
Which of the following will have metal deficiency defects?
A.NaCl
B.FeO
C.KCl
D.ZnO
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: Metal deficiency defects are caused due to missing cations. So, one of the nearest metal ions acquires an extra positive charge to maintain electrical neutrality and to do so the metal ion must be able to exhibit variable valency.
Complete step by step answer:
-It is a type of non-stoichiometric defect which comes under point defects. It means that this defect does not affect the stoichiometry of the crystalline compound.
-Metal deficiency defect arises due to a vacant lattice site caused by missing cation. Thus one of the nearest metal ions will acquire an extra positive charge to prevent or maintain the electrical neutrality of the crystalline compound.
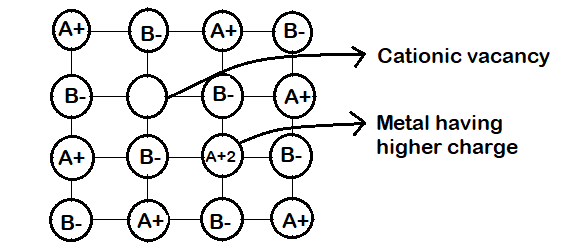
-This type of defect is usually shown by compounds that exhibit variable valance like the transition metal compounds like NiO, FeS, FeO, etc because they have the ability to take extra positive charge.
-Many crystalline solids which are very difficult to be prepared in the stoichiometric composition and thus the amount of metal they contain is less as compared to the stoichiometric proportions.
-An example of such solids is FeO. The composition of FeO may range from $F{e_{0.93}}O$ to $F{e_{0.96}}O$. But usually it is found with a composition of $F{e_{0.95}}O$. In FeO crystals some $F{e^{ + 2}}$ ions are missing, so this loss of positive ions is made up by turning some $F{e^{ + 2}}$ ions into $F{e^{ + 3}}$ ions.
-Since, this defect can only be shown by compounds exhibiting variable valency state. In the given options the only metal exhibiting variable valency state is Fe (iron).
So, the correct option is: B) FeO.
Note:
Metal deficiency means cationic vacancies and not anionic because metals have the ability to lose electrons and gain positive charge to become a cation. They cannot gain electrons to become an anion.
Complete step by step answer:
-It is a type of non-stoichiometric defect which comes under point defects. It means that this defect does not affect the stoichiometry of the crystalline compound.
-Metal deficiency defect arises due to a vacant lattice site caused by missing cation. Thus one of the nearest metal ions will acquire an extra positive charge to prevent or maintain the electrical neutrality of the crystalline compound.

-This type of defect is usually shown by compounds that exhibit variable valance like the transition metal compounds like NiO, FeS, FeO, etc because they have the ability to take extra positive charge.
-Many crystalline solids which are very difficult to be prepared in the stoichiometric composition and thus the amount of metal they contain is less as compared to the stoichiometric proportions.
-An example of such solids is FeO. The composition of FeO may range from $F{e_{0.93}}O$ to $F{e_{0.96}}O$. But usually it is found with a composition of $F{e_{0.95}}O$. In FeO crystals some $F{e^{ + 2}}$ ions are missing, so this loss of positive ions is made up by turning some $F{e^{ + 2}}$ ions into $F{e^{ + 3}}$ ions.
-Since, this defect can only be shown by compounds exhibiting variable valency state. In the given options the only metal exhibiting variable valency state is Fe (iron).
So, the correct option is: B) FeO.
Note:
Metal deficiency means cationic vacancies and not anionic because metals have the ability to lose electrons and gain positive charge to become a cation. They cannot gain electrons to become an anion.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




