
which of the following structures has R-configuration at the chiral centre?
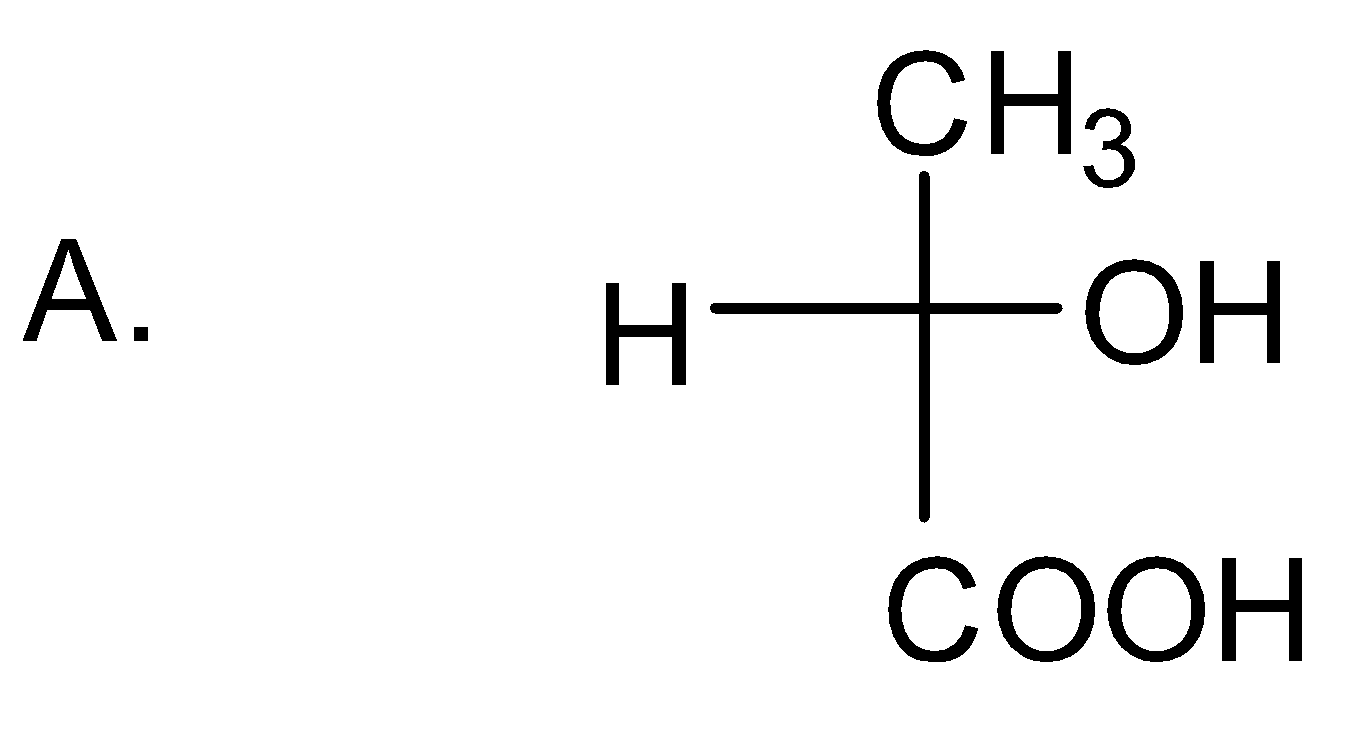
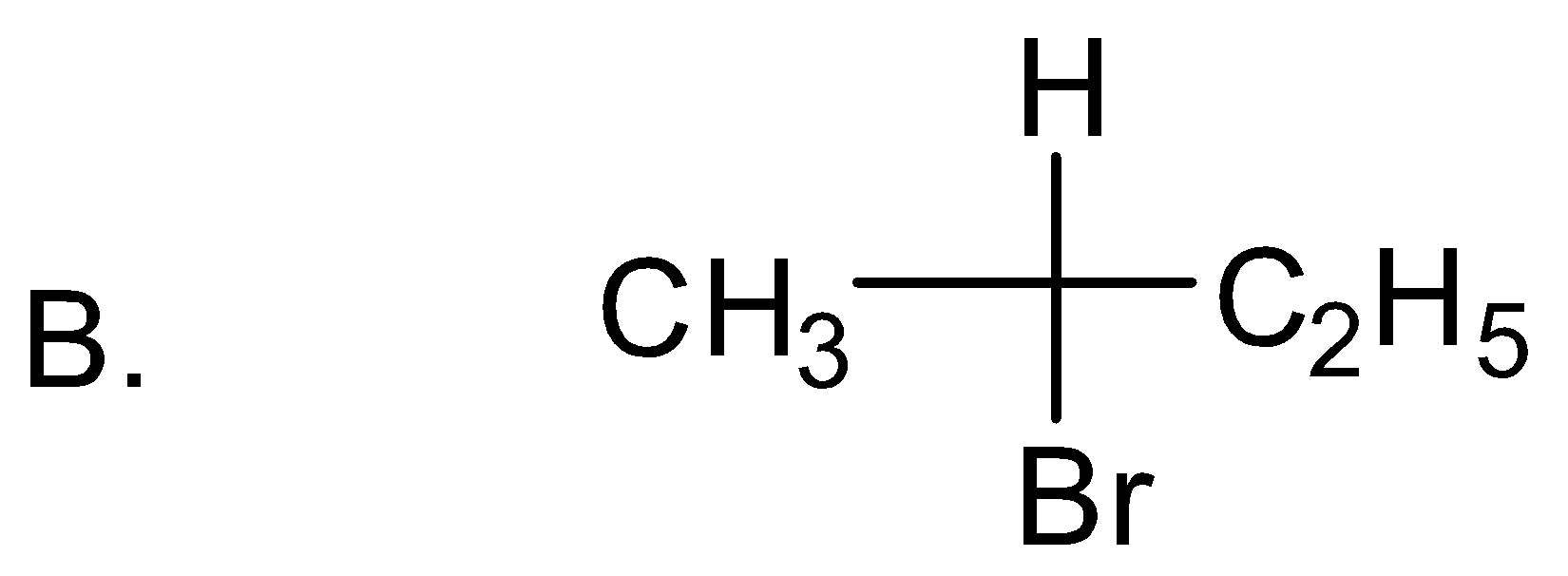
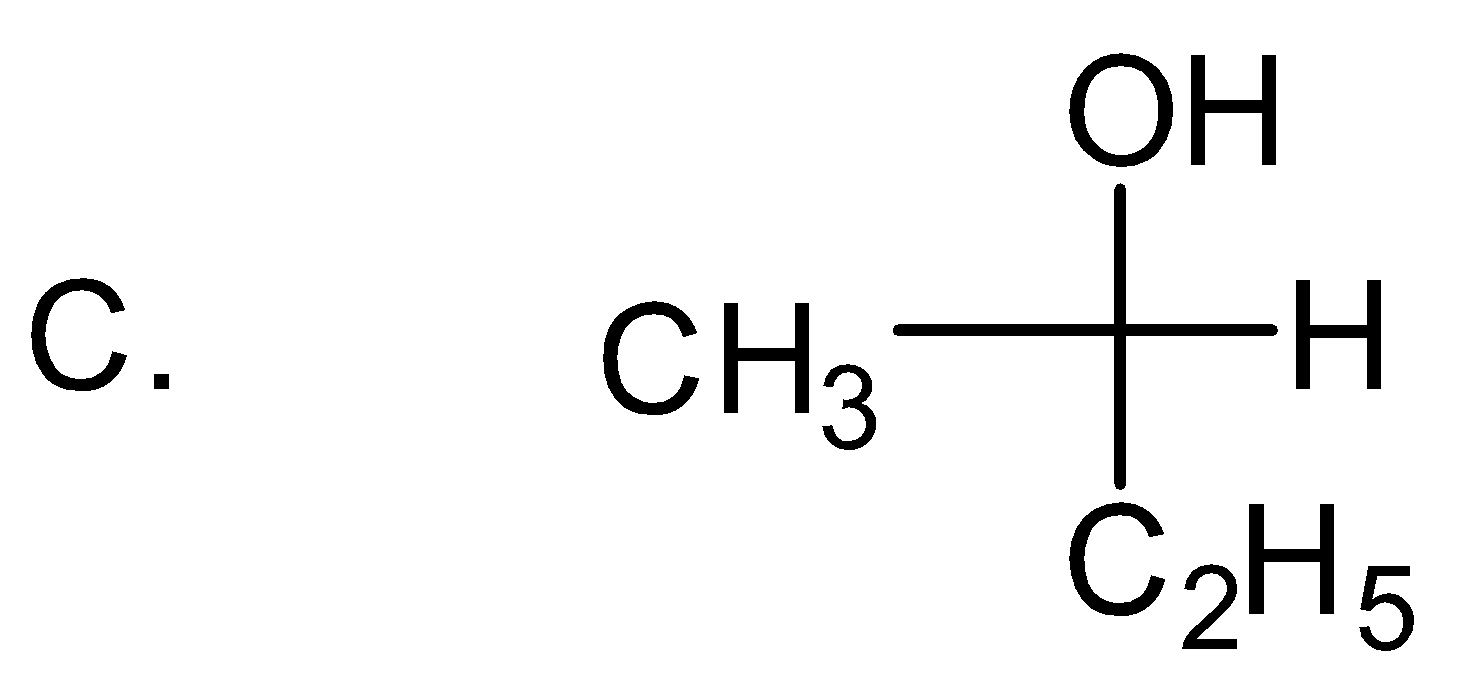




Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Chiral centre is the carbon that has four different types of substitutes attached to it. Such carbon is called as chiral carbon. The compounds having one chiral carbon can