
which of the following will best give resorcinol (1,3-dihydroxy benzene)?
A)
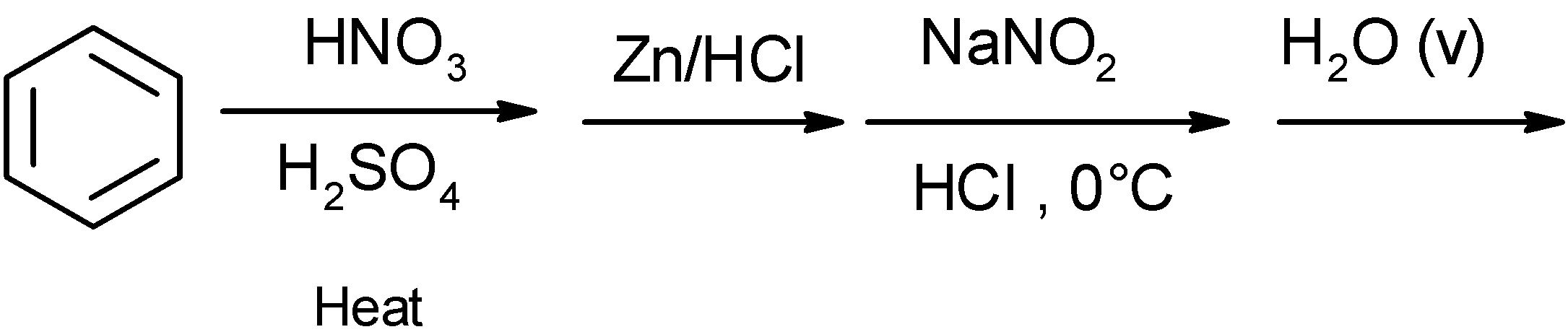
B)
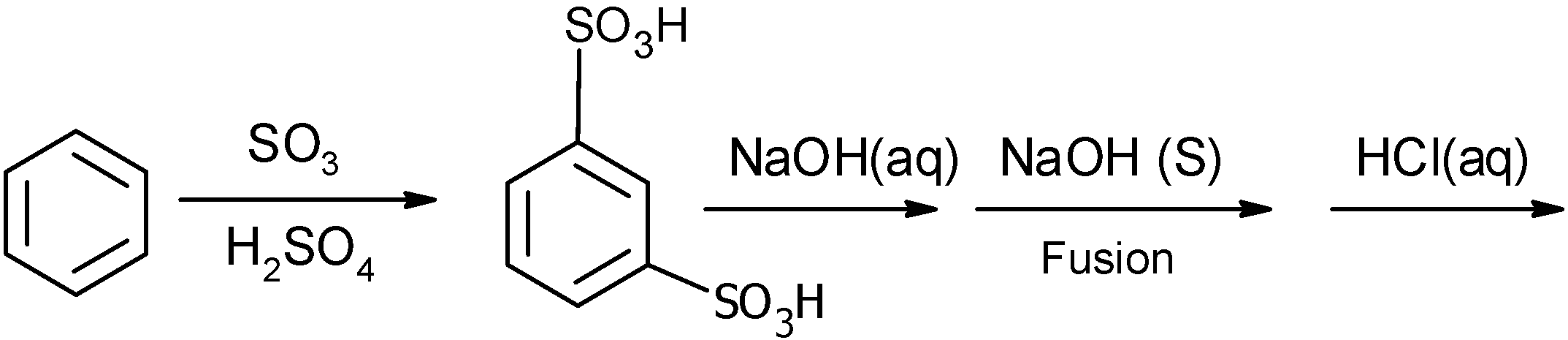
C)
D)
| A) | 
|
| B) | 
|
| C) | 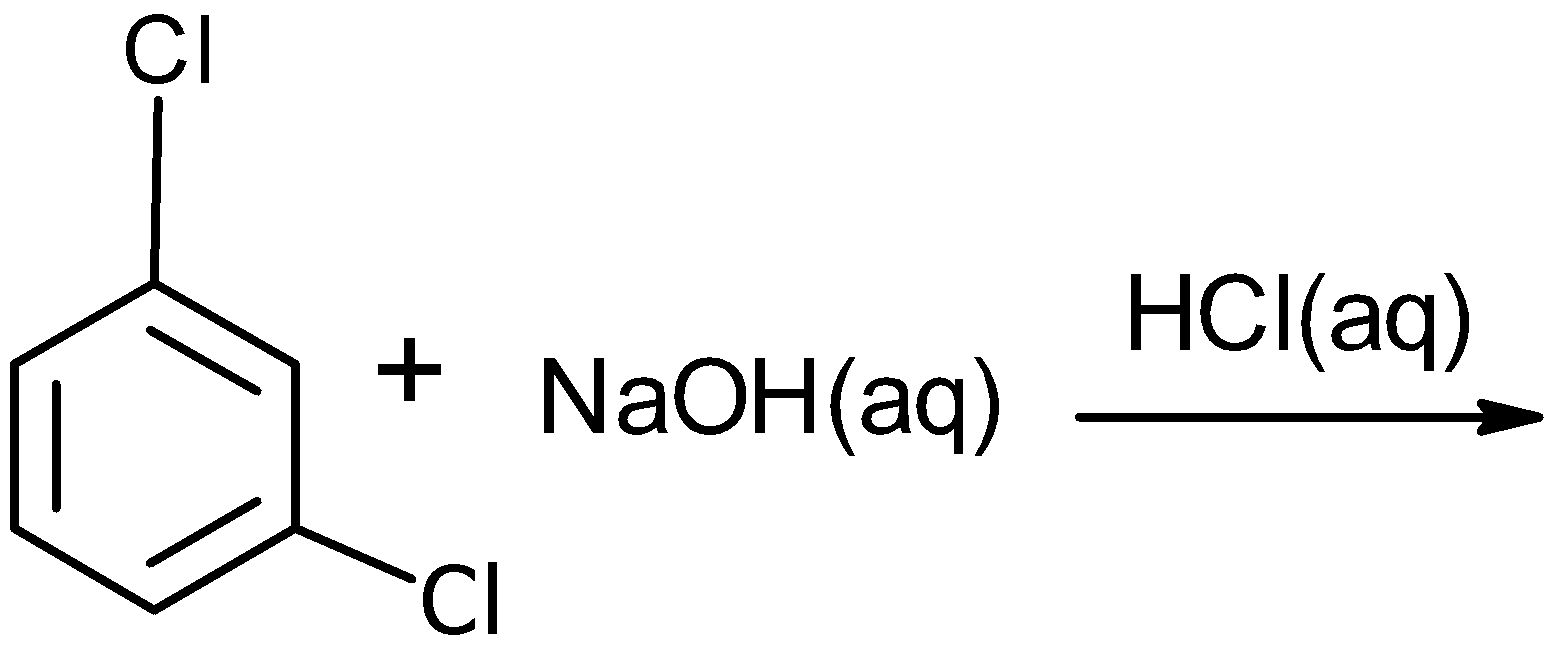
|
| D) | 
|
Answer
595.8k+ views
Hint: Resorcinol or the 1,3-dihydroxy benzene can be obtained by the sulphonation of benzene.The benzene is susceptible the electrophilic substitution reaction .The sulphur trioxide acts as an electrophile and generates the benzene disulfonic acid.The alkali fusion replaced the sulfonic groups by the hydroxyl group.
Complete step by step answer:
Resorcinol is a 1,3-dihydroxy benzene. It is a disubstituted derivative of phenol.
