
Which one of the following triplet codons is known as the initiation codon?
(a)UUU
(b)UAA
(c)AUG
(d)UGA
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: The first triplet codons on a strand of mRNA code at the start site of translation. Every triplet code translates into an amino acid and the first amino acid is always methionine.
Complete answer:
The initiation codon or the start codon is the first nucleotide triplet on mRNA that is translated by a ribosome to form an amino acid.
- The most common initiation codon is AUG, which codes for methionine in eukaryotes and archaea and fMet in bacteria, mitochondria, and plastids.
Additional Information: The corresponding DNA sequence for AUG is ATG.
- In prokaryotes, there are two more start codons - GUG and UUG.
- In human mitochondria, the alternate start codons are AUA and AUU.
- UUU codes for the amino acid Phenylalanine.
- UAA is one of the three ‘stop’ or ‘termination’ codons, which signals the termination of the translation process.
- UGA is another one of the three stop codons.
- fMet is a derivative of methionine and is N-formylmethionine.
- Candida albicans, a yeast, uses the start codon CAG.
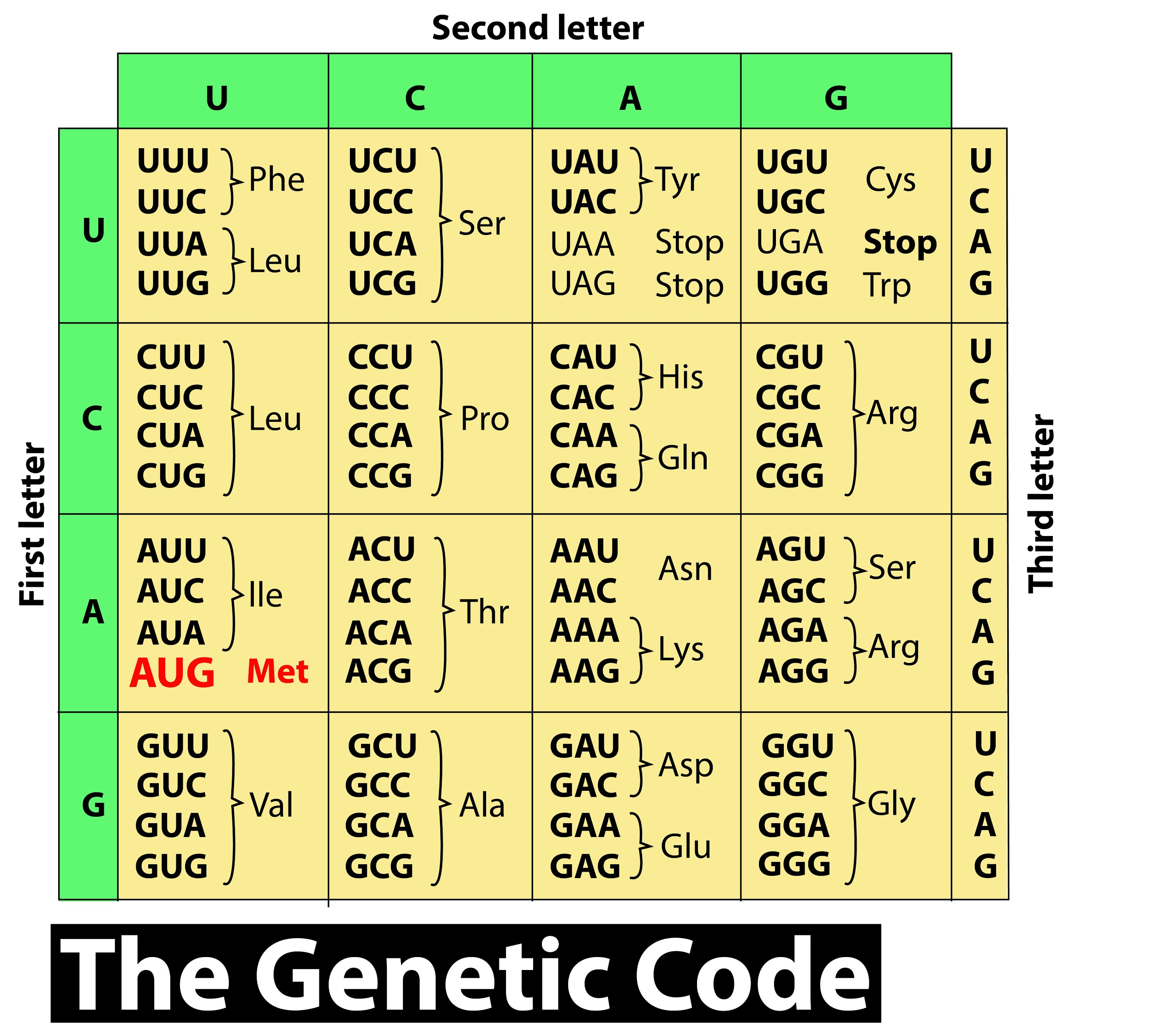
So, the correct answer is ‘AUG’.
Note: The initiation codon is often preceded by a 5’ Untranslated Region (UTR). In the case of prokaryotes, this forms the ribosome-binding site.
- The three stop codons are UAA (ochre), UGA (opal), UAG (amber).
- In prokaryotes, the initiation of translation occurs in the cytoplasm. Here, the small and large subunits of the ribosome bind to the mRNA. In eukaryotes, it occurs in the cytosol or across the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum.
Complete answer:
The initiation codon or the start codon is the first nucleotide triplet on mRNA that is translated by a ribosome to form an amino acid.
- The most common initiation codon is AUG, which codes for methionine in eukaryotes and archaea and fMet in bacteria, mitochondria, and plastids.
Additional Information: The corresponding DNA sequence for AUG is ATG.
- In prokaryotes, there are two more start codons - GUG and UUG.
- In human mitochondria, the alternate start codons are AUA and AUU.
- UUU codes for the amino acid Phenylalanine.
- UAA is one of the three ‘stop’ or ‘termination’ codons, which signals the termination of the translation process.
- UGA is another one of the three stop codons.
- fMet is a derivative of methionine and is N-formylmethionine.
- Candida albicans, a yeast, uses the start codon CAG.

So, the correct answer is ‘AUG’.
Note: The initiation codon is often preceded by a 5’ Untranslated Region (UTR). In the case of prokaryotes, this forms the ribosome-binding site.
- The three stop codons are UAA (ochre), UGA (opal), UAG (amber).
- In prokaryotes, the initiation of translation occurs in the cytoplasm. Here, the small and large subunits of the ribosome bind to the mRNA. In eukaryotes, it occurs in the cytosol or across the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