have two types of orientation for the same molecular structure and both are the mirror images of each-other. They show optical isomerism where if one configuration rotates the plane polarized light clockwise other will rotate it anticlockwise. Molecules of such pair are called enantiomers of each-other.
Complete Solution :
To differentiate between the enantiomers we use the R and S symbol before their name. Here R means right handed and S means left handed.
- In this type of arrangement we set the priorities of groups according to their atomic number. Highest atomic number atom that is attached to the chiral carbon will be at first priority and then rest follows in the same order.
For Fischer projections:
If the lowest priority group is at vertical position then R will be used for clockwise rotation and S will be used for anticlockwise rotation.
If the least priority group is at horizontal position then R will be used for anticlockwise rotation and S will be used for clockwise rotation.
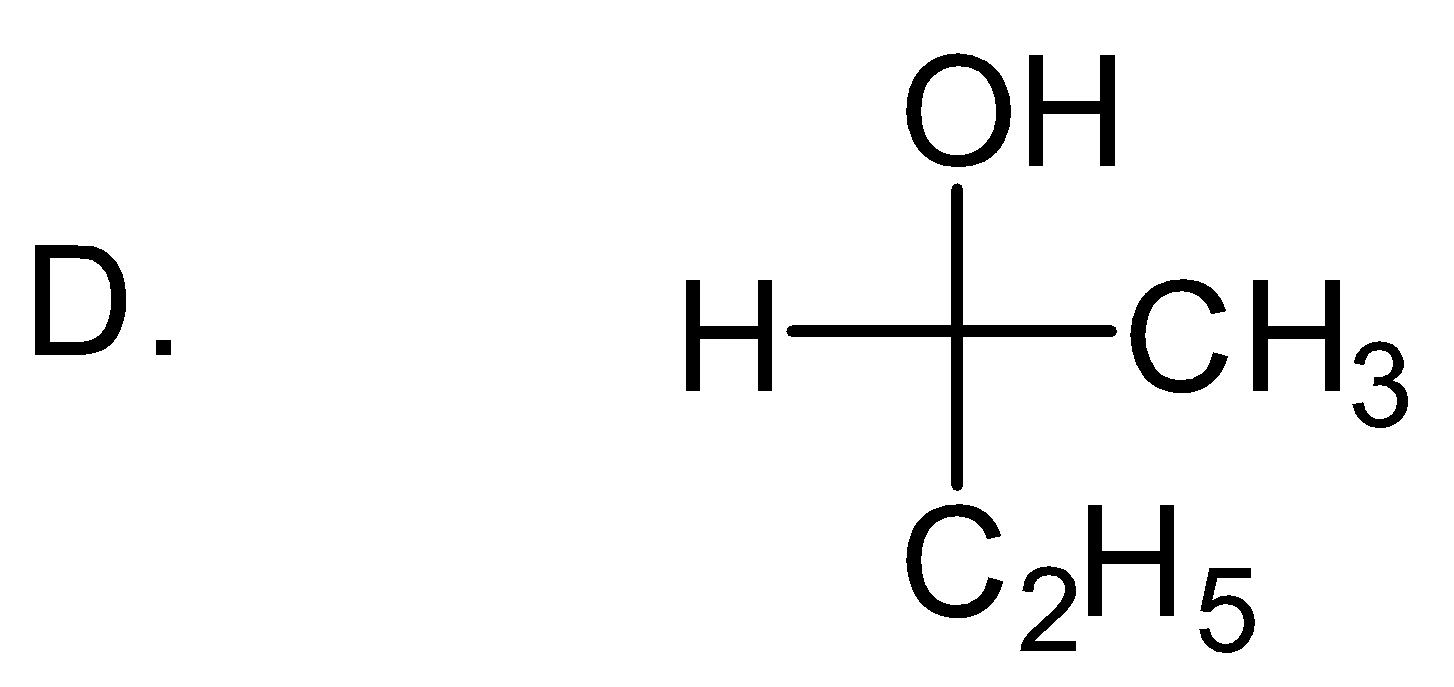
- Let’s take the example of one molecule given in Option (D) to understand this:
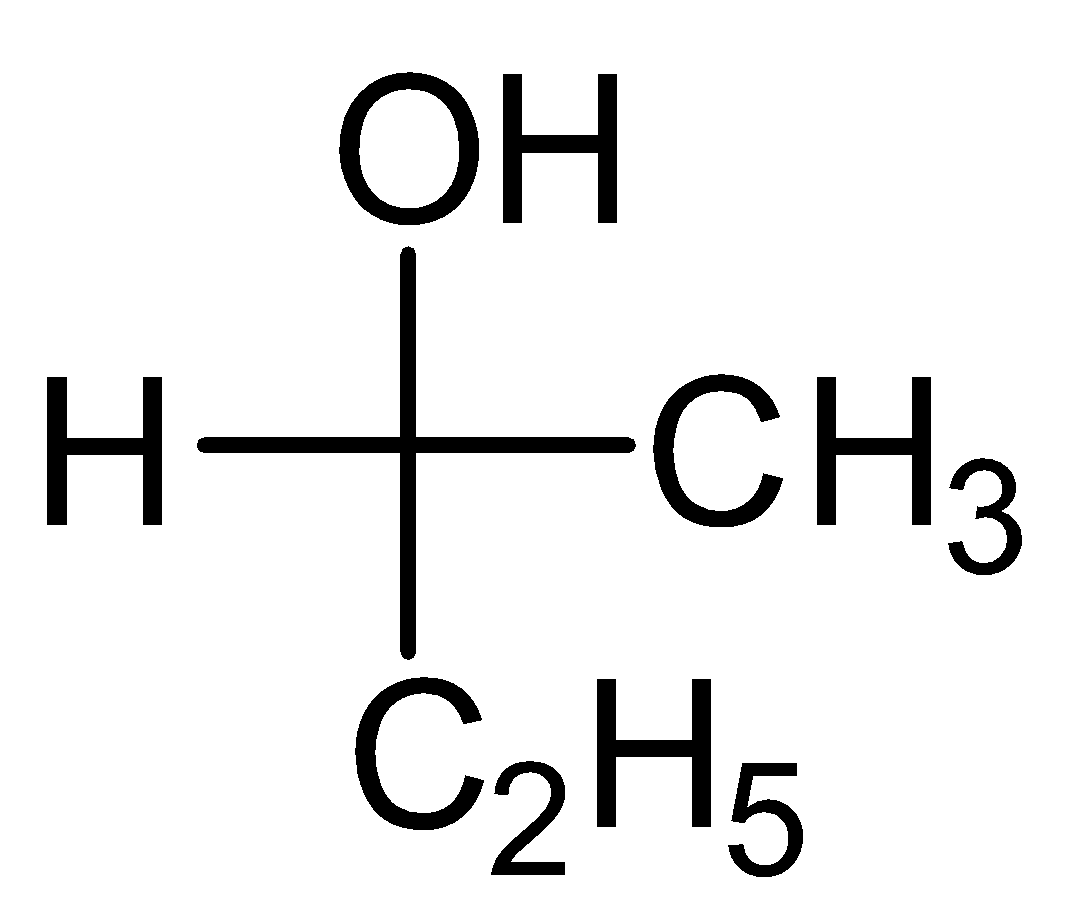
- Here the centre carbon is chiral and with it four different groups are hydroxide, ethyl, methyl and hydrogen are attached.