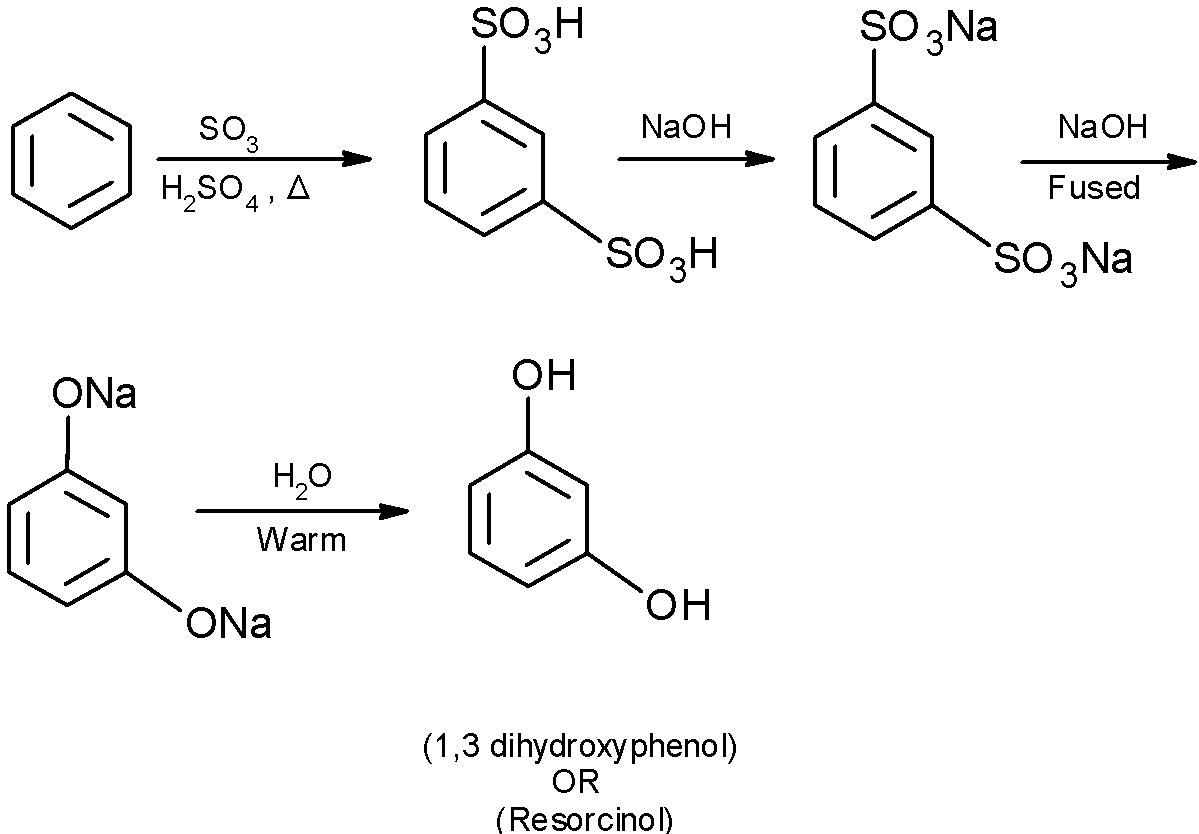
The resorcinol is produced from the benzene. The general reaction scheme for the generation of resorcinol from the benzene through the sulphonation.
Benzene is susceptible to the electrophilic substitution reaction. The benzene contains the delocalized electrons over the carbon ring and it is highly attractive towards the electrophiles.
