
Which of the following tests will be used to distinguish between methylamine and dimethylamine?
(A). Carbylamine test
(B). Liebermann's nitrosamine test
(C). Liebermann nitroso test
(D). Hinsberg reaction test
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: This reaction is also known as Hofmann isocyanide synthesis because the final product is an isocyanide. Here the primary amine reacts with chloroform and a base to form an isocyanide product.
Complete answer:
-The carbylamine reaction is also known as Hoffman isocyanide synthesis or the Saytzeff’s isocyanide test. In this a primary amine ($R - N{H_2}$) is reacted with chloroform ($CHC{l_3}$) and a base to produce am isocyanide. The intermediate formed in this reaction is dichlorocarbene.
This reaction is basically about addition of amine to the intermediate which will be formed from the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform (dichlorocarbene).
The secondary and tertiary amines do not give this reaction and thus it can be used to check for the presence of primary amines. The formation of isocyanide gives a foul smell in the end.
Generally this reaction can be written as:
$R - N{H_2} + CHC{l_3} + 3KOH \to RNC + 3KCl + 3{H_2}O$
-The first step in this reaction is the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform to form the dichlorocarbene intermediate. This intermediate is highly reactive and also electrophilic in nature.
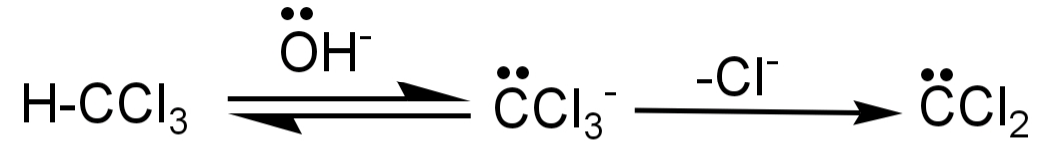
-This intermediate then attacks the electrophilic nitrogen of the primary amine, then there is elimination of HCl leading to the formation of isonitrile.
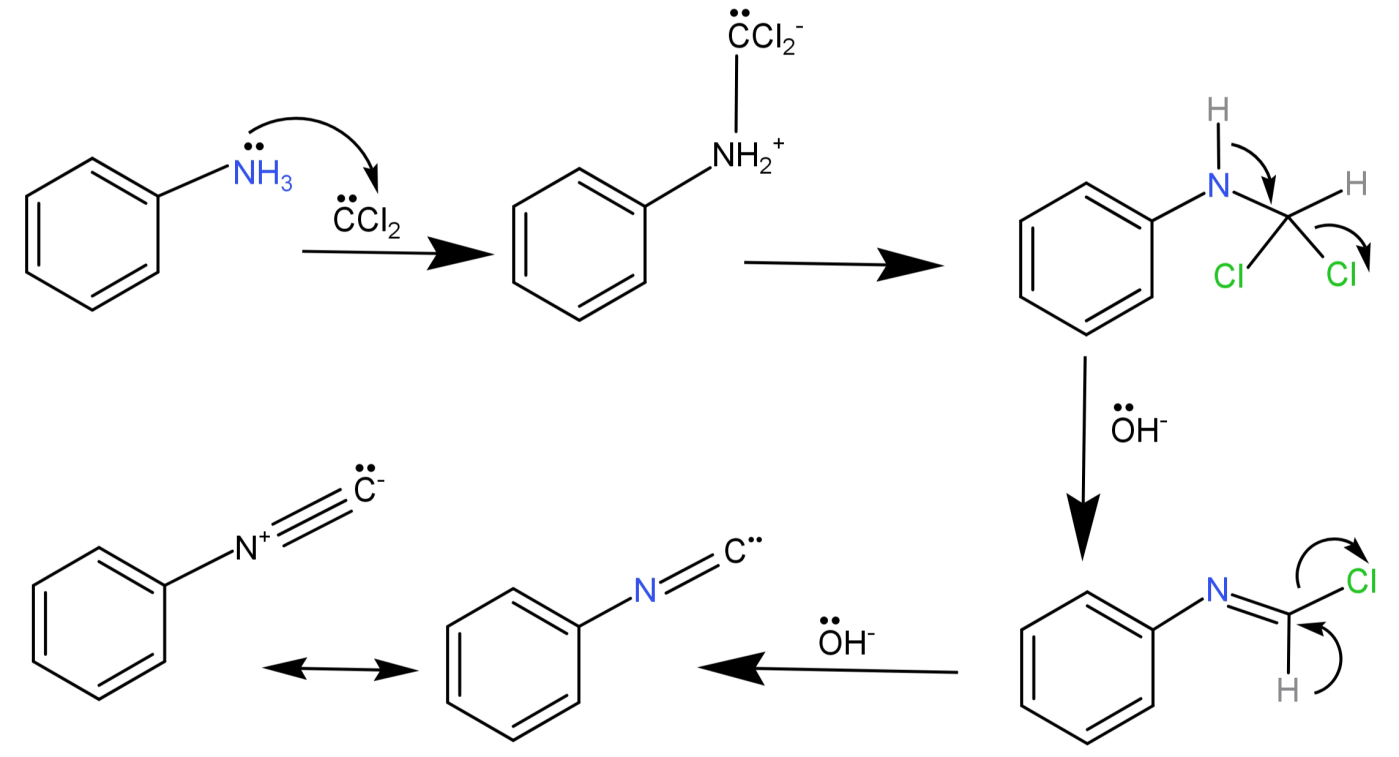
Methyl amine ($C{H_3} - N{H_2}$) is a primary amine and dimethylamine ($C{H_3} - NH - C{H_3}$) is a secondary amine, so the reaction to distinguish methylamine from dimethylamine is the Carbylamine test.
-Although we have the answer but just for knowledge let us see what the tests given in other options are for:
Liebermann nitroamine test is a test for the presence of secondary amines only.
Liebermann nitroso test is a test for phenol.
Hinsberg reaction test is a test for the presence of all primary, secondary and tertiary amine.
So, the correct option is: (A) Carbylamine test.
Note:
