
Which of the following will show optical is isomerism 1-bromobutane or 2-bromobutane?
1-Bromobutane –
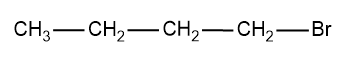
2-Bromobutane-
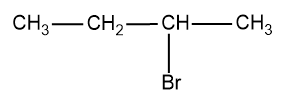

Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint: Optical isomers are the compounds in which the structures have the same formulae and same atoms, molecules or groups but they differ in the spatial arrangement.
Stereogenic centre is one of the main elements required to show optical isomerization.
Complete answer:
- In the branch of organic chemistry, we are always concerned about compounds of carbon and hydrogen i.e. the hydrocarbons. And some atoms like halogens, oxygen etc. replaces the H atom by different reactions and forms a range of compounds. At different reaction conditions C also gets replaced.
- One of the hot topics in organic chemistry is stereochemistry, which tells all about the arrangement of the atoms, molecules or groups of atoms present in a compound in space.
So in the question it is asked which of the given compounds, 1-bromobutane or 2-bromobutane show optical isomerism.
- We know that isomers are those molecules which possess the same molecular formulae and the same atoms, molecules or groups of atoms in two compounds but they differ in their arrangement.
According to the arrangement of the atoms, molecules and groups of atoms there are types of isomers:
Structural isomers-positional, chain and functional isomers.
Stereoisomers-optical and geometrical isomers.
- Here we have to deal with optical isomers, the prerequisite condition of molecules to show optical isomerism is that the molecule should have at least one stereogenic carbon or stereogenic centre in them.
- Stereogenic carbon or achiral carbon is the carbon in which the carbon is attached to four different groups.
- Another condition to optical isomerism is that they should possess non-superimposable mirror images of the same molecules and the non-superimposable mirror images formed are called enantiomers.
Now let’s check whether there is a stereogenic centre in the given molecules.
Now we can take a look at the different groups attached in 1-bromobutane.
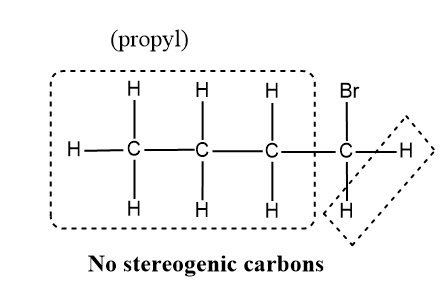
Here if we compare the carbon to which the Br is attached ,it possess only three different groups since the fourth valency is satisfied by the H atom and hence the molecule do not have stereogenic centre and the other carbon also in the compounds ,have the same atoms which satisfies the valency of C.
Hence 1-bromobutane cannot show optical isomerism.
2-bromobutane
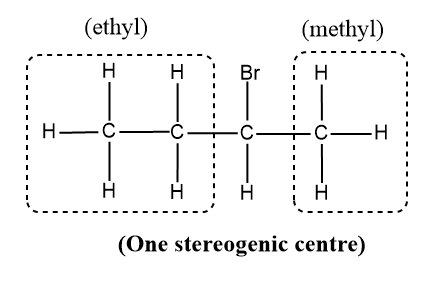
- Here, we compare the C-2 where the halogen, Br is attached and there are four different groups attached to that carbon and the other carbons have the same atoms (H atoms) attached to satisfy the valency of C.
Therefore there is one stereogenic carbon in the molecule and exhibits optical isomerism and they possess non-superimposable mirror image.
Therefore, only 2-bromobutane exhibits optical isomerism.
Note:
- So, as we all know optical isomerism is one of the types of stereoisomers. If in the question geometrical isomerism was asked, which is the other type of optical isomerism and is generally shown by the alkene molecules. The alkenes in which two different substituents are attached to each C which is doubly bonded with another carbon, and the other C also possess two different substituents and the double bond present restricted the rotation of the molecule forming non-superimposable mirror image.
- For determining the geometrical isomerism we have to consider the molecule part by part. Generally we refer geometrical isomerism as cis-trans isomerism or E and Z isomerism.
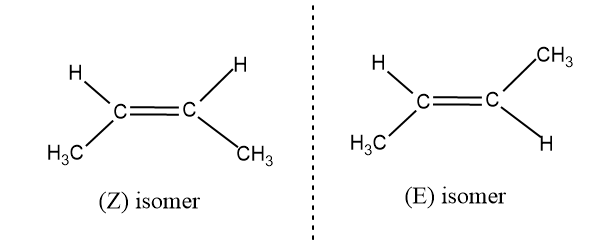
- Isomers which has similar substituent on same side is called as cis or Z isomers and which different substituents attached are called as trans or E isomers.
Stereogenic centre is one of the main elements required to show optical isomerization.
Complete answer:
- In the branch of organic chemistry, we are always concerned about compounds of carbon and hydrogen i.e. the hydrocarbons. And some atoms like halogens, oxygen etc. replaces the H atom by different reactions and forms a range of compounds. At different reaction conditions C also gets replaced.
- One of the hot topics in organic chemistry is stereochemistry, which tells all about the arrangement of the atoms, molecules or groups of atoms present in a compound in space.
So in the question it is asked which of the given compounds, 1-bromobutane or 2-bromobutane show optical isomerism.
- We know that isomers are those molecules which possess the same molecular formulae and the same atoms, molecules or groups of atoms in two compounds but they differ in their arrangement.
According to the arrangement of the atoms, molecules and groups of atoms there are types of isomers:
Structural isomers-positional, chain and functional isomers.
Stereoisomers-optical and geometrical isomers.
- Here we have to deal with optical isomers, the prerequisite condition of molecules to show optical isomerism is that the molecule should have at least one stereogenic carbon or stereogenic centre in them.
- Stereogenic carbon or achiral carbon is the carbon in which the carbon is attached to four different groups.
- Another condition to optical isomerism is that they should possess non-superimposable mirror images of the same molecules and the non-superimposable mirror images formed are called enantiomers.
Now let’s check whether there is a stereogenic centre in the given molecules.
Now we can take a look at the different groups attached in 1-bromobutane.

Here if we compare the carbon to which the Br is attached ,it possess only three different groups since the fourth valency is satisfied by the H atom and hence the molecule do not have stereogenic centre and the other carbon also in the compounds ,have the same atoms which satisfies the valency of C.
Hence 1-bromobutane cannot show optical isomerism.
2-bromobutane

- Here, we compare the C-2 where the halogen, Br is attached and there are four different groups attached to that carbon and the other carbons have the same atoms (H atoms) attached to satisfy the valency of C.
Therefore there is one stereogenic carbon in the molecule and exhibits optical isomerism and they possess non-superimposable mirror image.
Therefore, only 2-bromobutane exhibits optical isomerism.
Note:
- So, as we all know optical isomerism is one of the types of stereoisomers. If in the question geometrical isomerism was asked, which is the other type of optical isomerism and is generally shown by the alkene molecules. The alkenes in which two different substituents are attached to each C which is doubly bonded with another carbon, and the other C also possess two different substituents and the double bond present restricted the rotation of the molecule forming non-superimposable mirror image.
- For determining the geometrical isomerism we have to consider the molecule part by part. Generally we refer geometrical isomerism as cis-trans isomerism or E and Z isomerism.

- Isomers which has similar substituent on same side is called as cis or Z isomers and which different substituents attached are called as trans or E isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




