
Which one of the following reductions with lithium aluminium hydride yield a secondary amine?
A.Nitroethane
B.Methyl isocyanide
C.Acetamide
D.Methyl cyanide
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Alkyl isocyanide on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride forms a secondary amine containing methyl as one of the alkyl groups. It involves a catalytic reduction. Methyl isocyanide, also known as iso cyanomethane is an organic compound and a member of the isocyanide family and it is a colourless liquid.
Complete answer:
On catalytic reduction or with lithium aluminium hydride (\[LiAl{H_4}\]) or with the nascent hydrogen, alkyl isocyanide yields 2-degree amine whereas cyanide gives 1-degree amine on reduction.
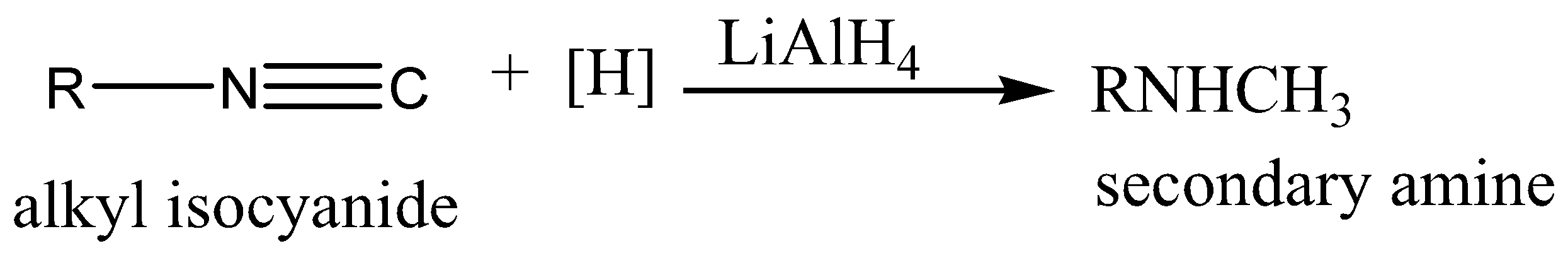
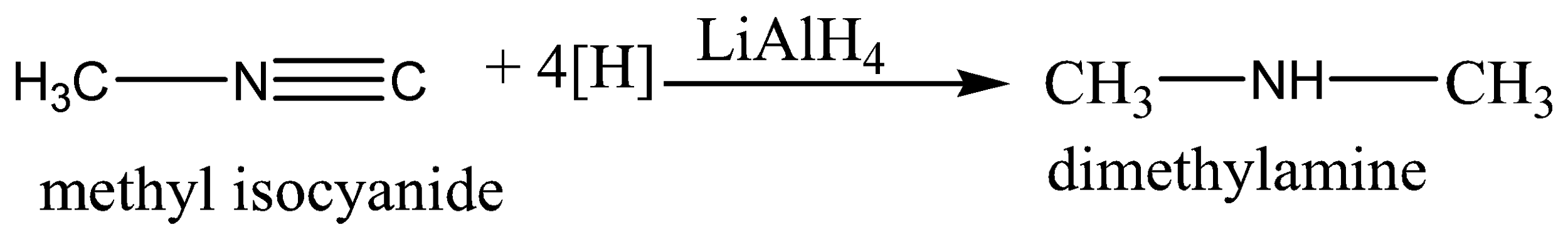
Two hydrogen molecules are added across \[N \equiv C\;\] triple bonds.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Methyl isocyanide which is also known as iso cyanomethane, it is an organic compound and a member of the isocyanide family. It is a colourless liquid which is isomeric to methyl cyanide (acetonitrile), but its reactivity is very different. Its molar mass is 41.053 g/mole. Its Melting point is − \[{45^0}C\]($ - {49^0}F$; 228 K) The application of Methyl isocyanide is mainly for making 5-membered heterocyclic rings. The C-N distance in methyl isocyanide is very short, \[1.158\mathop A\limits^0 \] as is characteristic of isocyanides. Methyl isocyanide was first prepared by A. Gautier by the reaction of silver cyanide with methyl iodide. The common method for preparing methyl isocyanides is by dehydrating N-methyl formamide. Many metal cyanides react with methylating agents to form complexes of methyl isocyanide. This type of reactivity has been invoked as being relevant to the origin of life.