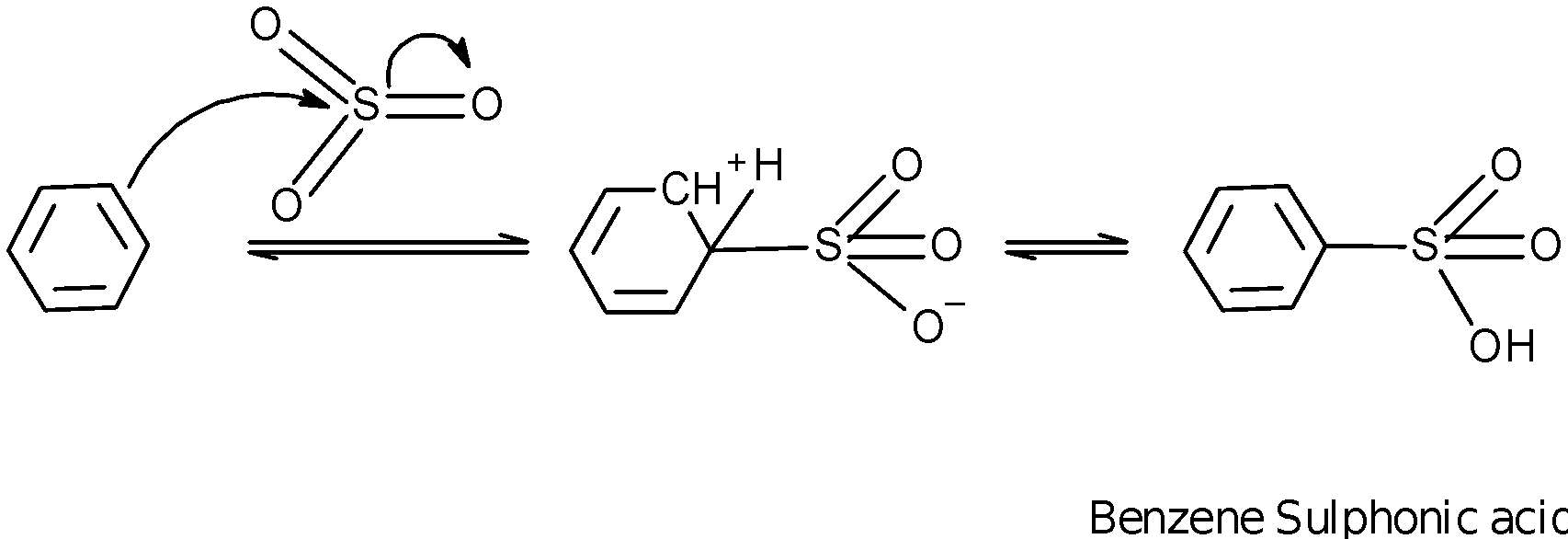
In the sulphonation of benzene, the benzene is heated in presence of fuming ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ to produce the benzene sulphonic acid. In excess of sulfonating reagent, benzene is converted into the substituted derivative of benzene.
Here, $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ is a neutral electrophile. The delocalized electrons of the benzene attacks on $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ and generate the benzene sulphonic acid.
In an alkaline medium $\text{(NaOH)}$, the obtained 1,3 benzenedisulfonic acid is converted into the disodium salt of 1,3 benzenedisulfonic acid.
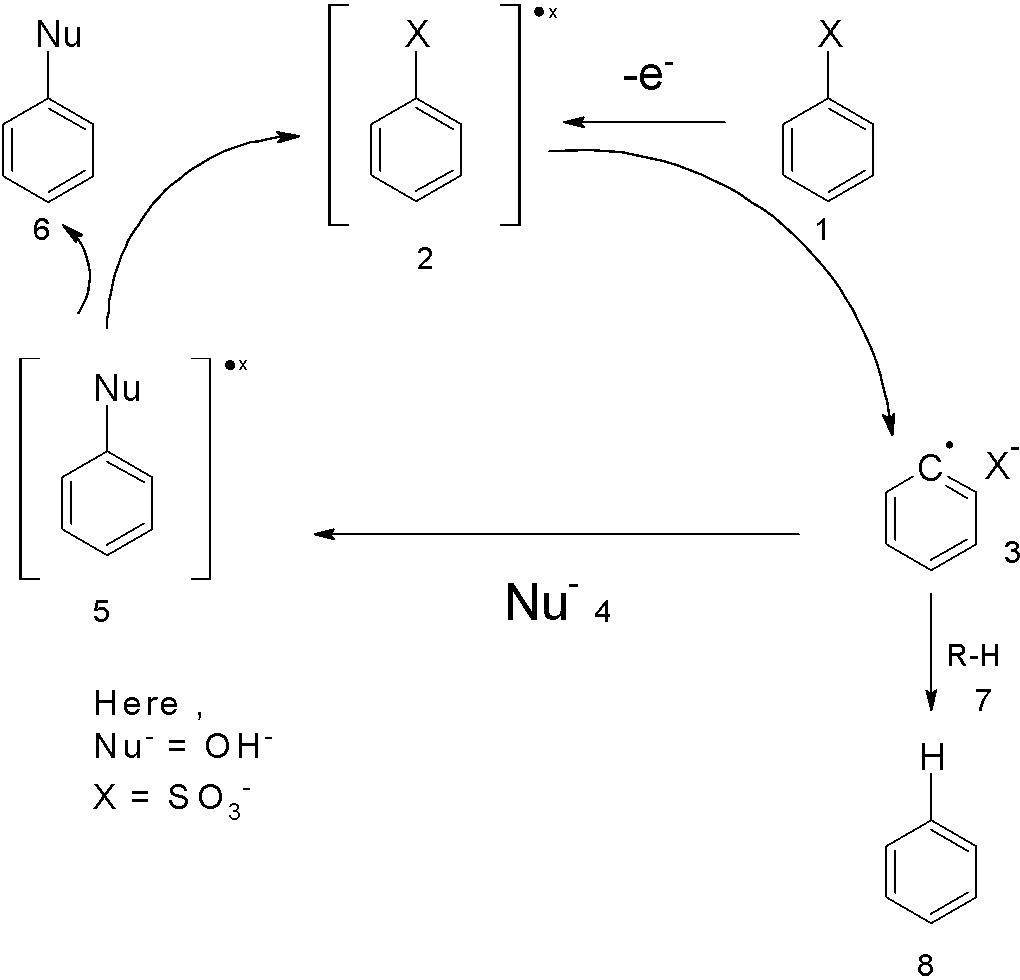
Alkali fusion is the base that is dissolved in water. It is an ionic salt of alkali or alkaline earth metal. Alkali fusion is useful to substitute the sulfonic group with the hydroxyl group which is substituted on the aromatic ring. the reaction requires a high temperature $(300-{{500}^{0}}\text{C})$. The mechanism can be explained by the nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
