
Which one of the following reactions proceeds through a free radical chain mechanism?
A. Addition of HBr on Ethene.
B. Halogenation of Benzene in the presence of $FeB{{r}_{3}}$
C. Photochemical chlorination of methane
D. Hydrolysis of tert-butyl chloride with aqueous KOH
E. Addition of $NaHS{{O}_{3}}$ on acetone.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Molecular chlorine and bromine both undergo homolytic cleavage to form radicals when subjected to heat or light. Other functional groups which also tend to form radicals when exposed to heat or light are chlorofluorocarbons, peroxides, and the halogenated amide N-bromosuccinimide (NBS).
Complete answer:
Let us first understand what we mean by a free radical chain mechanism before moving onto answering the given question.
Due to their high reactivity and incredibly short half-lives, free radicals are both powerful chemical tools and harmful contaminants. Free radicals are powerful tools due to the fact that they occur in a chain reaction. One free radical will keep creating other free radicals till termination. The reactions involving the bonding of free radicals and the formation of new free radicals have three distinct phases: initiation, propagation, and termination.
The initiation phase involves the formation of these free radicals. Free radicals are formed due to homolytic cleavage of bonds. Homolytic cleavage is seen when the two electrons that are involved in the making of the bond between two atoms attach themselves to two different atoms while cleavage. They have no spin partner and do not exist as a part of a lone pair. Homolytic cleavage is rare due to the high energy it requires for dissociation. The presence of heat, UV radiation, or a metal-containing catalyst is essential for overcoming this barrier.
The propagation phase is representative of the ‘chain’ part of chain reactions. When the free radical is generated, it reacts with stable molecules to form newer free radicals. These new free radicals then go on to generate more radicals. This process goes on till the chain terminates. Propagation steps also often involve the removal of hydrogen or addition of the radical to double bonds.
Termination of the chain reaction occurs when two free radical species react with each other to form a stable, non-radical product which terminates the process. Although this event releases a lot of energy and is thermodynamically stable, it is also rare because of the low abundance of radical species and the small probability of two radicals colliding with one another.
The chlorination of methane is the simplest example of a free radical chain reaction.
To begin the initiation phase, a chlorine molecule undergoes homolytic cleavage after absorbing energy from light:
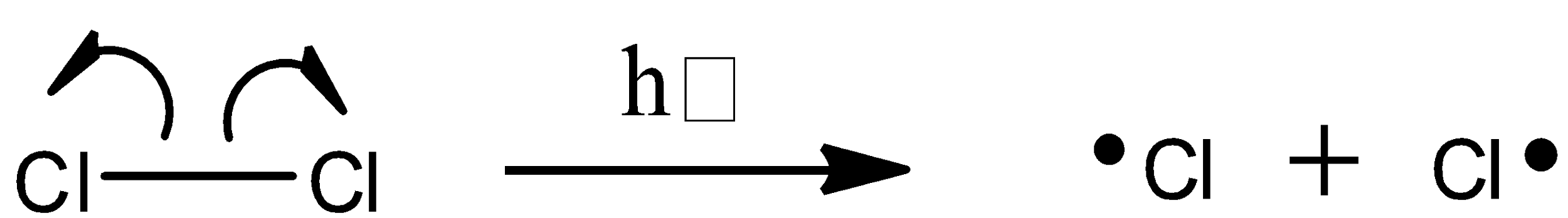
The chlorine radical then abstracts a hydrogen, leading to an alkyl radical (step 2), which reacts with a second chlorine molecule (step 3) to form the chloroalkane product plus chlorine radical, which then returns to repeat step 2.