Methyl isocyanide is very useful for the preparation of diverse heterocycles. It is often used to prepare transition metal isocyanide complexes.
Complete answer:
On catalytic reduction or with lithium aluminium hydride (\[LiAl{H_4}\]) or with the nascent hydrogen, alkyl isocyanide yields 2-degree amine whereas cyanide gives 1-degree amine on reduction.
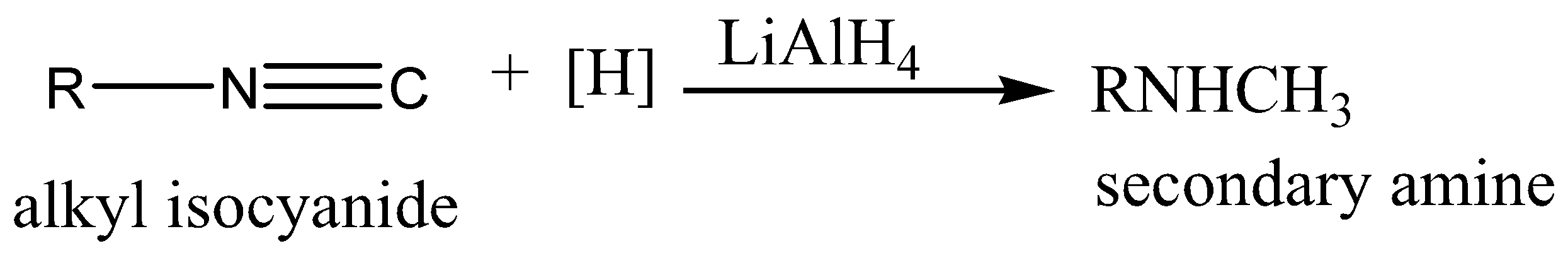
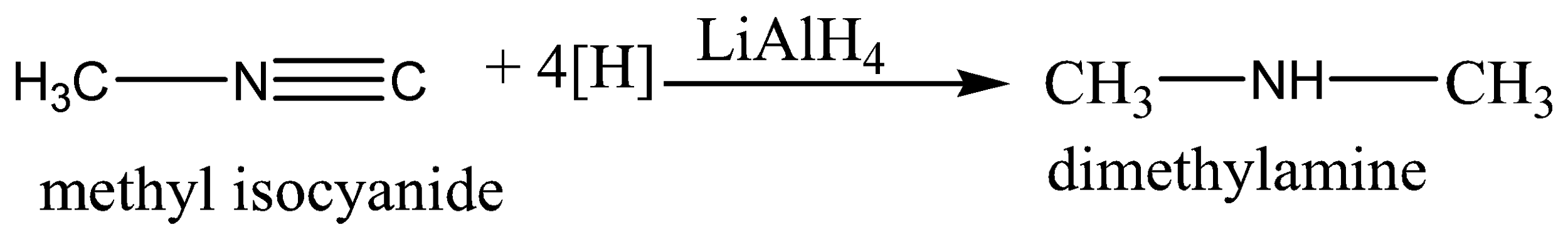
Two hydrogen molecules are added across \[N \equiv C\;\] triple bonds.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Methyl isocyanide which is also known as iso cyanomethane, it is an organic compound and a member of the isocyanide family. It is a colourless liquid which is isomeric to methyl cyanide (acetonitrile), but its reactivity is very different. Its molar mass is 41.053 g/mole. Its Melting point is − \[{45^0}C\]($ - {49^0}F$; 228 K) The application of Methyl isocyanide is mainly for making 5-membered heterocyclic rings. The C-N distance in methyl isocyanide is very short, \[1.158\mathop A\limits^0 \] as is characteristic of isocyanides. Methyl isocyanide was first prepared by A. Gautier by the reaction of silver cyanide with methyl iodide. The common method for preparing methyl isocyanides is by dehydrating N-methyl formamide. Many metal cyanides react with methylating agents to form complexes of methyl isocyanide. This type of reactivity has been invoked as being relevant to the origin of life.
Methyl isocyanide is very useful for the preparation of diverse heterocycles. It is often used to prepare transition metal isocyanide complexes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