Let us consider the $\text{X=S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{H}$ and $\text{Nu = O}{{\text{H}}^{-}}$. The sodium benzene sulphonate loses its electron to form a radical. This radical of the phenyl ring is attacked by the nucleophile to generate the disodium phenolate ion. The general scheme is as follows:
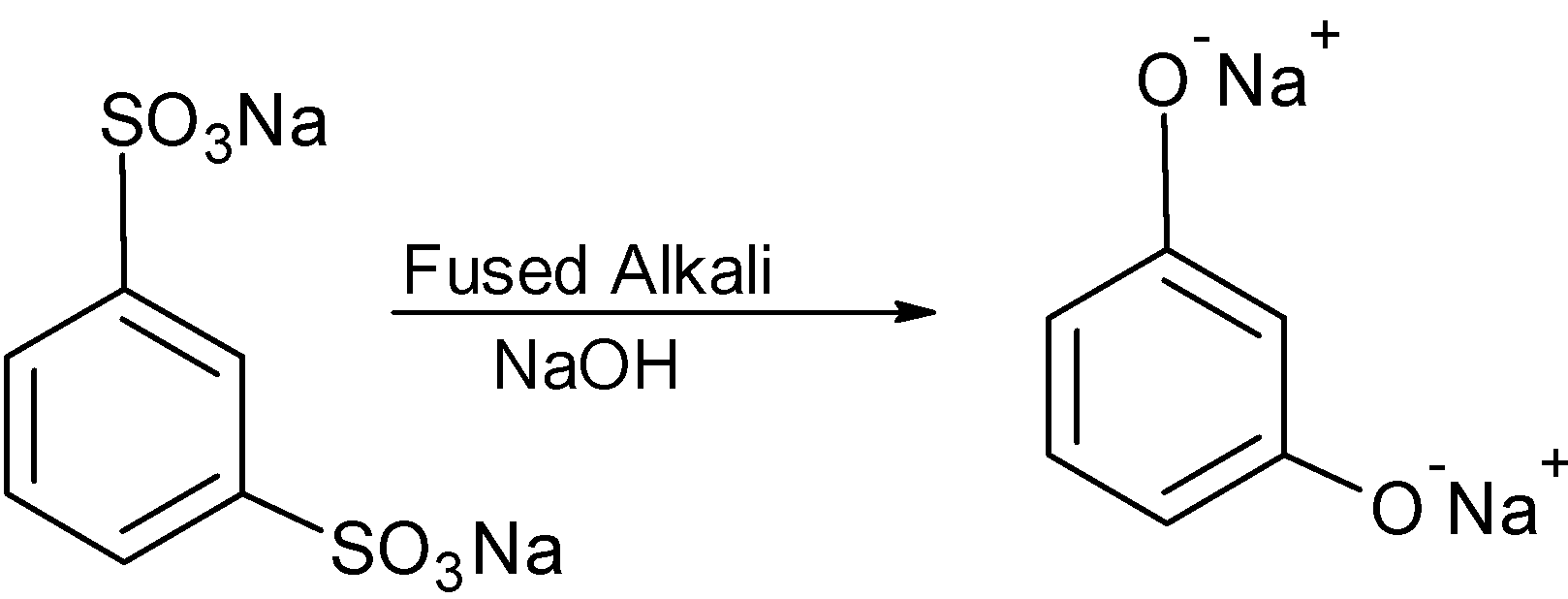
the disodium benzene sulphonate is converted into the disodium phenoxide. As follows:
The disodium phenol is treated with the water and generates the 1,3-dihydroxy benzene.
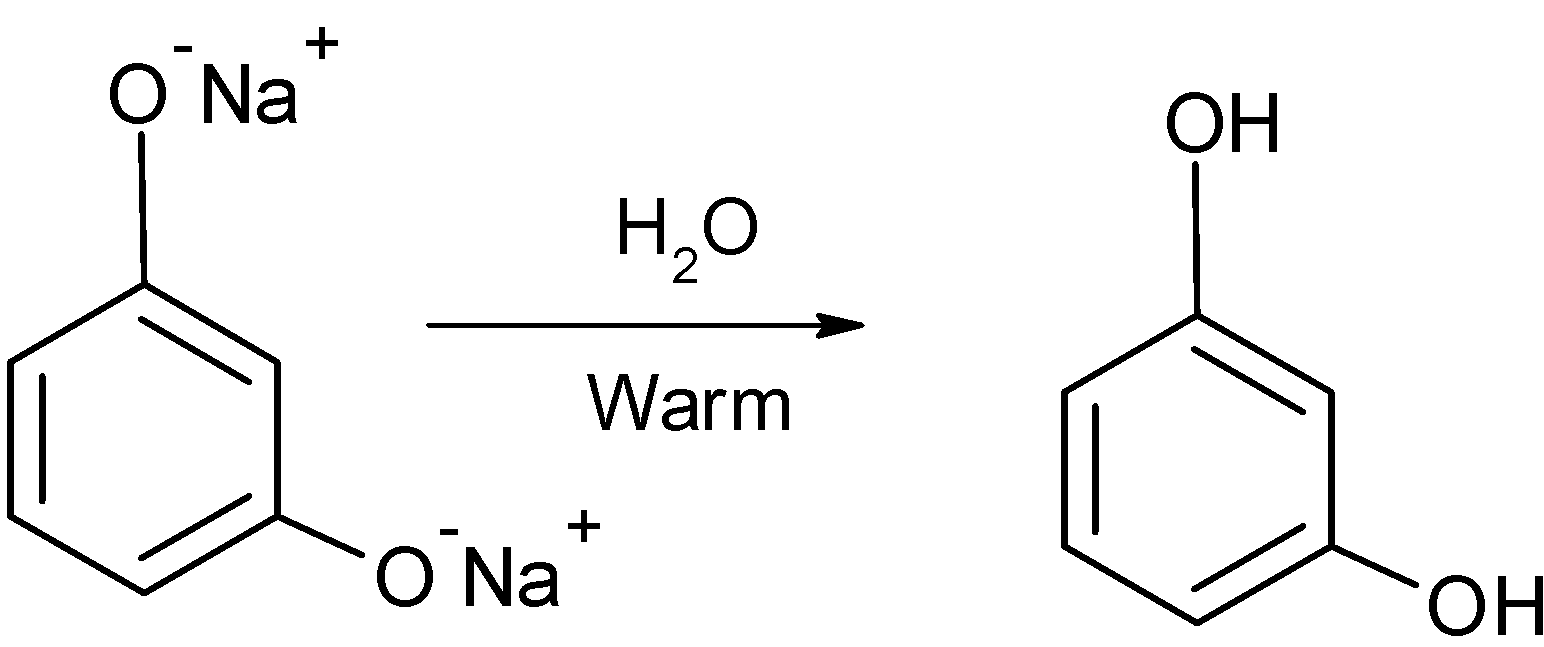
The complete reaction of conversion of benzene to the 1,3-dihydroxy benzene is as shown below:
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: the mechanism of alkali fusion has the alternate mechanism of radical anion intermediate. The carbon-bearing the $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{Na}$ group gives the tetrahedral intermediate. The excess of the negative charge leads to the attack and the removal of the group. The elimination of $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{Na}$ gives us a product.
Complete step by step answer:
Resorcinol is a 1,3-dihydroxy benzene. It is a disubstituted derivative of phenol.
The resorcinol is produced from the benzene. The general reaction scheme for the generation of resorcinol from the benzene through the sulphonation.
