
Which of these is not an aldose sugar?
(a)Glucose
(b)Maltose
(c)Fructose
(d)Ribose
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: This sugar is a monosaccharide and the simplest form of carbohydrate. It has a ketone group in its structure. It is the sweetest sugar and also one of the components of sucrose. It is also called fruit sugar.
Complete answer:
-Fructose is a 6-carbon ketose sugar.
-Fructose has a slower rate of uptake than glucose in the body.
-Fructose does not stimulate a substantial insulin release.
-Fructose is transported via a different transporter into the cells.
-Fructose provides glycerol which is the backbone of fat and increases fat formation.
-The major biological function of fructose is it acts as an alternative metabolite in providing energy especially when glucose is not enough while the metabolic energy demand is quite high.
Additional Information: -Fructose can enter glycolysis and produce intermediates for cellular respiration.
-Fructose also serves as soluble storage carbohydrates in ∼12–15% of all flowering plants including cereals (e.g., wheat, barley, oat), forage grasses, vegetables, and ornamental plants.
-In cereals, fructose can be found in young internodes
-Besides being an energy reserve in plants, fructose has a role in the regulation of osmotic pressure, sink strength, and resistance to cold and drought.
-The sweet taste of fructose is useful as low-calorie sweeteners and they have also been used as fat-replacers in foods.
So, the correct answer is ‘Fructose’.
Note: -Fructose with a low degree of polymerization is promoted as a soluble dietary fiber.
- It is used in the human diet as it is poorly digested in the small intestine, but meanwhile stimulates the growth of beneficial microbes in the large intestine.
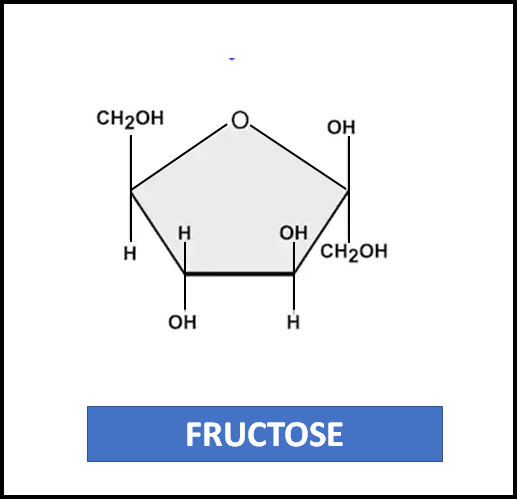
Complete answer:
-Fructose is a 6-carbon ketose sugar.
-Fructose has a slower rate of uptake than glucose in the body.
-Fructose does not stimulate a substantial insulin release.
-Fructose is transported via a different transporter into the cells.
-Fructose provides glycerol which is the backbone of fat and increases fat formation.
-The major biological function of fructose is it acts as an alternative metabolite in providing energy especially when glucose is not enough while the metabolic energy demand is quite high.
Additional Information: -Fructose can enter glycolysis and produce intermediates for cellular respiration.
-Fructose also serves as soluble storage carbohydrates in ∼12–15% of all flowering plants including cereals (e.g., wheat, barley, oat), forage grasses, vegetables, and ornamental plants.
-In cereals, fructose can be found in young internodes
-Besides being an energy reserve in plants, fructose has a role in the regulation of osmotic pressure, sink strength, and resistance to cold and drought.
-The sweet taste of fructose is useful as low-calorie sweeteners and they have also been used as fat-replacers in foods.
So, the correct answer is ‘Fructose’.
Note: -Fructose with a low degree of polymerization is promoted as a soluble dietary fiber.
- It is used in the human diet as it is poorly digested in the small intestine, but meanwhile stimulates the growth of beneficial microbes in the large intestine.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