- If we look at the atoms that are attached to carbon, then the heaviest atom is oxygen, therefore hydroxide group will be first one in our priority list.
- After that there are two carbon atoms of ethyl and methyl are attached to chiral carbon, as both are carbon then we will go for the next atom, in ethyl the next atom is carbon which is heavier then the next atom of methyl which is hydrogen. Therefore the second group in our priority list will be ethyl and third one will be methyl. Hydrogen will be the least priority group.
- Now neglecting the least priority group, focus on remaining three and make a rotation in priority order.
From hydroxide to ethyl and ethyl to methyl, the order will come anticlockwise but because hydrogen is on the horizontal bond so here usual order will be reversed and we will be having R-configuration for anticlockwise rotation. So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information. In plane-polarized light the component electric field oscillates as in ordinary light, except that the direction of oscillation is contained within a single plane. Likewise, the component magnetic field oscillates within a plane, the planes in question being perpendicular to each other.
Note: Compound having more than one chiral center may or may not be optical isomerism. If they have any element of symmetry, then they will not be optically active. This optically inactive isomer will be the diastereomer of the isomer that shows optical isomerism with the same molecular structure. Always remember that enantiomers will always be in pairs.
Complete Solution :
To differentiate between the enantiomers we use the R and S symbol before their name. Here R means right handed and S means left handed.
- In this type of arrangement we set the priorities of groups according to their atomic number. Highest atomic number atom that is attached to the chiral carbon will be at first priority and then rest follows in the same order.
For Fischer projections:
If the lowest priority group is at vertical position then R will be used for clockwise rotation and S will be used for anticlockwise rotation.
If the least priority group is at horizontal position then R will be used for anticlockwise rotation and S will be used for clockwise rotation.
- Let’s take the example of one molecule given in Option (D) to understand this:

- Here the centre carbon is chiral and with it four different groups are hydroxide, ethyl, methyl and hydrogen are attached.
- If we look at the atoms that are attached to carbon, then the heaviest atom is oxygen, therefore hydroxide group will be first one in our priority list.
- After that there are two carbon atoms of ethyl and methyl are attached to chiral carbon, as both are carbon then we will go for the next atom, in ethyl the next atom is carbon which is heavier then the next atom of methyl which is hydrogen. Therefore the second group in our priority list will be ethyl and third one will be methyl. Hydrogen will be the least priority group.
- Now neglecting the least priority group, focus on remaining three and make a rotation in priority order.
From hydroxide to ethyl and ethyl to methyl, the order will come anticlockwise but because hydrogen is on the horizontal bond so here usual order will be reversed and we will be having R-configuration for anticlockwise rotation. So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information. In plane-polarized light the component electric field oscillates as in ordinary light, except that the direction of oscillation is contained within a single plane. Likewise, the component magnetic field oscillates within a plane, the planes in question being perpendicular to each other.
Note: Compound having more than one chiral center may or may not be optical isomerism. If they have any element of symmetry, then they will not be optically active. This optically inactive isomer will be the diastereomer of the isomer that shows optical isomerism with the same molecular structure. Always remember that enantiomers will always be in pairs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




