
Which one of the following is the intermediate in the precipitation of a ketone by hydration of an alkyne in the presence of sulphuric acid and mercury (II) sulphate?
(a)
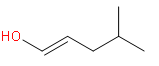
(b)
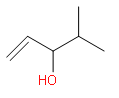
(c)
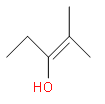
(d)
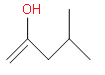




Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem, you need a thorough understanding of different organic reaction mechanisms. Initially, there is an alkyne. Hydration of alkyne means the introduction of hydrogen to this unsaturated triple bond.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the hydration of alkyne is the introduction of hydrogen to the unsaturation. Here, the reaction is carried out in the presence of sulphuric acid and mercury sulphate. Initially, one of the bonds in the triple bond will be heterolytically cleaved to form a positive and negative carbon centre. We know that the sulphuric acid will give ${{H}^{+}}$ and this will attack on the negative carbon. Then the $O{{H}^{-}}$ from the water molecules will attack on the carbocation. This is the enol form and it will convert to the keto form through tautomerism. So, this enol form is the intermediate in this reaction. The reaction is as follows:
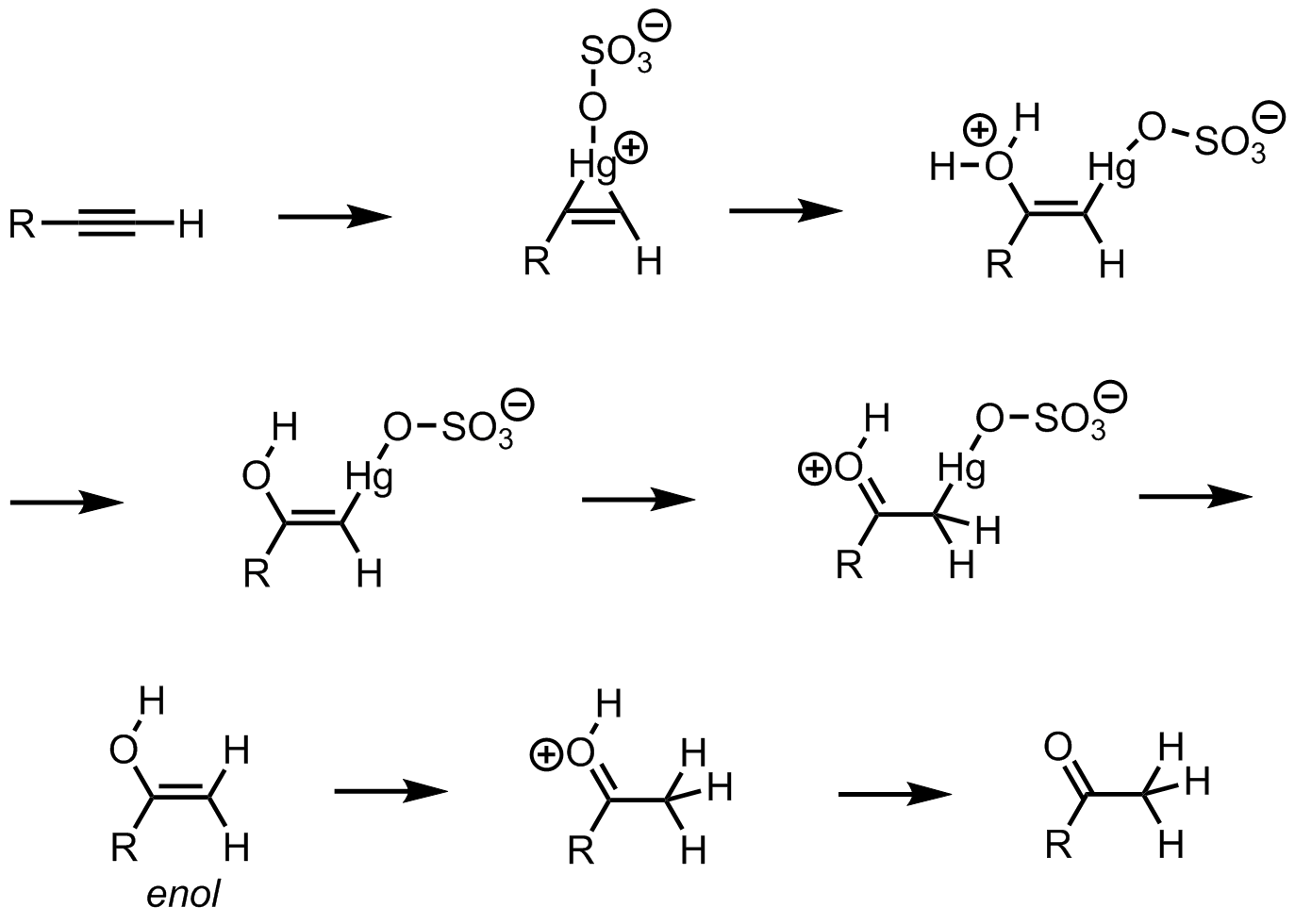
Since the enol form is the intermediate here So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: You may have doubt about the role of mercury sulphate. Alkynes have a very low rate of electrophilic addition reaction than the alkenes. The mercury sulphate is the metal catalyst which will enhance the rate of electrophilic addition as a promoter.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the hydration of alkyne is the introduction of hydrogen to the unsaturation. Here, the reaction is carried out in the presence of sulphuric acid and mercury sulphate. Initially, one of the bonds in the triple bond will be heterolytically cleaved to form a positive and negative carbon centre. We know that the sulphuric acid will give ${{H}^{+}}$ and this will attack on the negative carbon. Then the $O{{H}^{-}}$ from the water molecules will attack on the carbocation. This is the enol form and it will convert to the keto form through tautomerism. So, this enol form is the intermediate in this reaction. The reaction is as follows:

Since the enol form is the intermediate here So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: You may have doubt about the role of mercury sulphate. Alkynes have a very low rate of electrophilic addition reaction than the alkenes. The mercury sulphate is the metal catalyst which will enhance the rate of electrophilic addition as a promoter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




