
Which one of the following complexes is an outer orbital complex?
A. ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{6-}}$
B. ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]}^{4-}}$
C. ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$
D. ${{[Ni{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{2+}}$
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: If a ligand is a strong ligand then the ligand forms an inner orbital complex with metals and if the ligand is weak then the ligand forms an outer orbital complex with metals. The hybridization of the inorganic complexes is going to depend on the type of ligand.
Complete step by step answer:
- To know about the structure of the complexes we should know about the hybridization involved in the metal complexes.
- Coming to given options, option A ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{6-}}$ .
- The oxidation state of iron in ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{6-}}$ is
x + 4(-1) = - 6
x = -2, here x= oxidation state of iron.
- The oxidation state of iron in ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{6-}}$ is -2.
- The electronic configuration of iron is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}3{{d}^{6}}$
- The hybridization of iron in ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{6-}}$ is ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ .
- Cyanide is a strong ligand then it forms an inner orbital complex with iron metal. So, option A is wrong.
- Coming to option B, ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]}^{4-}}$ .
- The oxidation state of iron in ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]}^{4-}}$ is
x + 6(-1) = - 4
x = 2, here x= oxidation state of iron.
- The electronic configuration of iron is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}3{{d}^{6}}$
- The hybridization of iron in ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]}^{4-}}$ is ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ .
- Cyanide is a strong ligand then it forms an inner orbital complex with iron metal. So, option B is wrong.
- Coming to option C, ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$ .
- The oxidation state of cobalt in ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$ is
x + 6(0) = 3
x = 3, here x= oxidation state of cobalt.
- The electronic configuration of Cobalt (3+) is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{0}}4{{p}^{0}}3{{d}^{6}}$
- Ammonia is a strong ligand and it forms an inner orbital complex with ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization.
- So, option C is wrong.
- Coming to option D, ${{[Ni{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{2+}}$ .
- The oxidation state of nickel in ${{[Ni{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{2+}}$ is
x + 6(0) = 2
x = 2, here x= oxidation state of nickel.
- The electronic configuration of nickel (2+) is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{8}}4{{s}^{0}}4{{p}^{0}}4{{d}^{0}}$ .
- Ammonia is a strong ligand but due to the lack of 3d orbitals of nickel participation in the hybridization, ammonia forms an outer orbital complex with nickel.
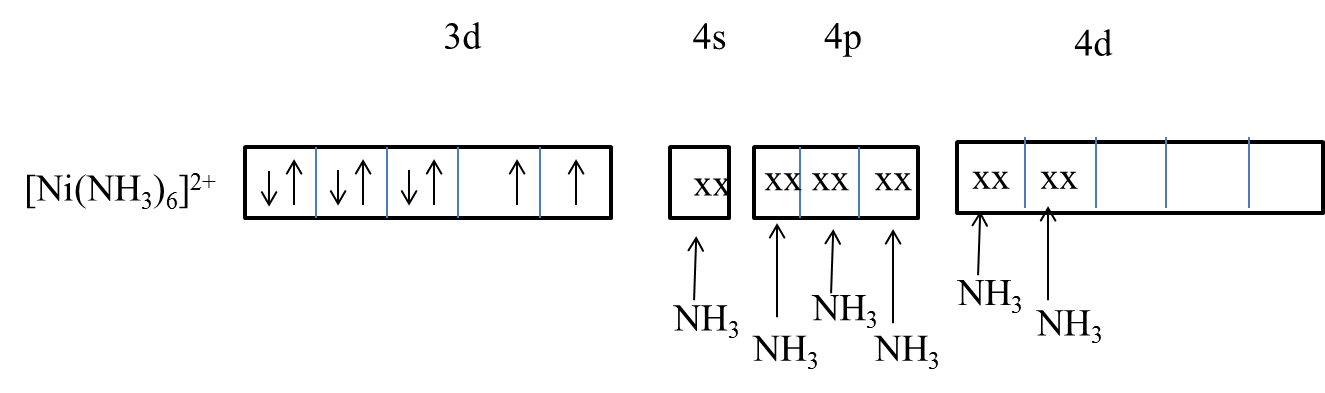
- Ammonia forms an outer orbital complex with $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization with nickel.
- So, the correct option is D.
Note: An inorganic metal complex in which the central metal atom utilizes outer d orbitals for hybridization then the complex is called outer orbital complex. An inorganic metal complex in which the central metal atom utilizes inner d orbitals for hybridization then the complex is called inner orbital complex.
Complete step by step answer:
- To know about the structure of the complexes we should know about the hybridization involved in the metal complexes.
- Coming to given options, option A ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{6-}}$ .
- The oxidation state of iron in ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{6-}}$ is
x + 4(-1) = - 6
x = -2, here x= oxidation state of iron.
- The oxidation state of iron in ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{6-}}$ is -2.
- The electronic configuration of iron is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}3{{d}^{6}}$
- The hybridization of iron in ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{4}}]}^{6-}}$ is ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ .
- Cyanide is a strong ligand then it forms an inner orbital complex with iron metal. So, option A is wrong.
- Coming to option B, ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]}^{4-}}$ .
- The oxidation state of iron in ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]}^{4-}}$ is
x + 6(-1) = - 4
x = 2, here x= oxidation state of iron.
- The electronic configuration of iron is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{2}}3{{d}^{6}}$
- The hybridization of iron in ${{[Fe{{(CN)}_{6}}]}^{4-}}$ is ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ .
- Cyanide is a strong ligand then it forms an inner orbital complex with iron metal. So, option B is wrong.
- Coming to option C, ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$ .
- The oxidation state of cobalt in ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$ is
x + 6(0) = 3
x = 3, here x= oxidation state of cobalt.
- The electronic configuration of Cobalt (3+) is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}4{{s}^{0}}4{{p}^{0}}3{{d}^{6}}$
- Ammonia is a strong ligand and it forms an inner orbital complex with ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridization.
- So, option C is wrong.
- Coming to option D, ${{[Ni{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{2+}}$ .
- The oxidation state of nickel in ${{[Ni{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{2+}}$ is
x + 6(0) = 2
x = 2, here x= oxidation state of nickel.
- The electronic configuration of nickel (2+) is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{8}}4{{s}^{0}}4{{p}^{0}}4{{d}^{0}}$ .
- Ammonia is a strong ligand but due to the lack of 3d orbitals of nickel participation in the hybridization, ammonia forms an outer orbital complex with nickel.

- Ammonia forms an outer orbital complex with $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization with nickel.
- So, the correct option is D.
Note: An inorganic metal complex in which the central metal atom utilizes outer d orbitals for hybridization then the complex is called outer orbital complex. An inorganic metal complex in which the central metal atom utilizes inner d orbitals for hybridization then the complex is called inner orbital complex.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