The dichlorocarbene intermediate ($CC{l_2}$) is a highly reactive intermediate which has not been isolated yet. It is highly reactive due to its diamagnetic nature and thus it very rapidly inserts into other bonds. This is why it so rapidly reacts with the nitrogen atom from primary amines.
Complete answer:
-The carbylamine reaction is also known as Hoffman isocyanide synthesis or the Saytzeff’s isocyanide test. In this a primary amine ($R - N{H_2}$) is reacted with chloroform ($CHC{l_3}$) and a base to produce am isocyanide. The intermediate formed in this reaction is dichlorocarbene.
This reaction is basically about addition of amine to the intermediate which will be formed from the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform (dichlorocarbene).
The secondary and tertiary amines do not give this reaction and thus it can be used to check for the presence of primary amines. The formation of isocyanide gives a foul smell in the end.
Generally this reaction can be written as:
$R - N{H_2} + CHC{l_3} + 3KOH \to RNC + 3KCl + 3{H_2}O$
-The first step in this reaction is the dehydrohalogenation of chloroform to form the dichlorocarbene intermediate. This intermediate is highly reactive and also electrophilic in nature.
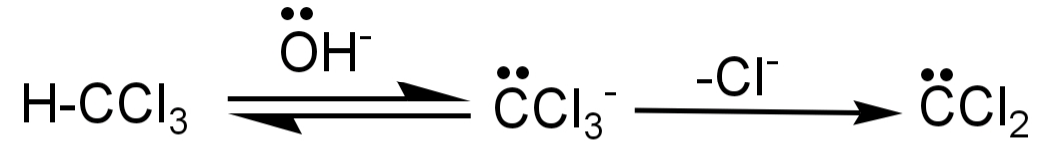
-This intermediate then attacks the electrophilic nitrogen of the primary amine, then there is elimination of HCl leading to the formation of isonitrile.

Methyl amine ($C{H_3} - N{H_2}$) is a primary amine and dimethylamine ($C{H_3} - NH - C{H_3}$) is a secondary amine, so the reaction to distinguish methylamine from dimethylamine is the Carbylamine test.
-Although we have the answer but just for knowledge let us see what the tests given in other options are for:
Liebermann nitroamine test is a test for the presence of secondary amines only.
Liebermann nitroso test is a test for phenol.
Hinsberg reaction test is a test for the presence of all primary, secondary and tertiary amine.
So, the correct option is: (A) Carbylamine test.
Note:
The dichlorocarbene intermediate ($CC{l_2}$) is a highly reactive intermediate which has not been isolated yet. It is highly reactive due to its diamagnetic nature and thus it very rapidly inserts into other bonds. This is why it so rapidly reacts with the nitrogen atom from primary amines.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