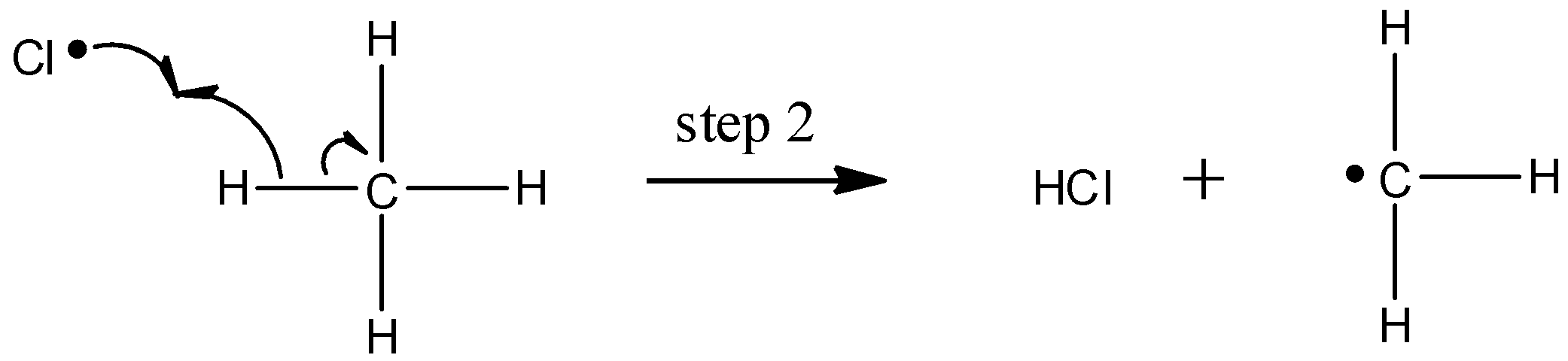
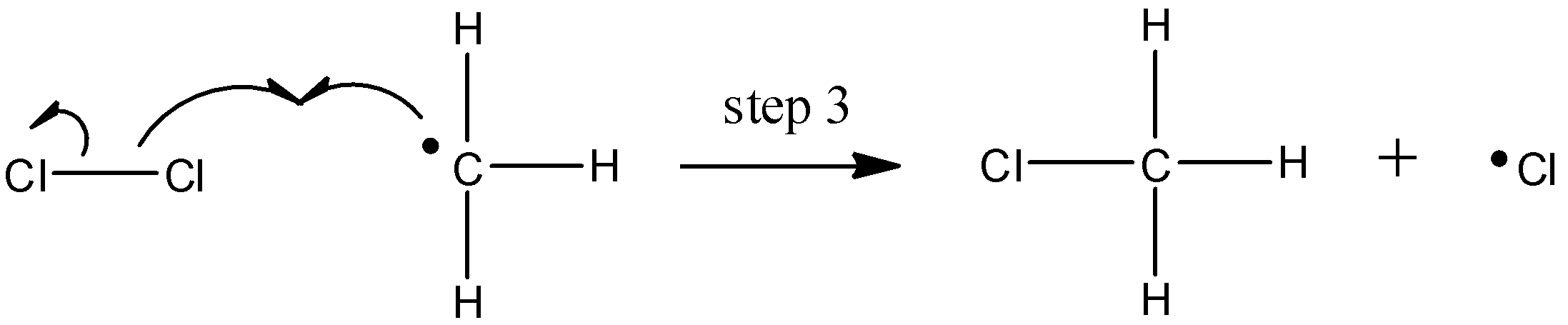
Likely chain termination steps result in the condensation of two alkyl radical intermediates or that of an alkane radical with a chlorine radical.
Therefore, we can conclude that the answer to this question is ‘C. Photochemical chlorination of methane’
Note: Alkanes can be brominated by a similar reaction. Bromination is more regioselective. The formation of free radicals of iodine cannot occur by the photochemical method since the reaction is thermodynamically unfavourable.
Complete answer:
Let us first understand what we mean by a free radical chain mechanism before moving onto answering the given question.
Due to their high reactivity and incredibly short half-lives, free radicals are both powerful chemical tools and harmful contaminants. Free radicals are powerful tools due to the fact that they occur in a chain reaction. One free radical will keep creating other free radicals till termination. The reactions involving the bonding of free radicals and the formation of new free radicals have three distinct phases: initiation, propagation, and termination.
The initiation phase involves the formation of these free radicals. Free radicals are formed due to homolytic cleavage of bonds. Homolytic cleavage is seen when the two electrons that are involved in the making of the bond between two atoms attach themselves to two different atoms while cleavage. They have no spin partner and do not exist as a part of a lone pair. Homolytic cleavage is rare due to the high energy it requires for dissociation. The presence of heat, UV radiation, or a metal-containing catalyst is essential for overcoming this barrier.
The propagation phase is representative of the ‘chain’ part of chain reactions. When the free radical is generated, it reacts with stable molecules to form newer free radicals. These new free radicals then go on to generate more radicals. This process goes on till the chain terminates. Propagation steps also often involve the removal of hydrogen or addition of the radical to double bonds.
Termination of the chain reaction occurs when two free radical species react with each other to form a stable, non-radical product which terminates the process. Although this event releases a lot of energy and is thermodynamically stable, it is also rare because of the low abundance of radical species and the small probability of two radicals colliding with one another.
The chlorination of methane is the simplest example of a free radical chain reaction.
To begin the initiation phase, a chlorine molecule undergoes homolytic cleavage after absorbing energy from light:

The chlorine radical then abstracts a hydrogen, leading to an alkyl radical (step 2), which reacts with a second chlorine molecule (step 3) to form the chloroalkane product plus chlorine radical, which then returns to repeat step 2.


Likely chain termination steps result in the condensation of two alkyl radical intermediates or that of an alkane radical with a chlorine radical.
Therefore, we can conclude that the answer to this question is ‘C. Photochemical chlorination of methane’
Note: Alkanes can be brominated by a similar reaction. Bromination is more regioselective. The formation of free radicals of iodine cannot occur by the photochemical method since the reaction is thermodynamically unfavourable.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




