
Which one of the following is laevorotatory?
A.glucose
B.fructose
C.sucrose
D.all the above
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Those which rotate the plane polarised light toward counter clockwise direction is known as laevorotatory which is denoted by l or -. Fructose is laevorotatory. It rotates the plane of polarized light in an anticlockwise direction.
Complete answer:
Some chiral compounds which don't have plane of symmetry have some property to rotate plane polarised light in either clockwise or counter clockwise direction.
Those compounds which rotate plane polarised light toward clockwise direction are known as dextrorotatory which is denoted by d or + and those which rotate the plane polarised light toward counter clockwise direction is known as laevorotatory which is denoted by l or -.
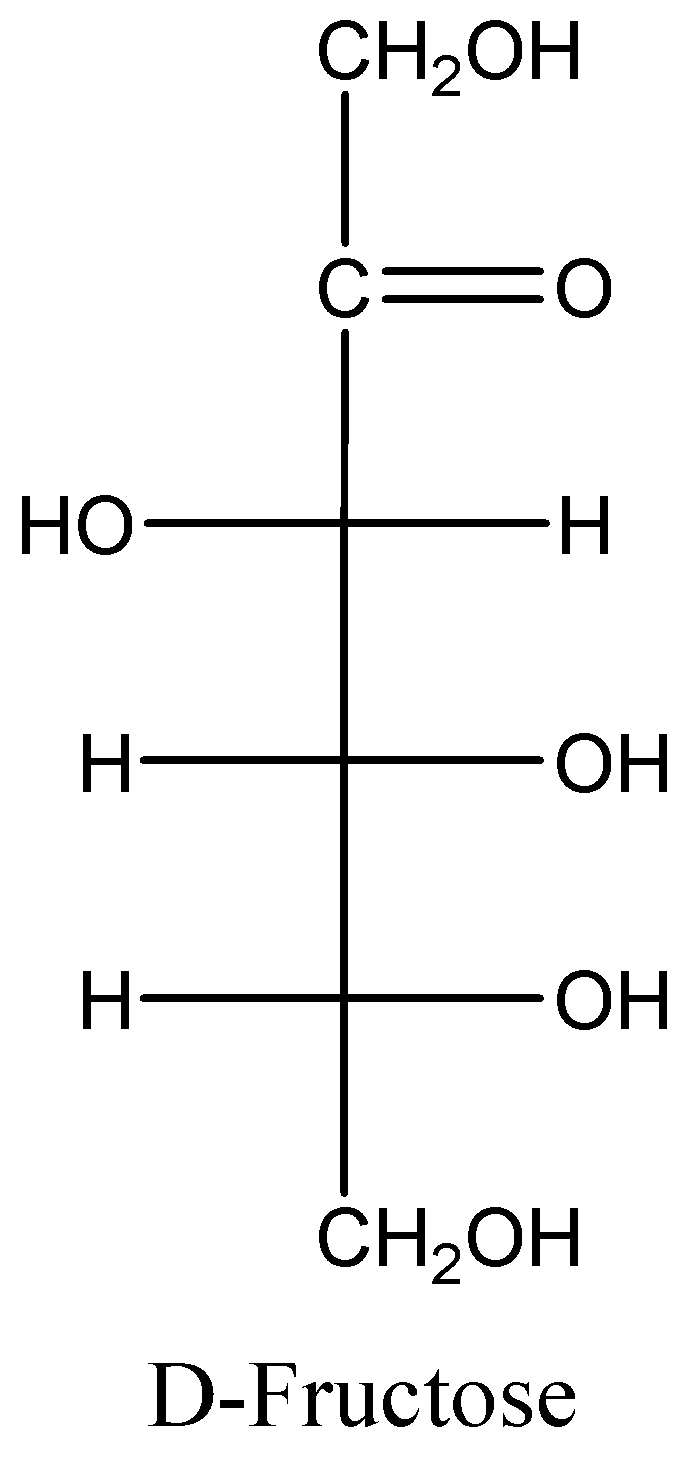
Fructose has three chiral centres, that is why it is optically active. Its specific rotation is -92.4. The negative sign shows that light rotates toward counter clockwise direction.
When the fructose solution is placed in a polariser it rotates the plane polarized light in an anti-clockwise direction which is towards the left side. So, it is a laevorotatory nature compound. Honey contains monosaccharides sugar fructose.
This specific rotation is an experimental phenomenon; we can’t predict specific rotation after seeing the structure.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: Fructose (fruit sugar) is a ketohexose which is a six-carbon ketonic sugar, and it occurs in sweet fruits and honey. Glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula, i.e. ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$, but they have different structures. Pure, dry fructose is very sweet in taste, white in colour, odourless and crystalline solid. Fructose is one of the sweetest of all sugars and is combined with glucose to make sucrose, or common table sugar. Fructose’s name is also levulose because of its levorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the left.
Complete answer:
Some chiral compounds which don't have plane of symmetry have some property to rotate plane polarised light in either clockwise or counter clockwise direction.
Those compounds which rotate plane polarised light toward clockwise direction are known as dextrorotatory which is denoted by d or + and those which rotate the plane polarised light toward counter clockwise direction is known as laevorotatory which is denoted by l or -.
Fructose has three chiral centres, that is why it is optically active. Its specific rotation is -92.4. The negative sign shows that light rotates toward counter clockwise direction.
When the fructose solution is placed in a polariser it rotates the plane polarized light in an anti-clockwise direction which is towards the left side. So, it is a laevorotatory nature compound. Honey contains monosaccharides sugar fructose.
This specific rotation is an experimental phenomenon; we can’t predict specific rotation after seeing the structure.

So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: Fructose (fruit sugar) is a ketohexose which is a six-carbon ketonic sugar, and it occurs in sweet fruits and honey. Glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula, i.e. ${C_6}{H_{12}}{O_6}$, but they have different structures. Pure, dry fructose is very sweet in taste, white in colour, odourless and crystalline solid. Fructose is one of the sweetest of all sugars and is combined with glucose to make sucrose, or common table sugar. Fructose’s name is also levulose because of its levorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the left.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




