
Which of the following statements related to hysteresis loop is incorrect?
A.)The curve of $B$ against $H$ for a ferromagnetic material is called hysteresis loop.
B.)The area of $B - H$ curve is a measure of power dissipated per cycle per unit area of the specimen.
C.)Coercivity is a measure of the magnetic field required to destroy the residual magnetism of ferromagnetic material.
D.)The retentivity of a specimen is the measure of magnetic field remaining in the specimen when the magnetizing field is removed.
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint – Start the solution by describing the hysteresis loop. Then describe the experimental process of plotting of the hysteresis loop showing retentivity and coercivity.
Hysteresis loop is a four quadrant graph, made by plotting $B$ (magnetic flux density) against $H$ (magnetic field).
Step By Step Answer:
To make a hysteresis loop, we take a magnetic material that has not been magnetized in any way. We apply a magnetic field on it by supplying current to the wire loop surrounding the magnetic material.
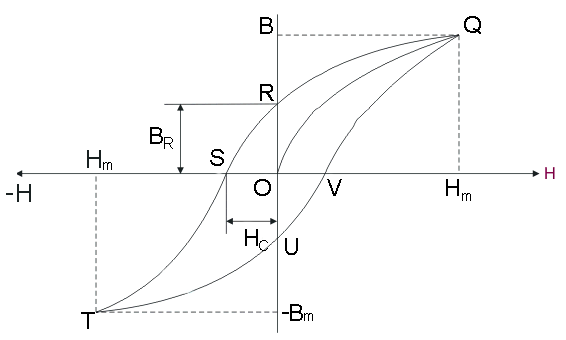
The steps to make hysteresis loop are –
1.)When there is no current ($I = 0$), there will be no flux density ($B$) and hence, no magnetizing force ($H$). This is the origin point ($O$) on the graph.
2.)When the value of current is increased, both the flux density ($B$) and magnetizing force ($H$) increase. On the diagram you can see path $OQ$
3.)At a certain value of current, flux density ($B$) becomes maximum and this is the point $Q$ on the graph.
4.)Now we start to decrease the current, the magnetizing force ($H$) decreases in an expected manner, but flux density ($B$) does not decrease as expected.
5.)The point$R$ indicates a state where $H = 0$ , $I = 0$ and a certain value of $B$, $B$ lags behind the magnetizing force ($H$). This is called hysteresis. Hysteresis is a property of a magnetic material by virtue of which $B$ lags behind $H$. The value of $B$ at this current stage is called retentivity.
6.)On reversing the direction of current, the direction of $H$ will also be reversed. The increase of $H$ in the reverse direction following the path $RS$. The point $S$, we get a negative value of $H$, where the value of $B$ becomes zero. This negative value of $H$is called the coercivity of the material
7.)On further increasing current in the negative direction, the loop follows a path $ST$. At point $T$, we obtain a negative maximum.
8.)Now we decrease the current again to zero. The hysteresis loop follows a path $TU$, again $B$ lags behind the magnetizing force ($H$). At point $U$, we again see a residual $B$ (in the negative direction).
9.)The direction of the current is again reversed and the loop follows a path $UV$, at point $V$, $B$ becomes zero, for some amount of $H$.
10.)On further increase the loop follows the path $VQ$ to reach a maximum $B$ value again.
Note: Importance of hysteresis loop –
1.)If the hysteresis loop is small, it means less hysteresis loss.
2.)The value of retentivity and coercivity can also be found through a hysteresis loop.
3.)We can choose the appropriate material for electromagnets, by finding out the residual magnetism through the $B - H$ graph.
The area of a hysteresis loop gives information about the amount of energy lost in applying the external magnetic field and not the power dissipated per cycle per unit area of the specimen.
Hence, option B is the correct choice.
Hysteresis loop is a four quadrant graph, made by plotting $B$ (magnetic flux density) against $H$ (magnetic field).
Step By Step Answer:
To make a hysteresis loop, we take a magnetic material that has not been magnetized in any way. We apply a magnetic field on it by supplying current to the wire loop surrounding the magnetic material.

The steps to make hysteresis loop are –
1.)When there is no current ($I = 0$), there will be no flux density ($B$) and hence, no magnetizing force ($H$). This is the origin point ($O$) on the graph.
2.)When the value of current is increased, both the flux density ($B$) and magnetizing force ($H$) increase. On the diagram you can see path $OQ$
3.)At a certain value of current, flux density ($B$) becomes maximum and this is the point $Q$ on the graph.
4.)Now we start to decrease the current, the magnetizing force ($H$) decreases in an expected manner, but flux density ($B$) does not decrease as expected.
5.)The point$R$ indicates a state where $H = 0$ , $I = 0$ and a certain value of $B$, $B$ lags behind the magnetizing force ($H$). This is called hysteresis. Hysteresis is a property of a magnetic material by virtue of which $B$ lags behind $H$. The value of $B$ at this current stage is called retentivity.
6.)On reversing the direction of current, the direction of $H$ will also be reversed. The increase of $H$ in the reverse direction following the path $RS$. The point $S$, we get a negative value of $H$, where the value of $B$ becomes zero. This negative value of $H$is called the coercivity of the material
7.)On further increasing current in the negative direction, the loop follows a path $ST$. At point $T$, we obtain a negative maximum.
8.)Now we decrease the current again to zero. The hysteresis loop follows a path $TU$, again $B$ lags behind the magnetizing force ($H$). At point $U$, we again see a residual $B$ (in the negative direction).
9.)The direction of the current is again reversed and the loop follows a path $UV$, at point $V$, $B$ becomes zero, for some amount of $H$.
10.)On further increase the loop follows the path $VQ$ to reach a maximum $B$ value again.
Note: Importance of hysteresis loop –
1.)If the hysteresis loop is small, it means less hysteresis loss.
2.)The value of retentivity and coercivity can also be found through a hysteresis loop.
3.)We can choose the appropriate material for electromagnets, by finding out the residual magnetism through the $B - H$ graph.
The area of a hysteresis loop gives information about the amount of energy lost in applying the external magnetic field and not the power dissipated per cycle per unit area of the specimen.
Hence, option B is the correct choice.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




