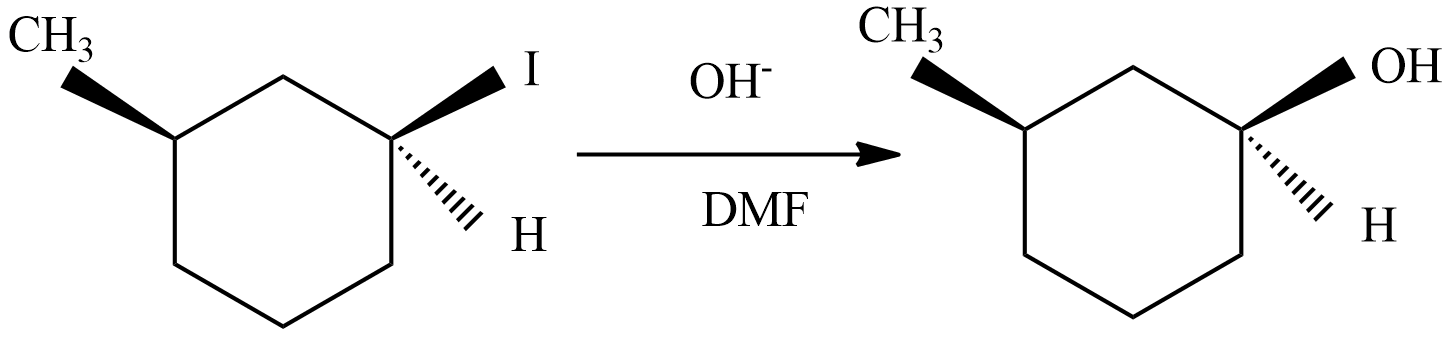
(D) In this reaction, the carbon cations form is not a chiral center (marked as ** ), so there is no chance of formation of enantiomeric pairs.
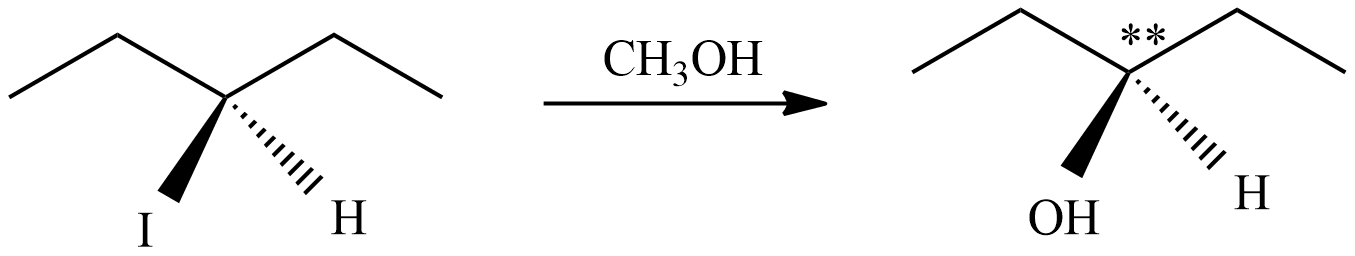
Hence, the product of the reaction (B) is 2-methyl pent-4-ol. In the product ‘*’ carbon represents chiral carbon and this product is a pair of enantiomers.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Two enantiomers have the same physical properties, unlike cis-trans isomers. These enantiomers have the same melting point and solubility. Due to the mirror images of enantiomers has the same intermolecular attraction with the same physical properties.
Complete Solution:
In a tetrahedral atom attached to four different functional groups, then the two ways are possible with four groups. The two compounds look like mirror images with each other. These images are called non-super imposable mirror images and this pair of stereoisomers is also called enantiomers.
These enantiomers consist of no mirror planes and no two equal, opposite halves. These are another example of stereoisomerism.
- Two enantiomers are equal but rotate oppositely plane-polarized light. (+) enantiomer and (-) enantiomer rotate light in clockwise and counter-clockwise direction respectively.
- When any compound with a chiral center participates in nucleophilic substitution reactions, then the product is formed as a pair of enantiomers.
Let us find out given four reactions, which product will form a pair of enantiomers as a product of the concern reaction!
(A) This reaction is a type of \[{S_N}1\] nucleophilic substitution reaction because this reaction undergoes in DMSO which is a polar aprotic solvent, and the substation of $C{{N}^{-}}$ with ${{I}^{-}}$ enantiomer pairs will not form in product with an inverted proton.

(B) In this reaction, weak nucleophiles $O{{H}^{-}}$ from ${{H}_{2}}O$ replaces ${{I}^{-}}$. The intermediate carbocation is a square planar structure that would possibly react under \[{S_N}1\] or \[{S_N}1\]. So, the chiral carbon cation will form an enantiomer pair in the product.

(C) This reaction undergoes with DMF-protic solvent with nucleophile $O{{H}^{-}}$ undergo $S{{N}^{2}}$, there are no enantiomer pairs that will form in the product.

(D) In this reaction, the carbon cations form is not a chiral center (marked as ** ), so there is no chance of formation of enantiomeric pairs.

Hence, the product of the reaction (B) is 2-methyl pent-4-ol. In the product ‘*’ carbon represents chiral carbon and this product is a pair of enantiomers.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Two enantiomers have the same physical properties, unlike cis-trans isomers. These enantiomers have the same melting point and solubility. Due to the mirror images of enantiomers has the same intermolecular attraction with the same physical properties.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