Benzene is susceptible to the electrophilic substitution reaction. The benzene contains the delocalized electrons over the carbon ring and it is highly attractive towards the electrophiles.
In the sulphonation of benzene, the benzene is heated in presence of fuming ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ and $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ to produce the benzene sulphonic acid. In excess of sulfonating reagent, benzene is converted into the substituted derivative of benzene.
Here, $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ is a neutral electrophile. The delocalized electrons of the benzene attacks on $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ and generate the benzene sulphonic acid.

In an alkaline medium $\text{(NaOH)}$, the obtained 1,3 benzenedisulfonic acid is converted into the disodium salt of 1,3 benzenedisulfonic acid.
Alkali fusion is the base that is dissolved in water. It is an ionic salt of alkali or alkaline earth metal. Alkali fusion is useful to substitute the sulfonic group with the hydroxyl group which is substituted on the aromatic ring. the reaction requires a high temperature $(300-{{500}^{0}}\text{C})$. The mechanism can be explained by the nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
Let us consider the $\text{X=S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{H}$ and $\text{Nu = O}{{\text{H}}^{-}}$. The sodium benzene sulphonate loses its electron to form a radical. This radical of the phenyl ring is attacked by the nucleophile to generate the disodium phenolate ion. The general scheme is as follows:

the disodium benzene sulphonate is converted into the disodium phenoxide. As follows:

The disodium phenol is treated with the water and generates the 1,3-dihydroxy benzene.

The complete reaction of conversion of benzene to the 1,3-dihydroxy benzene is as shown below:

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: the mechanism of alkali fusion has the alternate mechanism of radical anion intermediate. The carbon-bearing the $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{Na}$ group gives the tetrahedral intermediate. The excess of the negative charge leads to the attack and the removal of the group. The elimination of $\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{Na}$ gives us a product.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which country did Danny Casey play for class 12 english CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




