
Which one yields ATP required for Muscle contraction?
(a)Myoglobin
(b)Creatine Phosphate
(c)Creatine Phosphate
(d)Myosin
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: These function as a crucial reservoir of high-energy phosphates, like ATPs, in skeletal muscle, brain, retina, inner ear, spermatozoa, and, to a lesser degree, smooth muscle, which are tissues which will consume ATP rapidly.
Complete answer:
-Muscles require energy for contractions.
-The energy for the contractions is derived from ATP molecules present in muscles.
-Muscles are seen to contain only a limited amount of ATP, as when the ATP molecules get used up, there is a need for resynthesizing of ATP.
-Creatine phosphate present within all the muscle cells is a high-energy compound that cleaves them for making more ATP quickly.
-In the case of resting muscle, creatine combines with ATP to form creatine phosphate and ADP.
-During contraction, the creatine phosphate cleaves into creatine and releases phosphorus which will combine with ADP to form ATP. The ATP formed is used up as energy by the muscles for contraction.
Additional Information:
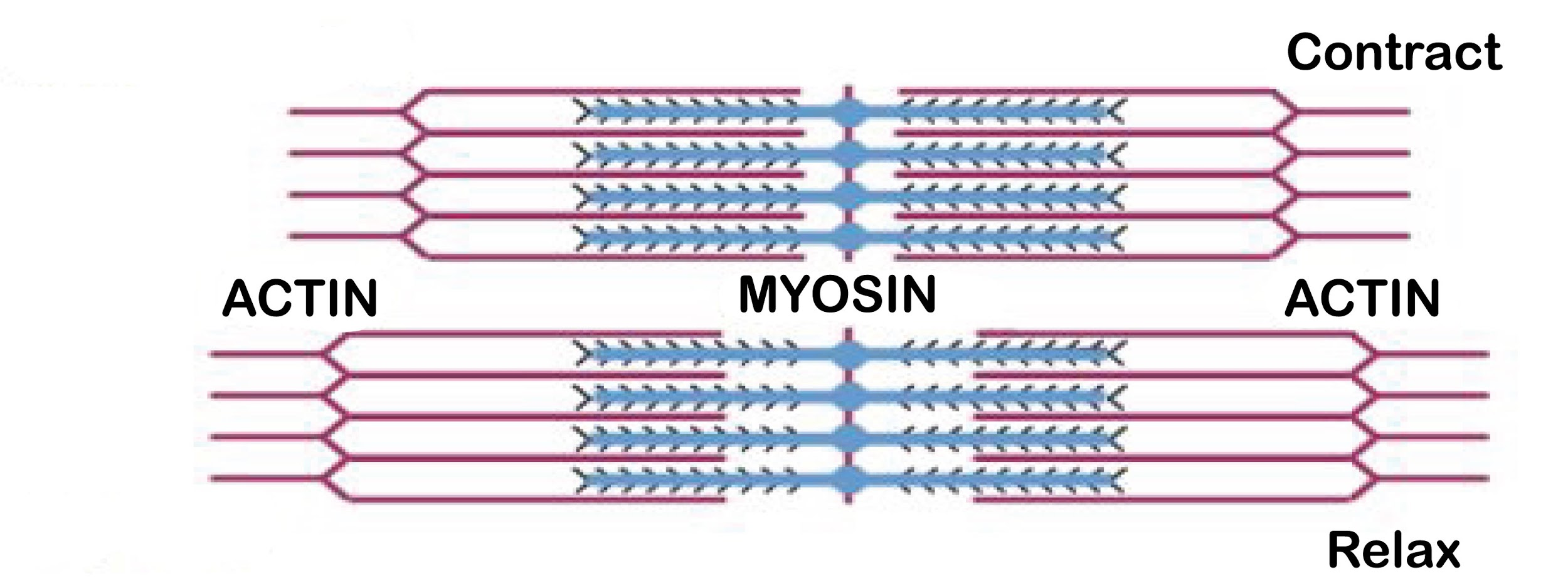
The events happening during the contraction of striated muscle fibrils are as follows:
-The theory proposed related to the working of striated muscle fibers was given by H.E and A.F Huxley, it is known as sliding filament theory.
-During the contraction of a skeletal muscle fiber, the A band or anisotropic band remains intact.
-I band shows a shortening in length and then disappears.
-H zone also disappears because the action filaments from both ends of the sarcomere almost overlap with each other at the M line.
-The Z lines and myosin filaments lie in close proximity.
-Overall shortening of sarcomeres takes place.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Creatine Phosphate.’
Note: It should be remembered that all the processes occur in reverse during the relaxation of the muscle fibril. The observations made by Huxley led to the proposition that shortening of fibrils during contraction is because of the sliding movement of actin filaments over the myosin filaments directed towards the M line, which was by rapid formation and deformation of cross-bridges between the actin and myosin filaments. Sarcomere was designated as the ultimate unit of muscle contraction. The cross-bridges are also known as ratchets.
Complete answer:
-Muscles require energy for contractions.
-The energy for the contractions is derived from ATP molecules present in muscles.
-Muscles are seen to contain only a limited amount of ATP, as when the ATP molecules get used up, there is a need for resynthesizing of ATP.
-Creatine phosphate present within all the muscle cells is a high-energy compound that cleaves them for making more ATP quickly.
-In the case of resting muscle, creatine combines with ATP to form creatine phosphate and ADP.
-During contraction, the creatine phosphate cleaves into creatine and releases phosphorus which will combine with ADP to form ATP. The ATP formed is used up as energy by the muscles for contraction.
Additional Information:
The events happening during the contraction of striated muscle fibrils are as follows:
-The theory proposed related to the working of striated muscle fibers was given by H.E and A.F Huxley, it is known as sliding filament theory.
-During the contraction of a skeletal muscle fiber, the A band or anisotropic band remains intact.
-I band shows a shortening in length and then disappears.
-H zone also disappears because the action filaments from both ends of the sarcomere almost overlap with each other at the M line.
-The Z lines and myosin filaments lie in close proximity.
-Overall shortening of sarcomeres takes place.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Creatine Phosphate.’
Note: It should be remembered that all the processes occur in reverse during the relaxation of the muscle fibril. The observations made by Huxley led to the proposition that shortening of fibrils during contraction is because of the sliding movement of actin filaments over the myosin filaments directed towards the M line, which was by rapid formation and deformation of cross-bridges between the actin and myosin filaments. Sarcomere was designated as the ultimate unit of muscle contraction. The cross-bridges are also known as ratchets.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




